Cefilavancin
Modify Date: 2024-01-11 15:55:56
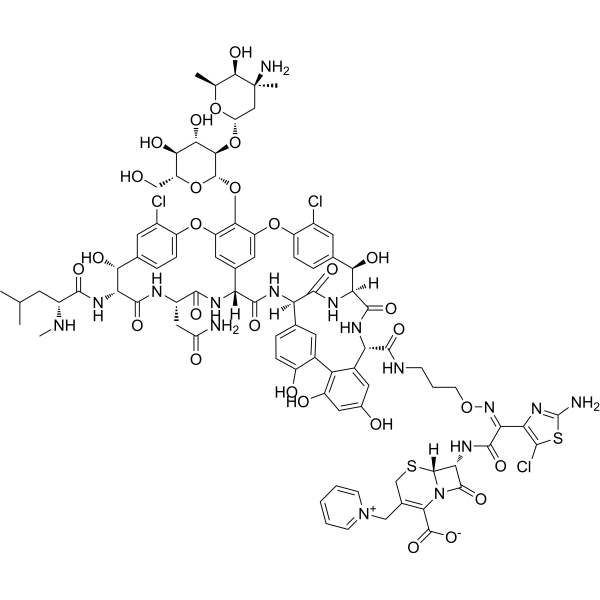
Cefilavancin structure
|
Common Name | Cefilavancin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1393900-12-3 | Molecular Weight | 1983.26 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C87H95Cl3N16O28S2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of CefilavancinCefilavancin (TD-1792) is a potent multivalent glycopeptide-cephalosporin heterodimer antibiotic with effective activity against Gram-positive bacteria. Cefilavancin has been used to research skin infections[1][2][3]. |
| Name | Cefilavancin |
|---|
| Description | Cefilavancin (TD-1792) is a potent multivalent glycopeptide-cephalosporin heterodimer antibiotic with effective activity against Gram-positive bacteria. Cefilavancin has been used to research skin infections[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Glycopeptide |
| In Vitro | Cefilavancin (TD-1792) has highly active against Methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus (MIC90 = 15 ng/mL), Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, and heterogeneous Vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus (MIC90 = 30 ng/mL)[1]. |
| In Vivo | Cefilavancin (0.03-10 mg/kg; s.c.) produces a dose-dependent reduction of thigh bacterial burden in infected mice[3]. Animal Model: Female NSA mice (18-30 g; neutropenia induced by administering cyclophosphamide, then injected bacteria into the posterior thigh)[3] Dosage: 0.03-10 mg/kg Administration: s.c.; single dosage (every 24 h) or two (every 12 h), three (every 8 h), or four (every 6 h) divided doses Result: Produced a maximal of approximately 1- to 2-log10 kill against MRSA ATCC 33591, MSSA ATCC 29213, and MRSE MED 820 and ≥3-log10 kill against VISA HIP 5836, MSSE SU03, PSSP MED35, PSSP MED1119, and Streptococcus pyogenes MED 2040 strains. |
| Molecular Formula | C87H95Cl3N16O28S2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 1983.26 |