Hexarelin
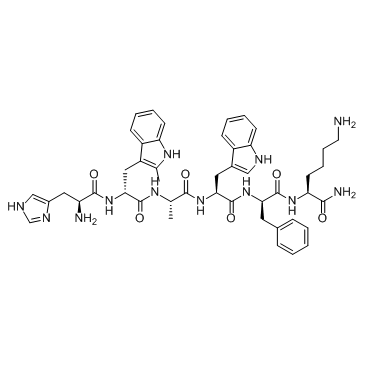
Hexarelin structure
|
Common Name | Hexarelin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 140703-51-1 | Molecular Weight | 887.04000 | |
| Density | 1.322 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 1403.6ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C47H58N12O6 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 802.7ºC | |
Use of HexarelinExamorelin, a synthetic growth hormone-releasing peptide, has been proven to possess cardioprotective actions through its binding to the growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR) 1a and the non-GHSR receptor CD36. |
| Name | Hexarelin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Examorelin, a synthetic growth hormone-releasing peptide, has been proven to possess cardioprotective actions through its binding to the growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR) 1a and the non-GHSR receptor CD36. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
GHSR[1] |
| In Vitro | Cultured MIN6 cells are incubated with serum-free medium (SFM) (control), 1 μM Examorelin (Hex), 1 mM Streptozotocin (STZ) alone or STZ followed by Examorelin for 6 hours. The viability of MIN6 is significantly affected by different treatments of the cells (F(3, 36)=5.244,P<0.01) . MIN6 cells treated with STZ followed by Examorelin receive a great increase in the cell viability (105.3% of control, P<0.01) as compared with those treated with STZ alone[2]. |
| In Vivo | Examorelin (Hexarelin) treatment improves cardiac systolic function, decreases malondialdehyde production, and increases the number of surviving cardiomyocytes. The beneficial effects of Examorelin treatment are slightly superior to those of equimolar ghrelin treatment. Examorelin also induces down-regulation of IL-1β expression and up-regulation of IL-1Ra expression in I/R myocardium, which could be neutralized by the GHSR antagonist (D-Lys3)-GHRP-6. Examorelin protects in vivo cardiomyocytes from I/R injury partly by modification of the IL-1 signaling pathway through the activation of cardiac GHSR1a receptors[1]. The effect of Examorelin (100 μg/kg) in STZ-induced diabetic rats is examined. STZ-injection dramatically increased blood glucose levels in rats whereas Examorelin (Hex) treatment diminished the effect of STZ. Plasma insulin levels of rats are measured under both fasting and fed conditions respectively. Different treatment exerted significant effects on fasting insulin level (F(3, 28)=7.472, P<0.01) . The Examorelin alone increases the plasma insulin (P<0.05) whereas the STZ dramatically decreases it (P<0.001). STZ+Examorelin -treated rats show an increased insulin level (P<0.001). Similar to fasting insulin level, fed insulin level (Ftreatment (3, 28)=61.89, P<0.001) are significantly increased in Examorelin-treated rats (P<0.001) and reduced in STZ-treated rats. Furthermore, the Examorelin also ameliorates STZ-induced decrease in fed plasma insulin level[2]. |
| Cell Assay | MIN6 and α-TC6 cells are seeded in 96-well plates and cultured in the presence or absence of Examorelin (1 μM) and STZ (1 mM) for 0.5, 1, 2, 4, and 6 hours. After the treatment, cells are replaced in fresh SFM and the number of viable cells is quantified using CellTiter 96 Aqueous One Solution Cell Proliferation Assay , which contains the tetrazolium compound MTS. Cell viability is determined by measuring absorbance at 490 nm with a microplate reader and expressed as a percentage relative to control cells[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats[2] Experiments are performed in male Wistar rats (180–200 g). Rats are housed separately under standard housing conditions (lights on from 06:00 to 18:00, temperature 22±2°C) and have access to food and water ad libitum. A single intraperitoneal injection of STZ dissolved in a 0.1 mol/L citrate buffer (pH 4.5) is used at a dose of 65 mg/kg body weight. Age-matched control rats receive an equal volume of vehicle (sodium citrate buffer). Four weeks after STZ or vehicle injection, rats are randomly assigned to 4 groups (n=16/group) according to the treatment: rats with vehicle then saline for 2 weeks (control group); or 100 μg/kg Examorelin for 2 weeks (Examorelin treated group); STZ-treated rats then saline for 2 weeks (STZ treated group); or 100 μg/kg Examorelin for 2 weeks (STZ+Examorelin treated group). Saline and Examorelin are intraperitoneally injected daily. |
| References |
| Density | 1.322 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 1403.6ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C47H58N12O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 887.04000 |
| Flash Point | 802.7ºC |
| Exact Mass | 886.46000 |
| PSA | 300.89000 |
| LogP | 5.39220 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.66 |
| Storage condition | ?20°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | OL4683333 |
|
Multiplex SSR-PCR approaches for semi-automated genotyping and characterization of loci linked to blast disease resistance genes in rice.
C R Biol. 338 , 709-22, (2015) In the present study, 63 polymorphic microsatellite markers related to rice blast resistance genes were fluorescently labelled at the 5'-end with either 6-FAM or HEX using the G5 dye set and incorpora... |
|
|
Concentrations, gas-particle partitioning, and seasonal variations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons at four sites in Turkey.
Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 68(1) , 46-63, (2015) Ambient air polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) samples were collected at traffic, residential, coastal, and semiurban sites in Bursa, Turkey, between June 2008 and June 2009. For the traffic, resid... |
|
|
Multivariate optimization for extraction of pyrethroids in milk and validation for GC-ECD and CG-MS/MS analysis.
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 11(11) , 11421-37, (2014) A simple and inexpensive method based on solvent extraction followed by low temperature clean-up was applied for determination of seven pyrethroids residues in bovine raw milk using gas chromatography... |
| MFCD00671439 |
| M.W. 887.04 C47H58N12O6 |
| L-Histidyl-2-methyl-D-tryptophyl-L-alanyl-L-tryptophyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-lysinamide |
| Hexarelin |
| HIS-D-2-METHYL-TRP-D-PHE-LYS-NH2 |
| Examorelin |
| GROWTH HORMONE RELEASING HEXAPEPTIDE |
| HIS-D-2-ME-TRP-ALA-TRP-D-PHE-LYS-NH2 |
| L-Lysinamide, L-histidyl-2-methyl-D-tryptophyl-L-alanyl-L-tryptophyl-D-phenylalanyl- |

