| Description |
Ilomastat (Galardin; GM6001) is a broad spectrum matrix metalloprotease (MMP) inhibitor, with Ki of 0.4 nM, 0.5 nM, 27 nM, 3.7 nM, 0.1 nM, 0.2 nM, 3.6 nM, 13.4 nM, 0.36 nM for MMP-1/2/3/7/8/9/12/14/26, respectively.
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| Target |
Ki: 0.4 nM (MMP-1), 0.5 nM (MMP-2), 27 nM (MMP-3), 3.7 nM (MMP-7), 0.1 nM (MMP-8), 0.2 nM (MMP-9), 3.6 nM (MMP-12), 13.4 nM (MMP-14), 0.36 nM (MMP-26)
|
| In Vitro |
Ilomastat (GM6001) inhibits human skin fibroblast collagenase with Ki of 0.4 nM when assayed with a synthetic thio ester substrate at pH 6.5, with 50-fold selectivity over two bacterial enzymes, thermolysin and Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase[1]. Ilomastat (0.1 nM-10 nM) inhibits gelatinase A and gelatinase B produced by T-cells, and thus inhibits T-cell homing[4].
|
| In Vivo |
Ilomastat (GM6001) (400 μg/mL) prevents corneal ulceration after severe alkali injury[2]. Ilomastat (GM6001) significantly inhibits intimal hyperplasia and intimalcollagen content, and it increases lumen area in stented arteries without effects on proliferation rates in rabbit model after stenting[3].
|
| Animal Admin |
To assess the effects of MMP inhibition, animals are given daily injections of either vehicle (“placebo group”) or Ilomastat (GM6001) (100 mg/kg per day as subcutaneous suspension), beginning one day before the second injury until seven days after the procedure. Ilomastat (GM6001) is a nonspecific hydroxamic acid-based MMPI with potent inhibitory activity against collagenase, gelatinases and stromelysin. Animals are euthanized at either 1 week or 10 weeks after the second injury. For biochemical studies, iliac artery tissue is removed under general anesthetic, followed by a fatal intracardiac injection of thiopentol. For histomorphometric studies, iliac arteries are perfusion-fixed in 10% buffered formalin for 20 min at a perfusion pressure of 80 mm Hg.
|
| References |
[1]. Grobelny D, et al. Inhibition of human skin fibroblast collagenase, thermolysin, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase by peptide hydroxamic acids. Biochemistry. 1992 Aug 11;31(31):7152-4. [2]. Schultz GS, et al. Treatment of alkali-injured rabbit corneas with a synthetic inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1992 Nov;33(12):3325-31. [3]. Li C, et al. Arterial repair after stenting and the effects of GM6001, a matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002 Jun 5;39(11):1852-8. [4]. Leppert D, et al. T cell gelatinases mediate basement membrane transmigration in vitro. J Immunol. 1995 May 1;154(9):4379-89.
|
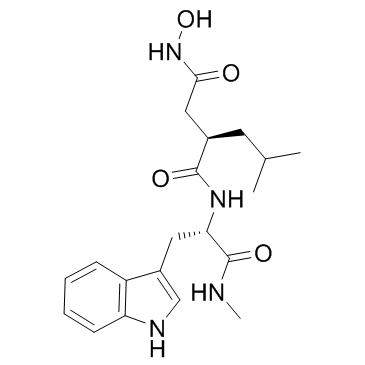
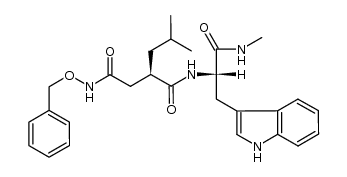 CAS#:171347-80-1
CAS#:171347-80-1 CAS#:53708-63-7
CAS#:53708-63-7 CAS#:18908-20-8
CAS#:18908-20-8 CAS#:142880-34-0
CAS#:142880-34-0 CAS#:122900-21-4
CAS#:122900-21-4![N-[(tert-Butoxy)carbonyl]-L-tryptophan Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/447/13139-14-5.png) CAS#:13139-14-5
CAS#:13139-14-5 CAS#:14035-83-7
CAS#:14035-83-7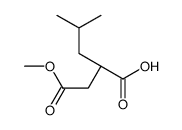 CAS#:162678-79-7
CAS#:162678-79-7
