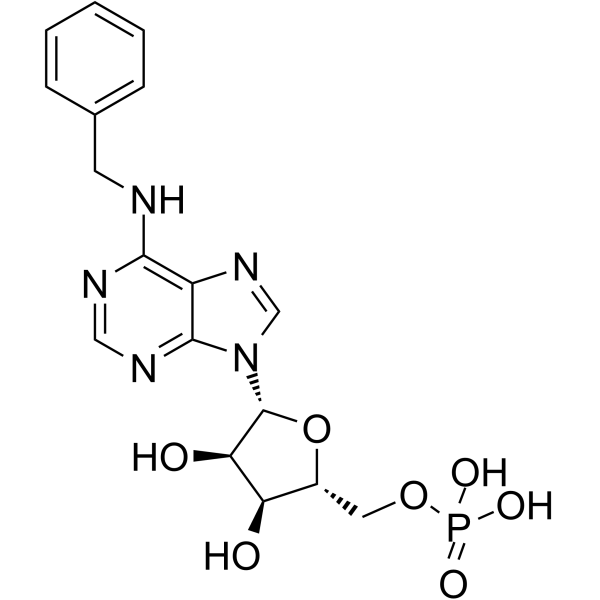
Benzyl-amp
Benzyl-amp structure
|
Common Name | Benzyl-amp | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 13484-66-7 | Molecular Weight | 437.34400 | |
| Density | 1.81g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 798.5ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H20N5O7P | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 436.7ºC | |
Use of Benzyl-ampIST5-002, a potent Stat5a/b inhibitor, selectively inhibits transcriptional activity of Stat5a/b (IC50s: 1.5 μM for Stat5a, 3.5 μM for Stat5b). IST5-002 inducs cell apoptotic and death of prostate cancer cells and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) cells. IST5-002 can be used in the research of prostate cancer and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)[1]. |
| Name | N6-Benzyladenosine-5'-phosphate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | IST5-002, a potent Stat5a/b inhibitor, selectively inhibits transcriptional activity of Stat5a/b (IC50s: 1.5 μM for Stat5a, 3.5 μM for Stat5b). IST5-002 inducs cell apoptotic and death of prostate cancer cells and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) cells. IST5-002 can be used in the research of prostate cancer and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
STAT5a:1.5 μM (IC50) STAT5b:3.5 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | IST5-002 (1.5-25 μM, 2 h) inhibits transcriptional activity of Stat5a and Stat5b in a dose-dependent manner[1]. IST5-002 (0-40 μM, 3 h) inhibits Bcr-Abl-induced Stat5a/b phosphorylation in K562 cells[1]. IST5-002 (5-100 μM, 2 h) inhibits Stat5a/b phosphorylation in T47D cells, and inhibits dimerization in PC-3 cells[1]. IST5-002 (5-100 μM, 2 h) suppresses Stat5 nuclear translocation in PC-3 cells, and inhibits DNA binding of Stat5 target genes and COS-7 cells[1]. IST5-002 (2-50 μM, 48 h) reduces expression of Stat5a/b target genes (Bcl-xL and cyclin D1) in CWR22Rv1 and LNCaP cells[1]. IST5-002 (3.1-50 μM, 72 h) inhibits cell growth through induction of apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells[1]. IST5-002 (25-100 μM, 7 days) induces epithelial cell death in patient-derived prostate cancers ex vivo in organ explant cultures[1]. IST5-002 (5 μM, 24-72h) inhibits Stat5a/b phosphorylation and induces apoptosis of Imatinib (HY-15463)-sensitive and -resistant CML cells[1]. Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Line: CWR22Rv1, LNCaP, and DU145 cells Concentration: 3.1, 6.3, 12.5, 25, 50 μM Incubation Time: 72 h Result: Decreased viable cells by 50% to 80% at 12.5 μM. Cell Cycle Analysis[1] Cell Line: LNCaP and CWR22Rv1 cells Concentration: 6, 12, 25 μM Incubation Time: 72 h Result: Increased the fraction of dead cells (sub-G1) and decreased the fraction of living cells (G2–M). Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: Bcr-Abl–positive K562 cells Concentration: 0, 1, 5, 10, 20, 40 μM Incubation Time: 3 h Result: Inhibited Bcr-Abl-induced Stat5a/b phosphorylation at 5 μM, without affecting Bcr-Abl tyrosine phosphorylation levels. Immunofluorescence[1] Cell Line: PC-3 cells Concentration: 5, 10, 15. 20, 40 μM Incubation Time: 2 h Result: Inhibited Prl (Prolactin)-induced nuclear translocation of Stat5. |
| In Vivo | RORγt inverse agonist 29 (intraperitoneal injection, 25-100 mg/kg, daily for 10 days) inhibits tumor growth in prostate cancer xenograft model[1]. Animal Model: Prostate cancer (CWR22Rv1) xenograft model[1] Dosage: 25, 50, and 100 mg/kg Administration: Intraperitoneal injection, daily for 10 days Result: Induced massive loss of viable tumor cells and dead rounded cells accumulation. Induced cell death through apoptosis (shown by fragmented DNA in tumor sections). Decreased nuclear Stat5a/b content by 60%, 78%, and 90% at 25, 50, and 100 mg/kg, respectively. |
| References |
| Density | 1.81g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 798.5ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C17H20N5O7P |
| Molecular Weight | 437.34400 |
| Flash Point | 436.7ºC |
| Exact Mass | 437.11000 |
| PSA | 181.89000 |
| LogP | 0.23990 |
| Vapour Pressure | 6.67E-27mmHg at 25°C |
|
~% 
Benzyl-amp CAS#:13484-66-7 |
| Literature: Kulak; Tkachenko; Grishan; Kukharskaya; Eroshevskaya; Kalinichenko; Zinchenko Chemistry of Natural Compounds, 2009 , vol. 45, # 1 p. 74 - 78 |
|
~% 
Benzyl-amp CAS#:13484-66-7 |
| Literature: Kulak; Tkachenko; Grishan; Kukharskaya; Eroshevskaya; Kalinichenko; Zinchenko Chemistry of Natural Compounds, 2009 , vol. 45, # 1 p. 74 - 78 |
|
~% 
Benzyl-amp CAS#:13484-66-7 |
| Literature: Kulak; Tkachenko; Grishan; Kukharskaya; Eroshevskaya; Kalinichenko; Zinchenko Chemistry of Natural Compounds, 2009 , vol. 45, # 1 p. 74 - 78 |
|
~% 
Benzyl-amp CAS#:13484-66-7 |
| Literature: Kulak; Tkachenko; Grishan; Kukharskaya; Eroshevskaya; Kalinichenko; Zinchenko Chemistry of Natural Compounds, 2009 , vol. 45, # 1 p. 74 - 78 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| [(2R,3R,4R,5R)-5-[6-(benzylamino)purin-9-yl]-3,4-dihydroxy-oxolan-2-yl ]methoxyphosphonic acid |
| N6-Benzyladenosin-5'-phosphat |
| Benzyl-adenosine monophosphate |
| BAR-5'-monophosphate |
| Benzyl-amp |
| N(6)-Benzyladenosine-5'-monophosphate |
| 6-N-benzyladenosine-5'-O-monophosphate |
| N6-Benzyladenosin-5'-monophosphat |
| N6-Benzyladenosine 5'-Phosphat |
| N6-benzyl-[5']adenylic acid |