Strontium Ranelate
Modify Date: 2024-01-02 16:29:50
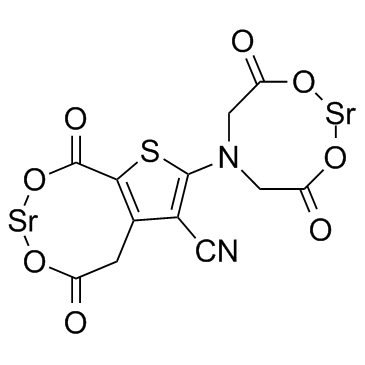
Strontium Ranelate structure
|
Common Name | Strontium Ranelate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 135459-87-9 | Molecular Weight | 513.49 | |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 778.8±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H6N2O8SSr2 | Melting Point | >310°C (dec.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 424.8±32.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Strontium RanelateStrontium ranelate(S12911) stimulates the calcium sensing receptors (CaSR) and leads to the differentiation of pre-osteoblast to osteoblast which increases the bone formation.IC50 value:Target: CaSRStrontium Ranelate is a bone metabolism modulator that inhibits bone resorption while maintaining bone formation. Strontium Ranelate acts by increasing bone formation and decreasing bone resorption, thus rebalancing bone turnover in favour of bone formation, an effect that results in increased bone mass and strength. Commonly used as an antiosteoporotic. Strontium Ranelate has shown efficacy in preventing early postmenopausal bone loss and reducing the risk of hip fracture in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis. |
| Name | 2,2'-((5-Carboxy-4-(carboxymethyl)-3-cyanothiophen-2-yl)azanediyl)diacetic acid, distrontium salt |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Strontium ranelate(S12911) stimulates the calcium sensing receptors (CaSR) and leads to the differentiation of pre-osteoblast to osteoblast which increases the bone formation.IC50 value:Target: CaSRStrontium Ranelate is a bone metabolism modulator that inhibits bone resorption while maintaining bone formation. Strontium Ranelate acts by increasing bone formation and decreasing bone resorption, thus rebalancing bone turnover in favour of bone formation, an effect that results in increased bone mass and strength. Commonly used as an antiosteoporotic. Strontium Ranelate has shown efficacy in preventing early postmenopausal bone loss and reducing the risk of hip fracture in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
[4]. Sorbera, L.A., Castaner, et al . Strontium Ranelate .Drugs Fut 2003, 28(4): 328 |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 778.8±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | >310°C (dec.) |
| Molecular Formula | C12H6N2O8SSr2 |
| Molecular Weight | 513.49 |
| Flash Point | 424.8±32.9 °C |
| PSA | 160.47000 |
| LogP | -0.90 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.695 |
| Storage condition | -20°C Freezer |
| Water Solubility | H2O: soluble1mg/mL, clear (warmed) |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
|---|
| 3-Thiopheneacetic acid, 5-[bis(carboxymethyl)amino]-2-carboxy-4-cyano- |
| 5-[Bis(carboxymethyl)amino]-3-(carboxymethyl)-4-cyano-2-thiophenecarboxylic acid |
| 5-[Bis(carboxymethyl)amino]-3-(carboxymethyl)-4-cyanothiophene-2-carboxylic acid |
| Strontium Ranelate |
| Ranelic Acid Strontium Salt |

