| Description |
Fananserin (RP 62203) is an orally bioavailable, potent and selective 5-hydroxytryptamine2 (5-HT2) receptor antagonist, with a Ki of 0.37 nM for the rat 5-HT2A receptor. Fananserin also is a selective dopamine D4 receptor antagonist, with a Ki of 2.93 nM for the human dopamine D4 receptor[1].
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| Target |
Ki: 0.37 nM (5-HT2), 2.93 nM (human DA D4 receptor)[1]
|
| In Vitro |
Fananserin is relatively selective for 5-HT2 receptor, having lower affinity for the 5-HT1A receptor and very low affinity for the 5-HT3 receptor[1]. Fananserin displaces [3H]spiperone binding to recombinant human dopamine D 4 receptors with a Ki of 2.93 nM[1]. RP 62203 displays low to moderate affinity for α1-adrenoceptors, dopamine D2 receptors and histamine H 1 receptors[2].
|
| In Vivo |
Fananserin displaces [125I]AMIK from 5-HT2 receptors with an IC50 of 0.21 nM in rat frontal cortex[2]. Fananserin shows moderate affinity for alpha 1-adrenoceptors in the rat thalamus (IC50 = 14 nM) and for histamine H1 receptors in the guinea-pig cerebellum (IC50 = 13 nM)[2]. Fananserin (0.5-4 mg/kg; p.o.) increases the duration of deep nonrapid eye movement (NREM) sleep at the expense of wakefulness in a dose-dependent manner[3]. Animal Model: Adult male Sprague Dawley rats (250-300 g)[3] Dosage: 0.5 mg/kg, 1 mg/kg,2 mg/kg, 4 mg/kg Administration: Oral administration Result: Increased the duration of deep nonrapid eye movement (NREM) sleep at the expense of wakefulness in a dose-dependent manner from 0.5 mg/kg.
|
| References |
[1]. Heuillet E, et al. The naphtosultam derivative RP 62203 (fananserin) has high affinity for the dopamine D4 receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1996 Oct 24;314(1-2):229-33. [2]. Malgouris C, et al. Autoradiographic studies of RP 62203, a potent 5-HT2 receptor antagonist. In vitro and ex vivo selectivity profile. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar 16;233(1):29-35. [3]. Stutzmann JM, et al. RP 62203, a 5-hydroxytryptamine2 antagonist, enhances deep NREM sleep in rats. Sleep. 1992 Apr;15(2):119-24.
|
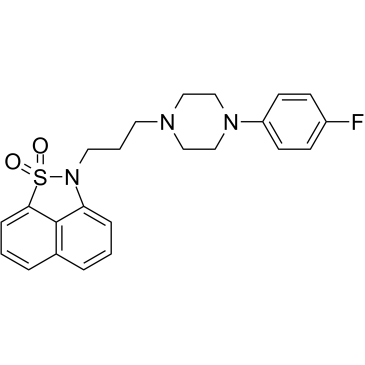
![2-(3-chloropropyl)-2H-naphth[1,8-cd]isothiazole 1,1-dioxide Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/386/127625-83-6.png) CAS#:127625-83-6
CAS#:127625-83-6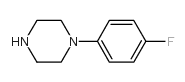 CAS#:2252-63-3
CAS#:2252-63-3![2H-naphth[1,8-cd]isothiazole 1,1-dioxide Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/455/603-72-5.png) CAS#:603-72-5
CAS#:603-72-5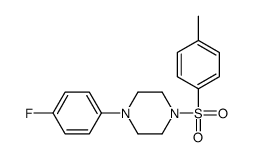 CAS#:4004-97-1
CAS#:4004-97-1 CAS#:371-40-4
CAS#:371-40-4