(-)-Terreic acid
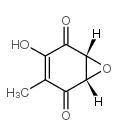
(-)-Terreic acid structure
|
Common Name | (-)-Terreic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 121-40-4 | Molecular Weight | 154.12000 | |
| Density | 1.613 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 333.6ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H6O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of (-)-Terreic acidTerreic acid, a quinone epoxide antibiotic, acts as an effective Btk inhibitor. Terreic acid blocks the interaction between PKC and the pleckstrin homology domain of Btk. Terreic acid inhibits the binding of GST-BtkPH to PKC in lysates of HMC-1 human mast cells with an IC50 of approximately 100 μM[1]. |
| Name | Terreic Acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Terreic acid, a quinone epoxide antibiotic, acts as an effective Btk inhibitor. Terreic acid blocks the interaction between PKC and the pleckstrin homology domain of Btk. Terreic acid inhibits the binding of GST-BtkPH to PKC in lysates of HMC-1 human mast cells with an IC50 of approximately 100 μM[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Btk; Antibiotic[1] |
| In Vitro | Terreic acid inhibits the association of Btk with PKCβII in mouse mast cells at lower concentrations (IC50 of ≈30 μM). Terreic acid inhibits the catalytic activity of Btk but not PKC[1]. Terreic acid (pretreatment for 30 min before stimulation by antigen for 3 min) inhibits both the basal and activation levels of Btk autophosphorylating activity with IC50s of 10 μM and 3 μM, respectively[1]. Terreic acid inhibits the autophosphorylating activity of Btk purified partially from recombinant baculovirus-infected Sf9 insect cells in a dose-dependent manner[1]. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: Mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells Concentration: 0, 5, 10, 20 μM Incubation Time: Pretreated for 30 min Result: Inhibited both the basal and activation levels of Btk autophosphorylating activity in a dose-dependent manner. |
| In Vivo | Terreic acid inhibits the late-phase response of in vivo allergic cutaneous reactions[1]. Animal Model: BALB/c mice[1] Dosage: 0, 0.15, 1.5, and 15 mg/kg Administration: Injected i.p. 1 hr before antigen challenge. Ear thicknesses were measured at 1 hr and 24 hr Result: The early response, as examined 1 hr after antigen challenge, was not affected by TA. In contrast, TA inhibited the late-phase (24 hr) response in a dose-dependent manner. |
| References |
| Density | 1.613 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 333.6ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C7H6O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 154.12000 |
| Exact Mass | 154.02700 |
| PSA | 66.90000 |
| Vapour Pressure | 9.63E-06mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.618 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 + H312 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
Studies on terreic acid.
Jpn. J. Antibiot. 33(3) , 320-8, (1980) It was found that Aspergillus sp. No. Y-8980 which was isolated from a soil sample collected at Yoron Island in Kagoshima Prefecture belonged to Aspergillus terreus group by morphological observation.... |
|
|
An improved mouse model of atopic dermatitis and suppression of skin lesions by an inhibitor of Tec family kinases.
Allergol. Int. 56(4) , 403-9, (2007) Atopic dermatitis is a chronic or chronically relapsing, pruritic inflammatory skin disease. The incidence of atopic dermatitis has dramatically increased during the past three decades in industrializ... |
|
|
Characterization of versilin-sensitive sites in self-sensitive producer and sensitive non-producer or unrelated organism.
J. Appl. Bacteriol. 67(2) , 191-200, (1989) Studies on self-sensitivity of producer mutant vs. sensitivity of non-producer parent and unrelated organism showed that versilin inhibited spore germination and sporulation in the self-sensitive prod... |
| (-)-Terreic acid,(1R,6S)-3-Hydroxy-4-methyl-7-oxabicyclo[4.1.0]hept-3-ene-2,5-dione |