Zinc Pyrithione
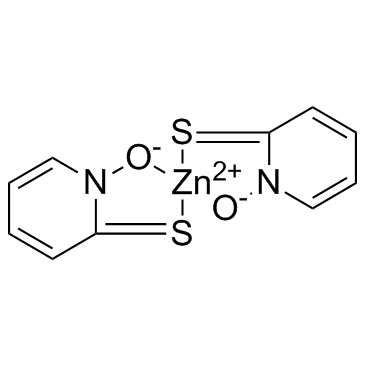
Zinc Pyrithione structure
|
Common Name | Zinc Pyrithione | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 13463-41-7 | Molecular Weight | 317.722 | |
| Density | 1.782 g/cm3 (25ºC) | Boiling Point | 253.8ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H8N2O2S2Zn | Melting Point | 262ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 107.3ºC | |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS06, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Zinc PyrithioneZinc Pyrithione is an antifungal and antibacterial agent disrupting membrane transport by blocking the proton pump.Target: Proton PumpZinc pyrithione is considered as a coordination complex of zinc. The pyrithione ligands, which are formally monoanions, are chelated to Zn 2+ via oxygen and sulfur centers. In the crystalline state, zinc pyrithione exists as a centrosymmetric dimer, where each zinc is bonded to two sulfur and three oxygen centers. In solution, however, the dimers dissociate via scission of one Zn-O bond. Zinc pyrithione, which is a dimer but is probably biologically active as a monomer, induces plasma membrane depolarization with half-maximal effect (K1/2) of about 0.3 mM [1]. Zinc pyrithione is an unusual synthetic potentiator that potently activates both heterologous and native M channels by inducing channel opening at the resting potential [2]. Zinc pyrithione rapidly accumulated in the tissues of the exposed mussels, proportionately to both exposure concentration and time. Even though the 7-d median lethal concentration (LC50) = 8.27 μM established here appears high with respect to reported ZnPT environmental concentrations, the results indicate that this biocide could represent a threat for marine organisms in coastal environments and that further investigations on its biological effects at sublethal doses are needed [3]. |
| Name | zinc pyrithione |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Zinc Pyrithione is an antifungal and antibacterial agent disrupting membrane transport by blocking the proton pump.Target: Proton PumpZinc pyrithione is considered as a coordination complex of zinc. The pyrithione ligands, which are formally monoanions, are chelated to Zn 2+ via oxygen and sulfur centers. In the crystalline state, zinc pyrithione exists as a centrosymmetric dimer, where each zinc is bonded to two sulfur and three oxygen centers. In solution, however, the dimers dissociate via scission of one Zn-O bond. Zinc pyrithione, which is a dimer but is probably biologically active as a monomer, induces plasma membrane depolarization with half-maximal effect (K1/2) of about 0.3 mM [1]. Zinc pyrithione is an unusual synthetic potentiator that potently activates both heterologous and native M channels by inducing channel opening at the resting potential [2]. Zinc pyrithione rapidly accumulated in the tissues of the exposed mussels, proportionately to both exposure concentration and time. Even though the 7-d median lethal concentration (LC50) = 8.27 μM established here appears high with respect to reported ZnPT environmental concentrations, the results indicate that this biocide could represent a threat for marine organisms in coastal environments and that further investigations on its biological effects at sublethal doses are needed [3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.782 g/cm3 (25ºC) |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 253.8ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 262ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C10H8N2O2S2Zn |
| Molecular Weight | 317.722 |
| Flash Point | 107.3ºC |
| Exact Mass | 315.931854 |
| PSA | 101.52000 |
| LogP | 3.34050 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.00275mmHg at 25°C |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble ( |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS06, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301 + H331-H318-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P273-P280-P301 + P310-P305 + P351 + P338-P311 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T+ |
| Risk Phrases | R24/25 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S28-S36/37/39-S45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | ZH0950000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| HS Code | 2933399010 |
|
~97% 
Zinc Pyrithione CAS#:13463-41-7 |
| Literature: KOLON INDUSTRIES, INC. Patent: EP1695963 A1, 2006 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 4-5 ; |
|
~% 
Zinc Pyrithione CAS#:13463-41-7 |
| Literature: US6432432 B1, ; |
|
~% 
Zinc Pyrithione CAS#:13463-41-7 |
| Literature: Thermochimica Acta, , vol. 186, p. 43 - 52 |
| HS Code | 2933399090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933399090. other compounds containing an unfused pyridine ring (whether or not hydrogenated) in the structure. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Acute toxicities of five commonly used antifouling booster biocides to selected subtropical and cosmopolitan marine species
Mar. Pollut. Bull. 62(5) , 1147-51, (2011) Highlights ► Tributyltin was not the most toxic antifouling biocides for 12 marine species. ► Irgarol was more toxic than TBT on the growth of autotrophic species. ► Toxicity of copper pyrithione was ... |
|
|
Effects of seven antifouling compounds on photosynthesis and inorganic carbon use in sugar kelp Saccharina latissima (Linnaeus).
Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 63(3) , 365-77, (2012) Macroalgae depend on carbon-concentrating mechanisms (CCMs) to maintain a high photosynthetic activity under conditions of low carbon dioxide (CO(2)) availability. Because such conditions are prevalen... |
|
|
Immunotoxicity in ascidians: antifouling compounds alternative to organotins-IV. The case of zinc pyrithione.
Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 169 , 16-24, (2015) New biocides such as the organometallic compound zinc pyrithione (ZnP) have been massively introduced by many countries in formulations of antifouling paints following the ban on tributyltin (TBT). Th... |
| Zinc pyrithione |
| 1-Hydroxypyridine-2-thione zinc salt |
| MFCD00067336 |
| EINECS 236-671-3 |
| 2-Pyridinethiol 1-Oxide Zinc Salt |
| Bis(2-pyridylthio) Zinc 1,1'-Dioxide |
| Mercaptopyridine N-oxide zinc salt |
| 2-Mercaptopyridine N-oxide zinc salt |