| Description |
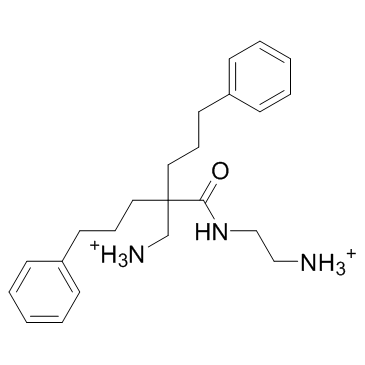
LTX-401, an oncolytic amino acid derivative, targets the Golgi apparatus.
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| Target |
Golgi apparatus[1].
|
| In Vitro |
LTX-401, an oncolytic amino acid derivative, targets the Golgi apparatus[2]. LTX-401 effectively reduces the viability of several tumor cell lines in vitro, with a similar degree of cytotoxicity against non-malignant cell lines such as HUV-EC-C endothelial cells, HaCat keratinocytes and MRC-5 fibroblasts. LTX-401 displays the highest cytotoxic activity against the human malignant melanoma cell line MDA-MB-435S (13.5 μM), and is least active against the human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HEPG2 (35.4 μM). For the remaining cell lines, LTX-401 exhibits similar IC50 values, varying slightly within the range of 19-32 μM. No in vitro hemolytic activity against RBCs is observed using the same concentrations required for the induction of cell death in cancer cell lines. A 50% hemolysis is observed using higher concentrations of LTX-401 (400 μg/mL=1087 μM)[1].
|
| In Vivo |
The majority (9/11) of the animals demonstrate a complete and lasting tumor regression after intratumoral treatment with LTX-401. Samples are collected from selected animals in the treatment group and control group on days 2 and 7 post-treatment with a single i.t injection. The immunolabelling of tumor tissue with anti-CD3 antibody reveals that a majority of the infiltrating cells are CD3+ T cells, whereas tumors injected with vehicle only exhibit tumors with a viable tumor tissue, with minimal necrosis and few lymphocytes[1].
|
| Cell Assay |
The MTT assay is employed to investigate the in vitro cytotoxicity of LTX-401 against a selection of both cancer and non-malignant cell lines. Pre-cultured cells are seeded at a density between 1x104-1.5x104 cells/well. The cytotoxic activity of LTX-401 against human red blood cells (RBCs) is determined by a hemolytic assay using freshly isolated blood from healthy individuals who gave their signed informed consent. RBCs are resuspended to a 10% hematocrit solution before being incubated for 1 h at 37°C with LTX-401 dissolved in PBS at concentrations ranging from 136-1358 μM (50-500 μg/mL). RBCs with PBS and 1% Triton solution alone serves as a negative and positive control, respectively. After centrifuging the samples at 4,000 rpm for 5 minutes, the absorbance of the supernatant is measured at 405 nm on a spectrophotometric microliter plate reader[1].
|
| Animal Admin |
Mice[1] Female C57BL/6 wild-type mice, 5-6 weeks old, are used. All animals are housed in the same room and in cages (containing 2-5 mice) specially designed for mice, with a 12 h/12 h day-night cycle, and allowed ad libitum access to high quality food and water. Animals are weighed weekly and monitored several times per week, and no unexpected deaths are observed. B16F1 cells are harvested, washed in serum-free RPMI and injected intradermally (i.d) into the right side of the abdomen in C57BL/6 mice (7.5x104 B16F1 cells per mouse/50 μL RPMI-1640). Palpable tumors (20-30 mm2) are injected intratumorally (i.t) with either LTX-401 (5 mg/mL) or a vehicle (saline) once per day for three consecutive days. Animals are euthanized according to humane endpoints such as a weight loss of >10%, general physical discomfort or reduced activity, severe tumor necrosis or ulceration, or if the tumor size exceeds 130 mm2. All animals are euthanized using cervical dislocation[1].
|
| References |
[1]. Liv-Marie Eike, et al. The Cytolytic Amphipathic β(2,2)-Amino Acid LTX-401 Induces DAMP Release in Melanoma Cells and Causes Complete Regression of B16 Melanoma. PLoS One. 2016; 11(2): e0148980. [2]. Heng Zhou, et al. The oncolytic compound LTX-401 targets the Golgi apparatus. Cell Death Differ. 2018 Jan; 25(1): 227–228.
|