QVD-OPh
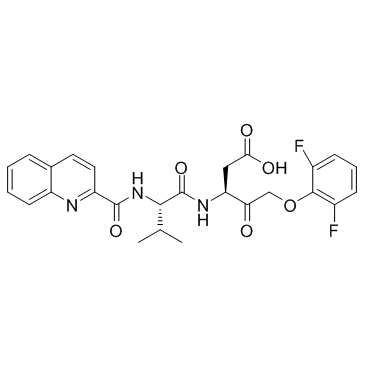
QVD-OPh structure
|
Common Name | QVD-OPh | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1135695-98-5 | Molecular Weight | 513.490 | |
| Density | 1.346±0.06 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 808.9±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C26H25F2N3O6 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 443.0±34.3 °C | |
Use of QVD-OPhQ-VD-OPha is a irreversible pan-caspase inhibitor with potent antiapoptotic properties; inhibits caspase 7 with IC50 of 48 nM and 25-400 nM for other caspases including caspase 1, 3, 8, 9, 10, and 12. Q-VD-OPha is able to cross the blood-brain barrier. |
| Name | (3S)-5-(2,6-difluorophenoxy)-3-[[(2S)-3-methyl-2-(quinoline-2-carbonylamino)butanoyl]amino]-4-oxopentanoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Q-VD-OPha is a irreversible pan-caspase inhibitor with potent antiapoptotic properties; inhibits caspase 7 with IC50 of 48 nM and 25-400 nM for other caspases including caspase 1, 3, 8, 9, 10, and 12. Q-VD-OPha is able to cross the blood-brain barrier. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Caspase-3:25-400 nM (IC50) Caspase-7:48 nM (IC50) Caspase-1:25-400 nM (IC50) Caspase-8:25-400 nM (IC50) Caspase-9:25-400 nM (IC50) Caspase-10:25-400 nM (IC50) Caspase-12:25-400 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Q-VD-OPh is a potent inhibitor of caspase-7 with an IC50 of 48 nM utilizing a cell-free assay consisting of human recombinant caspase-7, Q-VD-OPh, and the substrate AMC-DEVD-pNa[1]. Q-VD-OPh fully inhibits caspase-3 and -7 activity at 0.05 μM. Caspase-8 is also inhibited at low Q-VD-OPh concentrations. The cleavage of PARP-1 is fully prevented at 10 μM Q-VD-OPh. DNA fragmentation and disruption of the cell membrane functionality are both prevented at 2 μM Q-VD-OPh[2]. Q-VD-OPh is significantly more effective in preventing apoptosis than the widely used inhibitors, ZVAD-fmk and Boc-D-fmk, and is also equally effective in preventing apoptosis mediated by the three major apoptotic pathways, caspase 9/3, caspase 8/10, and caspase12. Q-VD-OPh is not toxic to cells even at extremely high concentrations[3]. QVD is also able to increase the expression of differentiation markers in acute myeloid leukemia (AmL) blasts. QVD alone or combined with VDDs increases differentiation and HPK1-cJun signaling in AmL cell context-dependent manner[4]. |
| In Vivo | Chronic treatment with Q-VD-OPh prevents caspase-7 activation and limits the pathological changes associated with tau, including caspase cleavage. Q-VD-OPh could be a potential therapeutic compound for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mouse: Stock solutions of Q-VD-OPh are prepared in DMSO and diluted in sterile PBS solution prior to injection. A final concentration of 10 mg/kg is chosen indicating neuroprotection at this concentration of Q-VD-OPh. Three-month old mice are divided into two groups: control, vehicle (n=3) or treated (n=2). Mice are injected i.p. three times a week with either Q-VD-OPh or vehicle for a total time period of 3 months[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.346±0.06 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 808.9±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C26H25F2N3O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 513.490 |
| Flash Point | 443.0±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 513.171143 |
| PSA | 138.18000 |
| LogP | 4.61 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.591 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | Insuluble (1.4E-3 g/L) (25 ºC) |
| (3S)-5-(2,6-Difluorophenoxy)-4-oxo-3-{[N-(2-quinolinylcarbonyl)-L-valyl]amino}pentanoic acid |
| Quinoline-Val-Asp-Difluorophenoxymethylketone |
| Q-VD-OPh hydrate |
| S7311 |
| Q-VD-OPh |
| N-(2-Quinolyl)valyl-aspartyl-(2,6-difluorophenoxy)methyl ketone |
| Pentanoic acid, 5-(2,6-difluorophenoxy)-3-[[(2S)-3-methyl-1-oxo-2-[(2-quinolinylcarbonyl)amino]butyl]amino]-4-oxo-, (3S)- |
| Q-Val-Asp-OPH |