| Description |
I-BET151 is a BET bromodomain inhibitor which inhibits BRD4, BRD2, and BRD3 with pIC50 of 6.1, 6.3, and 6.6, respectively.
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| Target |
pIC50: 6.1 (BRD4), 6.3 (BRD2), 6.6 (BRD3)[1]
|
| In Vitro |
I-BET151 (GSK1210151A) causes a significant dose- and time-dependent decrease in the proportion of myeloma cells in S/G2 phase at 24, 48, and 72 hours. The most pronounced effect is observed at 72 hours in all 6 myeloma cell lines, starting at 100 nM. Dual Ki67/propidium iodide staining confirmed that the majority of live cells resided in the G0 phase after treatment with I-BET151 at 1 μM for 72 hours commensurate with a dose- and time-dependent decrease in cell proliferation and abrogation of bromodeoxyuridine incorporation[2].
|
| In Vivo |
I-BET151 (GSK1210151A) demonstrates low blood clearance in the rat (~20% liver blood flow) and good oral systemic exposure which resulted in good oral bioavailability. High clearance is observed in the dog (~95% liver blood flow). The systemic exposure in the dog is low, resulting in a poor oral bioavailability of 16%. The high blood clearance in dog correlates well with the high intrinsic clearance observed in dog microsomes and hepatocytes, whereas the low intrinsic clearances seen in rat and mouse (mouse IVC 1.6 mL/min/g; CLb 8 mL/min/kg) correlate with lower in vivo blood clearances in these species. Due to the low systemic exposure observed in the dog, I-BET151 is investigated in the mini-pig as a potential second species for toxicological evaluation where it showed low clearance (~32% liver blood flow) and good bioavailability (65%)[1]. In an in vivo model of subcutaneous myeloma, I-BET151 (50 mg/kg)-treated mice has four- to five fold smaller myeloma tumors (P<0.001) and a significantly reduced rate of tumor size doubling than vehicle-treated mice (P<0.001)[2].
|
| Cell Assay |
For in vitro cell proliferation and apoptosis assays, myeloma cell lines are cultured by using RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 2 mM L-glutamine, penicillin 500 IU/mL, and streptomycin 500 μg/mL. Cells are placed in 96-well U-bottom plates at final concentration of 0.2×106 cells per milliliter in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2 at 37°C. For stroma vs nonstroma experiments, myeloma cells are placed in flat-bottom 96-well plates with MS5 cells at >90% confluence or in wells without stroma. Compounds (ie, I-BET151, I-BET762, the inactive isomer I-BET768, and JQ1) are serially diluted into media and added to the cultures at the indicated concentrations, starting from a 10-mM DMSO stock solution.Primary myeloma cells are cultured in flat-bottom 96-well plates in the presence of MS5 stroma cells by using complete medium as above, supplemented with interleukin-6 (IL-6) at 5 ng/mL[2].
|
| Animal Admin |
Mice[2] NOD.Cg-Prkdcscid Il2rgtm1Wjl/SzJ (NSG) mice are used. In total, 5×106 KMS11 myeloma cells are injected subcutaneously into 9- to 12-week-old NSG mice. When tumors are ≥5 mm in maximum diameter, mice are randomized to receive once daily intraperitoneal injection of either I-BET151 30 mg/kg in 0.9% NaCl plus Kleptose hydroxypropyl betadex 10% (w/v) and DMSO 5% (v/v) pH 5.0 or vehicle solution for a maximum of 21 days.
|
| References |
[1]. Seal J, et al. Identification of a novel series of BET family bromodomain inhibitors: Binding mode and profile of I-BET151 (GSK1210151A). Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 Apr 15;22(8):2968-72. [2]. Chaidos A, et al. Potent antimyeloma activity of the novel bromodomain inhibitors I-BET151 and I-BET762. Blood. 2014 Jan 30;123(5):697-705.
|
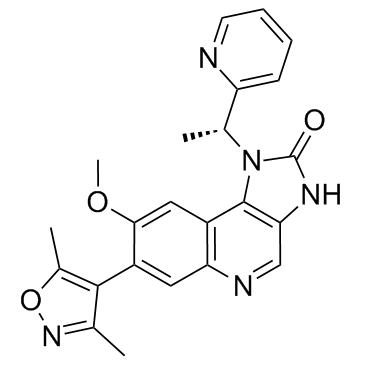

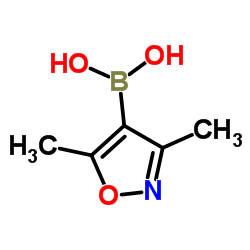 CAS#:16114-47-9
CAS#:16114-47-9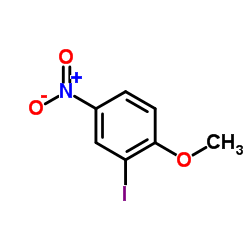 CAS#:5399-03-1
CAS#:5399-03-1![3,5-dimethyl-4-[2-(methyloxy)-5-nitrophenyl]isoxazole Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/374/1300031-62-2.png) CAS#:1300031-62-2
CAS#:1300031-62-2