Methyl laurate

Methyl laurate structure
|
Common Name | Methyl laurate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 111-82-0 | Molecular Weight | 214.344 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 263.0±3.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H26O2 | Melting Point | 4-5 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 114.6±6.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Methyl laurateMethyl laurate, a 12-carbon saturated fatty acid, is an esterified version of lauric acid[1]. |
| Name | methyl laurate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Methyl laurate, a 12-carbon saturated fatty acid, is an esterified version of lauric acid[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 263.0±3.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 4-5 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C13H26O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 214.344 |
| Flash Point | 114.6±6.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 214.193283 |
| PSA | 26.30000 |
| LogP | 5.49 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.433 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
Synonym:Methyl dodecanoate; Lauric acid methyl este Section 2 - COMPOSITION, INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS
Risk Phrases: None Listed. Section 3 - HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION EMERGENCY OVERVIEW
The toxicological properties of this material have not been fully investigated. Potential Health Effects Eye: May cause eye irritation. Skin: May cause skin irritation. Ingestion: May cause irritation of the digestive tract. The toxicological properties of this substance have not been fully investigated. Inhalation: May cause respiratory tract irritation. The toxicological properties of this substance have not been fully investigated. Chronic: Not available. Section 4 - FIRST AID MEASURES Eyes: Flush eyes with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes, occasionally lifting the upper and lower eyelids. Get medical aid. Skin: Get medical aid if irritation develops or persists. Flush skin with plenty of soap and water. Ingestion: If victim is conscious and alert, give 2-4 cupfuls of milk or water. Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Get medical aid. Inhalation: Remove from exposure and move to fresh air immediately. Get medical aid if cough or other symptoms appear. Notes to Physician: Section 5 - FIRE FIGHTING MEASURES General Information: As in any fire, wear a self-contained breathing apparatus in pressure-demand, MSHA/NIOSH (approved or equivalent), and full protective gear. Extinguishing Media: Use water spray, dry chemical, carbon dioxide, or chemical foam. Section 6 - ACCIDENTAL RELEASE MEASURES General Information: Use proper personal protective equipment as indicated in Section 8. Spills/Leaks: Absorb spill with inert material (e.g. vermiculite, sand or earth), then place in suitable container. Section 7 - HANDLING and STORAGE Handling: Wash thoroughly after handling. Use with adequate ventilation. Avoid contact with eyes, skin, and clothing. Keep container tightly closed. Avoid ingestion and inhalation. Storage: Store in a tightly closed container. Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from incompatible substances. Section 8 - EXPOSURE CONTROLS, PERSONAL PROTECTION Engineering Controls: Use adequate ventilation to keep airborne concentrations low. Exposure Limits CAS# 111-82-0: Personal Protective Equipment Eyes: Wear appropriate protective eyeglasses or chemical safety goggles as described by OSHA's eye and face protection regulations in 29 CFR 1910.133 or European Standard EN166. Skin: Wear appropriate protective gloves to prevent skin exposure. Clothing: Wear appropriate protective clothing to prevent skin exposure. Respirators: Follow the OSHA respirator regulations found in 29 CFR 1910.134 or European Standard EN 149. Use a NIOSH/MSHA or European Standard EN 149 approved respirator if exposure limits are exceeded or if irritation or other symptoms are experienced. Section 9 - PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES Physical State: Liquid Color: clear, colorless Odor: Oil,winey,fatty odor pH: Not available. Vapor Pressure: Not available. Viscosity: Not available. Boiling Point: 262 deg C @ 766.00mm Hg Freezing/Melting Point: 4.8 deg C Autoignition Temperature: Not available. Flash Point: > 112 deg C (> 233.60 deg F) Explosion Limits, lower: Not available. Explosion Limits, upper: Not available. Decomposition Temperature: Solubility in water: insoluble Specific Gravity/Density: .8700g/cm3 Molecular Formula: C13H26O2 Molecular Weight: 214.35 Section 10 - STABILITY AND REACTIVITY Chemical Stability: Not available. Conditions to Avoid: Incompatible materials. Incompatibilities with Other Materials: Strong oxidizing agents - strong bases. Hazardous Decomposition Products: Carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide. Hazardous Polymerization: Has not been reported. Section 11 - TOXICOLOGICAL INFORMATION RTECS#: CAS# 111-82-0: OF0670000 LD50/LC50: Not available. Carcinogenicity: METHYL LAURATE - Not listed by ACGIH, IARC, or NTP. Other: See actual entry in RTECS for complete information. Section 12 - ECOLOGICAL INFORMATION Section 13 - DISPOSAL CONSIDERATIONS Dispose of in a manner consistent with federal, state, and local regulations. Section 14 - TRANSPORT INFORMATION IATA Not regulated as a hazardous material. IMO Not regulated as a hazardous material. RID/ADR Not regulated as a hazardous material. Section 15 - REGULATORY INFORMATION European/International Regulations European Labeling in Accordance with EC Directives Hazard Symbols: Not available. Risk Phrases: Safety Phrases: S 24/25 Avoid contact with skin and eyes. WGK (Water Danger/Protection) CAS# 111-82-0: 1 Canada CAS# 111-82-0 is listed on Canada's DSL List. CAS# 111-82-0 is not listed on Canada's Ingredient Disclosure List. US FEDERAL TSCA CAS# 111-82-0 is listed on the TSCA inventory. SECTION 16 - ADDITIONAL INFORMATION N/A |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
|
Direct quantification of fatty acids in wet microalgal and yeast biomass via a rapid in situ fatty acid methyl ester derivatization approach.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 99 , 10237-47, (2015) Accurate determination of fatty acid contents is routinely required in microalgal and yeast biofuel studies. A method of rapid in situ fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) derivatization directly from wet f... |
|
|
Optimization of supercritical fluid consecutive extractions of fatty acids and polyphenols from Vitis vinifera grape wastes.
