Oxalic acid
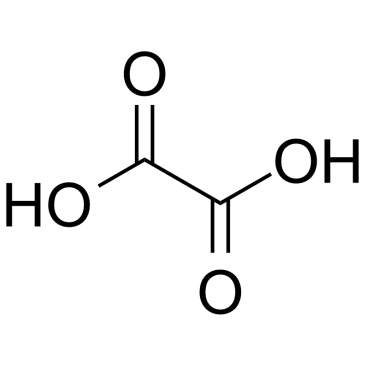
Oxalic acid structure
|
Common Name | Oxalic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 144-62-7 | Molecular Weight | 90.035 | |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 365.1±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C2H2O4 | Melting Point | 189.5 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 188.8±19.7 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Oxalic acidOxalic Acid is a strong dicarboxylic acid occurring in many plants and vegetables and can be used as an analytical reagent and general reducing agent. |
| Name | Oxalic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Oxalic Acid is a strong dicarboxylic acid occurring in many plants and vegetables and can be used as an analytical reagent and general reducing agent. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Oxalic Acid, a pathogenicity factor for sclerotinia sclerotiorum, suppresses the Oxidative burst of the host plant and directly inhibits the OGA-stimulated production of H2O2 by soybean cells, even in the absence of other fungal components[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 365.1±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 189.5 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C2H2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 90.035 |
| Flash Point | 188.8±19.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 89.995308 |
| PSA | 74.60000 |
| LogP | -1.19 |
| Vapour density | 4.4 (vs air) |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.480 |
| Water Solubility | 90 g/L (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302 + H312-H318 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R21/22 |
| Safety Phrases | S24/25-S23-S36/37/39-S27-S26 |
| RIDADR | UN 3261 8/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | RO2450000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 8 |
| HS Code | 2917111000 |
|
~% 
Oxalic acid CAS#:144-62-7 |
| Literature: Johnson, I.; Partington, J. R. Journal of the Chemical Society, 1930 , p. 1510 - 1511 Full Text View citing articles Show Details Gmelin Handbook: C: MVol.C4, 7.2.2, page 199 - 199 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2917111000 |
|---|
|
Mechanism of chemical activation of sodium chloride in the presence of amino acids.
Food Chem. 166 , 301-8, (2014) Sodium chloride has been shown to promote chlorination of glycerol during thermal processing. However, the detailed mechanism of this reaction is not well understood. Preliminary experiments have indi... |
|
|
A kinetic study of the enhancement of solution chemiluminescence of glyoxylic acid oxidation by manganese species.
Luminescence 30 , 507-11, (2015) In order to study the mechanism of the enhancement of solution chemiluminescence, the kinetics of the decay of the oxidant and the chemiluminescence emission were followed for oxidations by permangana... |
|
|
Oxalate secretion by ectomycorrhizal Paxillus involutus is mineral-specific and controls calcium weathering from minerals.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 12187, (2015) Trees and their associated rhizosphere organisms play a major role in mineral weathering driving calcium fluxes from the continents to the oceans that ultimately control long-term atmospheric CO2 and ... |
| Aktisal |
| Aquisal |
| Oxaalzuur |
| ethane-1,2-dioic acid |
| Oxalic acid |
| Ethanedioic acid |
| EINECS 205-634-3 |
| BETZ 0295 |
| oxalic |
| MFCD00002573 |
| DeerClean |
| HOOCCOOH |
 CAS#:108779-67-5
CAS#:108779-67-5 CAS#:20205-10-1
CAS#:20205-10-1 CAS#:10574-37-5
CAS#:10574-37-5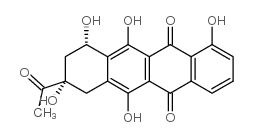 CAS#:52744-22-6
CAS#:52744-22-6 CAS#:50-81-7
CAS#:50-81-7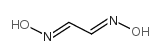 CAS#:557-30-2
CAS#:557-30-2 CAS#:471-47-6
CAS#:471-47-6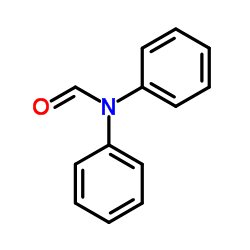 CAS#:607-00-1
CAS#:607-00-1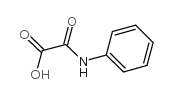 CAS#:500-72-1
CAS#:500-72-1![2-Methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/076/615-15-6.png) CAS#:615-15-6
CAS#:615-15-6
