Z-Pro-OH
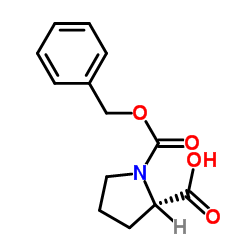
Z-Pro-OH structure
|
Common Name | Z-Pro-OH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1148-11-4 | Molecular Weight | 249.262 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 432.3±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H15NO4 | Melting Point | 76-78ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 215.3±28.7 °C | |
Use of Z-Pro-OHCarbobenzoxyproline (L-Cbz-Proline) is an inhibitor of prolidase. Carbobenzoxyproline can be used for prolidase deficiency (PD) research[1]. |
| Name | (2S)-1-phenylmethoxycarbonylpyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Carbobenzoxyproline (L-Cbz-Proline) is an inhibitor of prolidase. Carbobenzoxyproline can be used for prolidase deficiency (PD) research[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Carbobenzoxyproline (6 mM; 0-10 d; pH=6.0) causes mitochondrial depolarization and increases cellular death by 33% as reported for long-term culture of fibroblasts from prolidase deficiency (PD) patients[1]. Carbobenzoxyproline (0, 1, 3, 6 mM; 1 min; pH=6.0) results fibroblasts prolidase (FBP) hydrolysis, shows linear competitive inhibition[1]. |
| In Vivo | Carbobenzoxyproline (60 mg/kg; injection; once daily; 3 weeks) serves as in vivo inhibitor of erythrocytes prolidase in mice model[1]. Animal Model: C57Bl/6J mice (4-week-old)[1] Dosage: 60 mg/kg Administration: Injection; once daily for 3 weeks Result: Resulted significant reduction of erythrocytes prolidase activity. |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 432.3±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 76-78ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C13H15NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 249.262 |
| Flash Point | 215.3±28.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 249.100113 |
| PSA | 66.84000 |
| LogP | 1.17 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.582 |
| Storage condition | 2~8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Prolidase is required for early trafficking events during influenza A virus entry.
J. Virol. 88(19) , 11271-83, (2014) Influenza A virus (IAV) entry is a multistep process that requires the interaction of the virus with numerous host factors. In this study, we demonstrate that prolidase (PEPD) is a cellular factor req... |
|
|
N-benzyloxycarbonyl-L-proline: an in vitro and in vivo inhibitor of prolidase.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1744(2) , 157-63, (2005) Prolidase deficiency (PD) is a recessive disorder of the connective tissue caused by mutations in the prolidase, a specific peptidase, cleaving the dipeptides with a C-terminal prolyl and hydroxyproly... |
|
|
Proline prodrug of melphalan targeted to prolidase, a prodrug activating enzyme overexpressed in melanoma.
Pharm. Res. 24(7) , 1290-8, (2007) To determine the bioactivation and uptake of prolidase-targeted proline prodrugs of melphalan in six cancer cell lines with variable prolidase expression and to evaluate prolidase-dependence of prodru... |
| (S)-N-(benzyloxycarbonyl)-proline |
| Cbz-L-proline |
| 1,2-Pyrrolidinedicarboxylic acid, 1-benzyl ester, L- |
| EINECS 214-557-4 |
| (S)-1-(benzyloxycarbonyl)-pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid |
| (S)-N-CBZ-pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid |
| N-Benzyloxycarbonyl-L-proline |
| N-Carbobenzyloxy-L-proline |
| (2S)-1-[(Phenylmethoxy)carbonyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid |
| Carbobenzyloxy-L-proline |
| MFCD00003170 |
| 1,2-Pyrrolidinedicarboxylic acid, 1-(phenylmethyl) ester, (2S)- |
| N-Carbobenzoxy-L-proline |
| (S)-1-carbobenzoxypyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid |
| MFCD00020830 |
| 1,2-Pyrrolidinedicarboxylic acid, 1-(phenylmethyl) ester, (S)- |
| Carbobenzoxy-L-proline |
| 1-[(Benzyloxy)carbonyl]-L-proline |
| N-Cbz-L-proline |
| N-benzyloxycarbonyl-(S)-proline |
| (2S)-1-Phenylmethoxycarbonylpyrrolidine-2-carboxylicacid |
| Z-L-Proline |
| 1,2-Pyrrolidinedicarboxylic acid, 1-(phenylmethyl) ester, (S)- (9CI) |
| Z-Pro-OH |
| N-[(phenyl-methoxy)carbonyl]-L-proline |
| Benzyloxycarbonyl-L-proline |
 CAS#:501-53-1
CAS#:501-53-1 CAS#:147-85-3
CAS#:147-85-3 CAS#:1885-14-9
CAS#:1885-14-9 CAS#:6216-63-3
CAS#:6216-63-3 CAS#:107196-98-5
CAS#:107196-98-5 CAS#:5211-23-4
CAS#:5211-23-4 CAS#:250296-57-2
CAS#:250296-57-2 CAS#:108645-62-1
CAS#:108645-62-1![benzyl (2S)-2-[5-(4-bromophenyl)-1H-imidazol-2-yl]pyrrolidine-1-c arboxylate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/414/1007882-39-4.png) CAS#:1007882-39-4
CAS#:1007882-39-4![tert-butyl N-[(5S)-5-amino-6-[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[2-chloroethyl(nitroso)carbamoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]carbamoyl]pyrrolidin-1-yl]-6-oxohexyl]carbamate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/346/106039-80-9.png) CAS#:106039-80-9
CAS#:106039-80-9![(2S)-2-N-[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-amino-6-formamidohexanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]amino]-3-methylbutanoyl]-1-N-(2-chloroethyl)-1-N-nitrosopyrrolidine-1,2-dicarboxamide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/146/106039-85-4.png) CAS#:106039-85-4
CAS#:106039-85-4 CAS#:105706-84-1
CAS#:105706-84-1 CAS#:3304-59-4
CAS#:3304-59-4 CAS#:34079-31-7
CAS#:34079-31-7 CAS#:14485-80-4
CAS#:14485-80-4![1-[(2S)-2-Pyrrolidinylmethyl]pyrrolidine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/419/51207-66-0.png) CAS#:51207-66-0
CAS#:51207-66-0 CAS#:50888-84-1
CAS#:50888-84-1 CAS#:223785-66-8
CAS#:223785-66-8