J. Food Sci. 80(1) , E101-7, (2015) In this study, supercritical fluid extraction has been successfully applied to a sequential fractionation of fatty acids and polyphenols from wine wastes (2 different vitis vinifera grapes). To this a... |
|
|
Evaluation of injection methods for fast, high peak capacity separations with low thermal mass gas chromatography.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1392 , 82-90, (2015) Low thermal mass gas chromatography (LTM-GC) was evaluated for rapid, high peak capacity separations with three injection methods: liquid, headspace solid phase micro-extraction (HS-SPME), and direct ... |
| EINECS 203-911-3 |
| Lauric acid methyl ester,Methyl dodecanoate |
| Lauric acid methyl ester |
| Methyl laurate |
| Dodecanoic acid, methyl ester |
| Dodecanoic acid methyl ester |
| Lauric acid, methyl ester |
| Methyl n-dodecanoate |
| 11VO1 |
| MFCD00008966 |
| Methyldodecanoate |
| methyl dodecanoate |
| Methyl dodecylate |
 CAS#:67-56-1
CAS#:67-56-1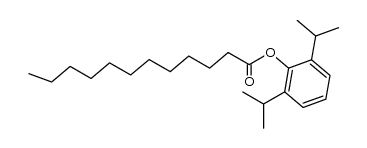 CAS#:32604-48-1
CAS#:32604-48-1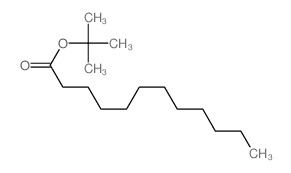 CAS#:7143-18-2
CAS#:7143-18-2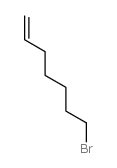 CAS#:4117-09-3
CAS#:4117-09-3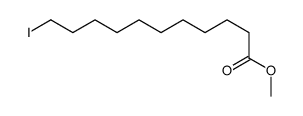 CAS#:929-33-9
CAS#:929-33-9 CAS#:917-54-4
CAS#:917-54-4 CAS#:106-33-2
CAS#:106-33-2 CAS#:505-95-3
CAS#:505-95-3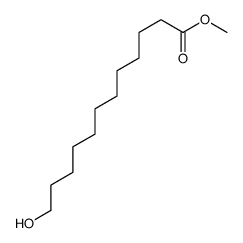 CAS#:71655-36-2
CAS#:71655-36-2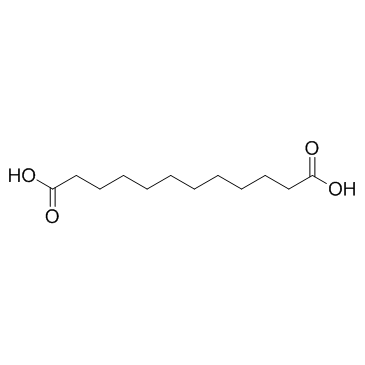 CAS#:693-23-2
CAS#:693-23-2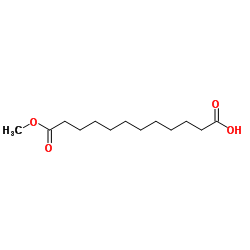 CAS#:3903-40-0
CAS#:3903-40-0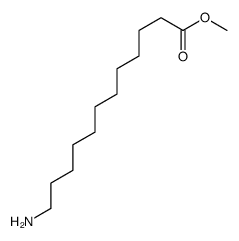 CAS#:53005-24-6
CAS#:53005-24-6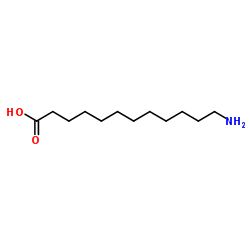 CAS#:693-57-2
CAS#:693-57-2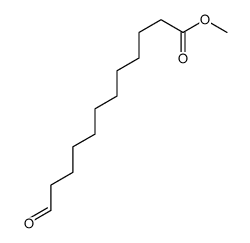 CAS#:2009-59-8
CAS#:2009-59-8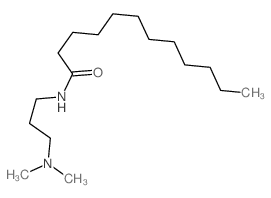 CAS#:3179-80-4
CAS#:3179-80-4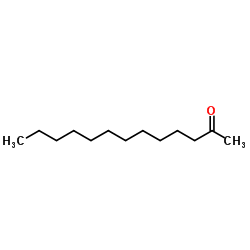 CAS#:593-08-8
CAS#:593-08-8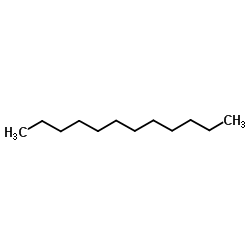 CAS#:112-40-3
CAS#:112-40-3
