NCX 470
Modify Date: 2024-01-06 12:58:31
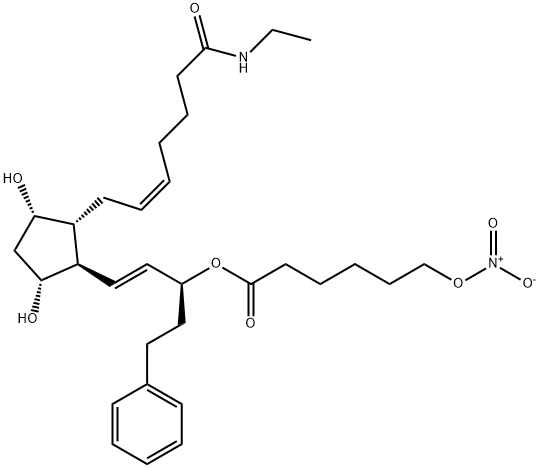
NCX 470 structure
|
Common Name | NCX 470 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1194396-71-8 | Molecular Weight | 574.71 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C31H46N2O8 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of NCX 470NCX 470 is a second-generation nitric oxide (NO)-donating prostaglandin analogue. NCX 470 effectively lowers intraocular pressure (IOP) in animal models of ocular hypertension and glaucoma by activating bimatoprost-mediated uveoscleral outflow and NO mediated conventional outflow. NCX 470 can be used for the research of cular hypertension and glaucoma[1][2]. |
| Name | Hexanoic acid, 6-(nitrooxy)-, (1S,2E)-3-[(1R,2R,3S,5R)-2-[(2Z)-7-(ethylamino)-7-oxo-2-hepten-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxycyclopentyl]-1-(2-phenylethyl)-2-propen-1-yl ester |
|---|
| Description | NCX 470 is a second-generation nitric oxide (NO)-donating prostaglandin analogue. NCX 470 effectively lowers intraocular pressure (IOP) in animal models of ocular hypertension and glaucoma by activating bimatoprost-mediated uveoscleral outflow and NO mediated conventional outflow. NCX 470 can be used for the research of cular hypertension and glaucoma[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vivo | NCX 470 shows a better intraocular pressure-lowering efficacy than that of equimolar doses of bimatoprost in well-established animal models of glaucoma and ocular hypertension[1]. NCX 470 (0.14% 30 μL; instillation; once) reduces IOP in transient ocular hypertensive rabbits[2]. NCX 470 (0.042% 30 μL; instillation; once) is more effective than equimolar bimatoprost in ONT-dogs and in OHT-monkeys at 18 hours post dosing[2]. Animal Model: New Zealand white rabbits with 0.1 mL 5% sodium chloride solution injection[2] Dosage: 0.14% Administration: Instillation; 0.14% 30 μL; once Result: Significantly blunted the IOP rise throughout the experimental period in transiently ocular hypertensive New Zealand white rabbits. |
| Molecular Formula | C31H46N2O8 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 574.71 |