| Description |
Filorexant (MK-6096) is an orally bioavailable potent and selective reversible antagonist of OX1 and OX2 receptor(<3 nM in binding).
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| Target |
Ki: < 3 nM(Orexin receptor)[1].
|
| In Vitro |
In radioligand binding and functional cell based assays Filorexant (MK-6096) demonstrated potent binding and antagonism of both human OX(1)R and OX(2)R (<3 nM in binding, 11 nM in FLIPR), with no significant off-target activities against a panel of >170 receptors and enzymes. Filorexant (MK-6096) occupies 90% of human OX(2)Rs expressed in transgenic rats at a plasma concentration of 142 nM.
|
| In Vivo |
Filorexant (MK-6096) dose-dependently reduced locomotor activity and significantly increased sleep in rats (3-30 mg/kg) and dogs (0.25 and 0.5 mg/kg).
|
| Animal Admin |
Animal administration[1] The male Sprague Dawley rats (n = 8/study; age: 3-6 months; weight: 450-600 g) were singly housed with water and food ad libitum and a 12 h light: 12 h dark cycle with lights on at 04:00 and off at 16:00. Sleep studies were conducted to evaluate Filorexant (3 and 10 mg/kg, p.o.), DORA-22 (10 mg/kg, p.o.) and almorexant (3 and 30 mg/kg, p.o.), employing a counterbalanced crossover design in which all animals were alternatively treated with drug and vehicle daily for either 3 or 7 consecutive days (for DORA-22 and Filorexant, respectively): 2 baseline days (no dosing), a 2 day vehicle-only run-in, a 3 or 7-day arm of drug or vehicle followed by 3 or 7 days of conditional crossover. Effects of compound treatments relative to vehicle (20% Vitamin E TPGS, p.o.) were evaluated following administration in the active phase).
|
| References |
[1]. Winrow CJ, et al. Pharmacological characterization of MK-6096 - a dual orexin receptor antagonist for insomnia. Neuropharmacology. 2012 Feb;62(2):978-87. [2]. Coleman PJ, et al. Discovery of [(2R,5R)-5-{[(5-fluoropyridin-2-yl)oxy]methyl}-2-methylpiperidin-1-yl][5-methyl-2-(pyrimidin-2-yl)phenyl]methanone (MK-6096): a dual orexin receptor antagonist with potent sleep-promoting properties. ChemMedChem. 2012 Mar 5;7(3):415-24, 337.
|
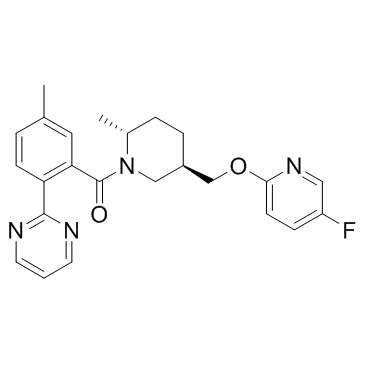
 CAS#:1088994-22-2
CAS#:1088994-22-2 CAS#:1088993-93-4
CAS#:1088993-93-4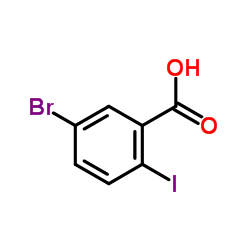 CAS#:21740-00-1
CAS#:21740-00-1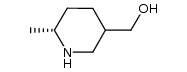 CAS#:1088994-07-3
CAS#:1088994-07-3![[(3R,6R)-6-methylpiperidin-3-yl]methanol Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/357/1088994-09-5.png) CAS#:1088994-09-5
CAS#:1088994-09-5 CAS#:1088994-12-0
CAS#:1088994-12-0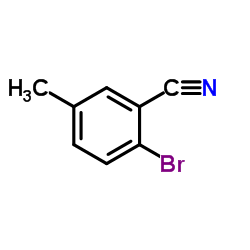 CAS#:42872-83-3
CAS#:42872-83-3 CAS#:1088994-14-2
CAS#:1088994-14-2 CAS#:52548-14-8
CAS#:52548-14-8