Zeaxanthin
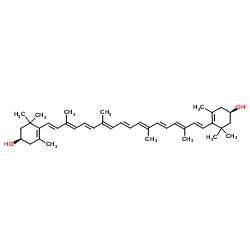
Zeaxanthin structure
|
Common Name | Zeaxanthin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 144-68-3 | Molecular Weight | 568.871 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 711.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C40H56O2 | Melting Point | 203-2050C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 273.4±26.1 °C | |
Use of ZeaxanthinZeaxanthin, a diet-obtained carotenoid, presents in the macula region of the eye. Zeaxanthin shows antioxidant effects[1][2]. |
| Name | zeaxanthin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Zeaxanthin, a diet-obtained carotenoid, presents in the macula region of the eye. Zeaxanthin shows antioxidant effects[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Much of the Lutein and Zeaxanthin in the leaves of plants is protein-bound.In fruits and flower petals, the xanthophylls are esterified and are concentrated into chromoplasts where they are found to be solubilized in the membranes. In humans and higher animals, Lutein and Zeaxanthin are accumulated in lipophilic tissues such as adipose tissue and are carried in the blood by the lipoproteins, probably in a nonspecific manner similar to cholesterol. Lutein and Zeaxanthin are distributed equally between LDL and HDL fractions in human blood, in contrast to the hydrocarbon carotenoids that are preferentially found in LDL fractions, up to 75%[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 711.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 203-2050C |
| Molecular Formula | C40H56O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 568.871 |
| Flash Point | 273.4±26.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 568.428040 |
| PSA | 40.46000 |
| LogP | 11.84 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±5.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.585 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | - |
|
Phenolic and carotenoid profiles and antiproliferative activity of foxtail millet.
Food Chem. 174 , 495-501, (2014) Commonly consumed foxtail millet varieties Jingu28 and Jingu34 were compared in terms of phytochemical composition, antioxidant property, and antiproliferative activity. The cellular antioxidant activ... |
|
|
An improved UHPLC-UV method for separation and quantification of carotenoids in vegetable crops.
Food Chem. 165 , 475-82, (2014) Carotenoid identification and quantitation is critical for the development of improved nutrition plant varieties. Industrial analysis of carotenoids is typically carried out on multiple crops with pot... |
|
|
Determination of sugars, organic acids, aroma components, and carotenoids in grapefruit pulps.
Food Chem. 205 , 112-21, (2016) The composition and content of sugars, organic acids, volatiles and carotenoids, in the pulps of six grapefruit cultivars, were examined by HPLC and GC-MS. The results showed that sucrose was the domi... |
| (3R,3'R)-Dihydroxy-b-carotene |
| all-trans-Zeaxanthin |
| EINECS 205-636-4 |
| (1R,1'R)-4,4'-[(1E,3E,5E,7E,9E,11E,13E,15E,17E)-3,7,12,16-Tetramethyl-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17-octadecanonaene-1,18-diyl]bis(3,5,5-trimethyl-3-cyclohexen-1-ol) |
| β,β-Carotene-3,3'-diol, (3R,3'R)- |
| MFCD00075654 |
| (1R,1'R)-4,4'-[(1E,3E,5E,7E,9E,11E,13E,15E,17E)-3,7,12,16-Tetramethyl-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17-octadecanonaen-1,18-diyl]bis(3,5,5-trimethyl-3-cyclohexen-1-ol) |
| (1R)-4-[(1E,3E,5E,7E,9E,11E,13E,15E,17E)-18-[(4R)-4-hydroxy-2,6,6-trimethylcyclohexen-1-yl]-3,7,12,16-tetramethyloctadeca-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17-nonaenyl]-3,5,5-trimethylcyclohex-3-en-1-ol |
| (3R,3'R)-β,β-Carotene-3,3'-diol |
| Zeaxanthin |
| Zeaxanthol |
| Xanthophyll 3 |
| Anchovyxanthin |
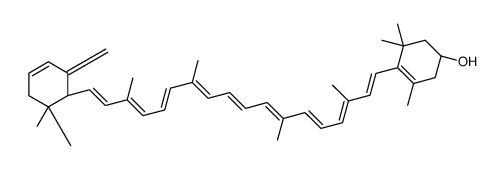 CAS#:92760-20-8
CAS#:92760-20-8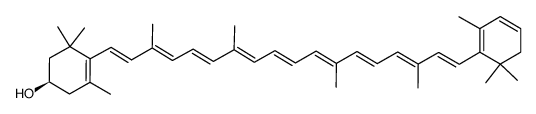 CAS#:54422-80-9
CAS#:54422-80-9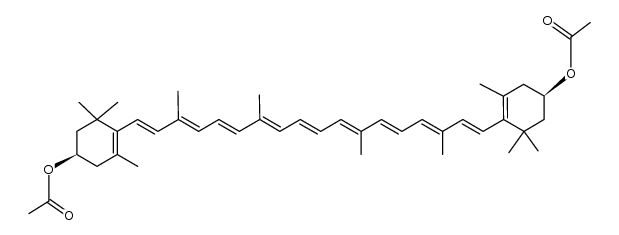 CAS#:115406-45-6
CAS#:115406-45-6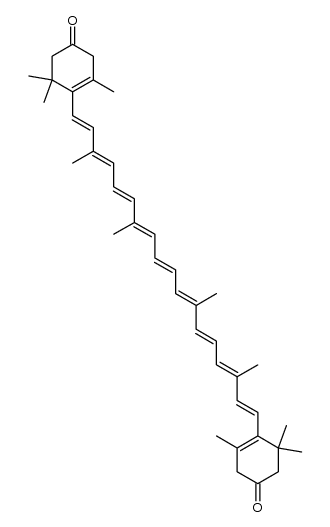 CAS#:14656-56-5
CAS#:14656-56-5 CAS#:106-88-7
CAS#:106-88-7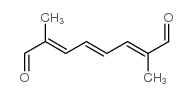 CAS#:5056-17-7
CAS#:5056-17-7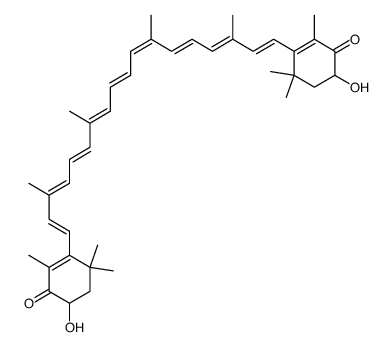 CAS#:7542-45-2
CAS#:7542-45-2
