Ginsenoside Rg3
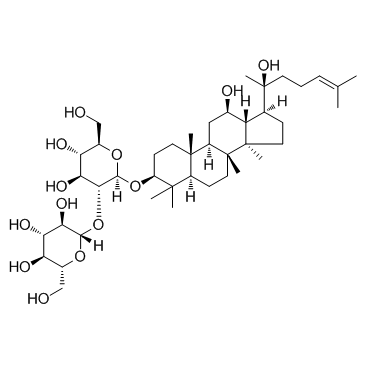
Ginsenoside Rg3 structure
|
Common Name | Ginsenoside Rg3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 14197-60-5 | Molecular Weight | 785.013 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 885.0±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C42H72O13 | Melting Point | 315-318°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 489.0±34.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Ginsenoside Rg3Ginsenoside Rg3 is the main component of Red ginseng. Ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits Na+ and hKv1.4 channel with IC50s of 32.2±4.5 and 32.6±2.2 μM, respectively. Ginsenoside Rg3 also inhibits Aβ levels, NF-κB activity, and COX-2 expression. |
| Name | (20S)-ginsenoside Rg3 |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ginsenoside Rg3 is the main component of Red ginseng. Ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits Na+ and hKv1.4 channel with IC50s of 32.2±4.5 and 32.6±2.2 μM, respectively. Ginsenoside Rg3 also inhibits Aβ levels, NF-κB activity, and COX-2 expression. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
p65 COX-2 Na+ channel:32.2 μM (IC50) hKv1.4 channel:32.6 μM (IC50) Aβ40 Aβ42 |
| In Vitro | Ginsenoside Rg3 plays an important role in its effect on the Na+ channel. Treatment with Ginsenoside Rg3 reversibly inhibits the inward Na+ peak current (INa) with an IC50 of 32.2±4.5 μM, and the inhibition is voltage-dependent[1]. Ginsenoside Rg3 at 100 μM inhibits the hKv1.4 channel currents by an average of 65%.The Ginsenoside Rg3 effect is concentration-dependent and reversible. The IC50 value and Hill coefficient are 32.6±2.2 μM and 1.59±0.13, respectively[2]. Ginsenoside Rg3 shows the significant inhibition of NF-κB activity thereby reduced COX-2 expression. To examine the cytotoxicity of Ginsenoside Rg3 on IL-1β-induced inflamed A549 cells, the cells are firstly treated with IL-1β (10 ng/mL) for 4 h and treated with 100 to 900 ng/mL concentration of Ginsenoside Rg3 for 12 h. Cell viability is analyzed using an MTT assay. There is no observed cytotoxicity of Ginsenoside Rg3 in IL-1β-induced inflamed A549 cells compared to only PBS-treated cells (Con).To obtain the anti-inflammatory effects of Ginsenoside Rg3 on inflammation induced human lung epithelial cells, A549 cells inflammation is induced by IL-1β (10 ng/mL) and then treated by 5 μM of Dexamethasone (Dex) or 900 nM of Rg3. The NF-κB activation is analyzed by a western blot analysis to evaluate the effect of Ginsenoside Rg3 treatment on A549 cells. Phospho-NF-κB p65/total NF-κB p65 densitometry in the cells treated with Rg3 shows the significant decrease compared to IL-1β-induced inflamed A549 cells. The meaning of reducing the ratio of p-p65/p65 by Rg3 treatment is associated with NF-κB activation. Ginsenoside Rg3 also downregulates the expression of COX-2 effectively[3]. |
| In Vivo | Ginsenoside Rg3 ((20S)-Rg3) is an Aβ-lowering Natural Compound. APP/PS1 mice are treated with Ginsenoside Rg3 once a day for 4 weeks by intraperitoneal injection (10 mg/kg/day). Aβ ELISA analysis of brain tissues reveal that Ginsenoside Rg3 treatment results in a significant reduction of Aβ40 and Aβ42 in the brain[4]. |
| Cell Assay | MTT assays are performed to evaluate the cytotoxicity of Ginsenoside Rg3 on inflamed cells. Ten thousands of A549 cells cultured each well of 96-well plate and are incubated at 37°C and 5% CO2 overnight. After serum starvation using DMEM low glucose without FBS, the medium is changed into RPMI containing IL-1β (10 ng/mL) and the cells are incubated at 37°C and 5% CO2 for 4 h. After 4 h incubation, the cells are treated with Ginsenoside Rg3 (100-900 nM) for 12 h. Thirty microliters of MTT solution (5 mg/mL) is added to each well and the cells are incubated for 2 h. After 2 h incubation in cell culture incubator, the medium containing MTT solution of each well is removed and 50 μL of DMSO is added. Using an automated spectrophotometric plate reader at 570 nm, the optical density of formazan is measured[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[4] The mice used are heterozygous, double transgenic animals expressing both human APP(K670N/M671L) and PS1(M146L) proteins. These Alzheimer disease model mice are age-matched (3 months old) in all experiments with wild-type littermates. Both sets of mice are produced by crossing heterozygous APP mice with heterozygous PS1 mice and are weaned at 3 weeks and genotyped by PCR of digested tail samples. Ginsenoside Rg3 is prepared in a saline solution containing 0.01% DMSO at a concentration of 10 mg/kg of body weight. Ginsenoside Rg3 (or saline with 0.01% DMSO for controls) is administered daily via intraperitoneal injection. After sacrifice, one hemibrain from each mouse is frozen on dry ice, homogenized in sucrose buffer, and extracted via formic acid for Aβ quantification using a commercial sandwich ELISA kit. