MCB-613
Modify Date: 2024-01-02 20:42:08
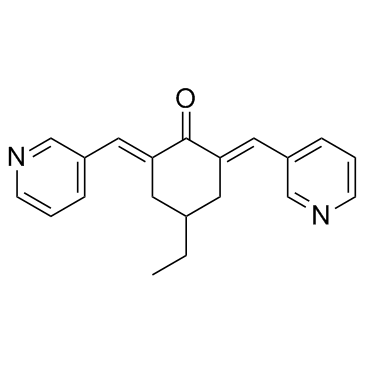
MCB-613 structure
|
Common Name | MCB-613 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1162656-22-5 | Molecular Weight | 304.386 | |
| Density | 1.159±0.06 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 510.4±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H20N2O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 257.9±36.5 °C | |
Use of MCB-613MCB-613 is a potent, pan steroid receptor coactivator (SRC) stimulator.Target: SRCin vitro: MCB-613 exerts the greatest activation of SRC-1 in the primary screen, is confirmed to be a strong activator of all three SRCs. MCB-613 can super-stimulate SRCs' transcriptional activity. MCB-613 increases SRCs' interactions with other coactivators and markedly induces ER stress coupled to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). MCB-613 selectively and reversibly binds to the RID of SRC-3, and selectively kills cancer cells including MCF-7 (breast), PC-3 (prostate), H1299 (lung), and HepG2 (liver) cells, without toxicity to mouse primary hepatocytes and mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs). MCB-613 also increases SRCs' interactions with other coactivators and markedly induces ER stress coupled to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). [1]in vivo: In an MCF-7 breast cancer mouse xenograft model, MCB-613 (20 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly and dramatically inhibits the growth of the tumor while causing no obvious animal toxicity and body weight less. [1] |
| Name | 4-ethyl-2,6-bis(pyridin-3-ylmethylene)cyclohexanone |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | MCB-613 is a potent, pan steroid receptor coactivator (SRC) stimulator.Target: SRCin vitro: MCB-613 exerts the greatest activation of SRC-1 in the primary screen, is confirmed to be a strong activator of all three SRCs. MCB-613 can super-stimulate SRCs' transcriptional activity. MCB-613 increases SRCs' interactions with other coactivators and markedly induces ER stress coupled to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). MCB-613 selectively and reversibly binds to the RID of SRC-3, and selectively kills cancer cells including MCF-7 (breast), PC-3 (prostate), H1299 (lung), and HepG2 (liver) cells, without toxicity to mouse primary hepatocytes and mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs). MCB-613 also increases SRCs' interactions with other coactivators and markedly induces ER stress coupled to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). [1]in vivo: In an MCF-7 breast cancer mouse xenograft model, MCB-613 (20 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly and dramatically inhibits the growth of the tumor while causing no obvious animal toxicity and body weight less. [1] |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.159±0.06 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 510.4±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C20H20N2O |
| Molecular Weight | 304.386 |
| Flash Point | 257.9±36.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 304.157562 |
| PSA | 42.85000 |
| LogP | 4.55 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.640 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
| Water Solubility | Practically insoluble (0.061 g/L) (25 ºC) |
| (2E,6E)-4-Ethyl-2,6-bis(3-pyridinylmethylene)cyclohexanone |
| Cyclohexanone, 4-ethyl-2,6-bis(3-pyridinylmethylene)-, (2E,6E)- |
| MCB-613 |

