Sodium orthovanadate
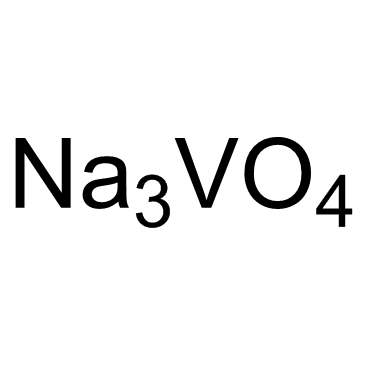
Sodium orthovanadate structure
|
Common Name | Sodium orthovanadate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 13721-39-6 | Molecular Weight | 183.908 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | Na3O4V | Melting Point | 850-866 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Sodium orthovanadateSodium orthovanadate is an inhibitor of protein tyrosine phosphatases, alkaline phosphatases and a number of ATPases, most likely acting as a phosphate analogue. |
| Name | trisodium vanadate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Sodium orthovanadate is an inhibitor of protein tyrosine phosphatases, alkaline phosphatases and a number of ATPases, most likely acting as a phosphate analogue. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
PPTPase[1]. |
| In Vitro | In the presence of oxidizing agents vanadium ions exist as the hydrated monomer of Sodium orthovanadate (vanadate: HVO42- or H2VO4-) at micromolar concentations near neutral pH. Sodium orthovanadate (vanadate) also begins to polymerize at concentrations greater than 0.1 mM at neutral pH. The yellow-orange solutions of decavanadate can be converted to the colorless solutions of monomeric Sodium orthovanadate (vanadate) by dilution after a period of many hours. The process is hastened by boiling at pH 10, which encourages the kinetically sluggish depolymerization process[1]. Sodium orthovanadate could alter the phosphorylation status of ASK1 at serine 83 and threonine 845 induced by ischemia. Sodium orthovanadate could increase the tyrosine posphorylation of PTEN and further inhibit the activation of ASK1 via activating Akt during cerebral ischemia[2]. |
| References |
| Melting Point | 850-866 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | Na3O4V |
| Molecular Weight | 183.908 |
| Exact Mass | 183.892929 |
| PSA | 86.25000 |
| Storage condition | Store at RT |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 + H312 + H332 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R20/21/22 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S36 |
| RIDADR | UN3285 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | YW1120000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
|
A survey of the interactome of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF45 revealed its binding to viral ORF33 and cellular USP7, resulting in stabilization of ORF33 that is required for production of progeny viruses.
J. Virol. 89(9) , 4918-31, (2015) The ORF45 protein of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is a gammaherpesvirus-specific immediate-early tegument protein. Our previous studies have revealed its crucial roles in both early ... |
|
|
Progressive accumulation of activated ERK2 within highly stable ORF45-containing nuclear complexes promotes lytic gammaherpesvirus infection.
PLoS Pathog. 10(4) , e1004066, (2014) De novo infection with the gammaherpesvirus Rhesus monkey rhadinovirus (RRV), a close homolog of the human oncogenic pathogen, Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), led to persistent activat... |
|
|
Disturbed Hsp70 and Hsp27 expression and thiol redox status in porcine kidney PK15 cells provoked by individual and combined ochratoxin A and citrinin treatments.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 71 , 97-105, (2014) The aim of this study was to explore the oxidative properties of ochratoxin A (OTA) and citrinin (CTN) as a possible underlying mechanism of their individual and/or combined cytotoxicity. Metabolic ac... |
| Trisodium tetraoxovanadate(3-) |
| Vanadate(3-), tetraoxo-, sodium (1:3) |
| sodium tetraoxovanadate(3-) |
| MFCD00003511 |
| Sodium orthovanadate |
| EINECS 237-287-9 |