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 885.0±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 315-318°C |
| Molecular Formula | C42H72O13 |
| Molecular Weight | 785.013 |
| Flash Point | 489.0±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 784.497314 |
| PSA | 218.99000 |
| LogP | 5.27 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.594 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Hazard Codes | T,N,Xi |
| Risk Phrases | R23/24/25:Toxic by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed . R33:Danger of cumulative effects. R50/53:Very Toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment . |
| Safety Phrases | S28-S36/37-S45-S60-S61-S28A |
| RIDADR | UN 3442 6.1/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | CX9862655 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 29214210 |
|
~% 
Ginsenoside Rg3 CAS#:14197-60-5 |
| Literature: Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, , vol. 37, # 11 p. 2961 - 2970 |
|
~% 
Ginsenoside Rg3 CAS#:14197-60-5 |
| Literature: Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, , vol. 37, # 11 p. 2961 - 2970 |
|
~% 
Ginsenoside Rg3 CAS#:14197-60-5 |
| Literature: Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, , vol. 37, # 11 p. 2961 - 2970 |
|
~% 
Ginsenoside Rg3 CAS#:14197-60-5 |
| Literature: Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, , vol. 37, # 11 p. 2961 - 2970 |
|
~% 
Ginsenoside Rg3 CAS#:14197-60-5 |
| Literature: Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, , vol. 37, # 11 p. 2961 - 2970 |
|
~% 
Ginsenoside Rg3 CAS#:14197-60-5 |
| Literature: Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, , vol. 37, # 11 p. 2961 - 2970 |
|
~% 
Ginsenoside Rg3 CAS#:14197-60-5 |
| Literature: Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, , vol. 31, # 9 p. 3353 - 3356 |
| HS Code | 29214210 |
|---|
|
Characterization of Panax ginseng UDP-Glycosyltransferases Catalyzing Protopanaxatriol and Biosyntheses of Bioactive Ginsenosides F1 and Rh1 in Metabolically Engineered Yeasts.
Mol. Plant 8 , 1412-24, (2015) Ginsenosides, the main pharmacologically active natural compounds in ginseng (Panax ginseng), are mostly the glycosylated products of protopanaxadiol (PPD) and protopanaxatriol (PPT). No uridine dipho... |
|
|
Comparative study on intestinal metabolism and absorption in vivo of ginsenosides in sulphur-fumigated and non-fumigated ginseng by ultra performance liquid chromatography quadruple time-of-flight mass spectrometry based chemical profiling approach.
Drug Test. Anal. 7(4) , 320-30, (2015) Our previous study indicated that sulphur-fumigation of ginseng in post-harvest handling processes could induce chemical transformation of ginsenosides to generate multiple ginsenoside sulphur derivat... |
|
|
Red ginseng extract promotes the hair growth in cultured human hair follicles.
J. Med. Food 18(3) , 354-62, (2015) Ginseng has been shown to promote hair growth in several recent studies. However, its effects on human hair follicles and its mechanisms of action have not been sufficiently elucidated. This study aim... |
| β-D-Glucopyranoside, (3β,12β)-12,20-dihydroxydammar-24-en-3-yl 2-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl- |
| 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 |
| opyransoyl)oxy) |
| Ginsenoside 20(s)-Rg3 |
| GinsenosideRg3 |
| GINSENOSIDE Rg3(SH) |
| (20S)-PROPANAXADIOL |
| MFCD06410950 |
| (3β,12β)-12,20-Dihydroxydammar-24-en-3-yl 2-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-β-D-glucopyranoside |
| 20S-Ginseniside Rg3 |
| Ginsenoside Rg3 |
| 20(S)-Ginsenoside-Rg3 |

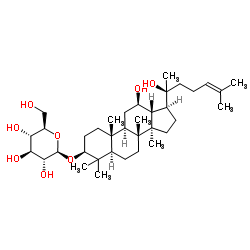 CAS#:67400-17-3
CAS#:67400-17-3 CAS#:6892-79-1
CAS#:6892-79-1
