Calcein-AM
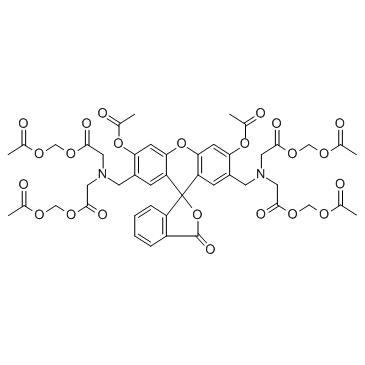
Calcein-AM structure
|
Common Name | Calcein-AM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 148504-34-1 | Molecular Weight | 994.86 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 982.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C46H46N2O23 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 548.1±34.3 °C | |
Use of Calcein-AMCalcein-AM is cell-permeable fluorescent dye used to determine the cell viability. |
| Name | Cellstain Calcein-AM |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Calcein-AM is cell-permeable fluorescent dye used to determine the cell viability. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | The calcein-AM dye used to stain the living cells is shown to have a low spontaneousleakage rate less than 15% in 4 hours at 37°C. Dilutions of targets stained by calcein-AM has a linear relationship with measured fluorescence values. NK cells, LAKs, and CTLs are readily detectable by this microtest. Quantitation of killing and kinetic analysis is readily performed with the test system[1]. Calcein-AM is pH independent, better retained and more photostable. In addition, the high level of intracellular retention of calcein-AM and its low-level release after incorporation exclude possible cell-monolayer labeling and allow its use in a cell-cell interaction assay. Moreover, the bright fluorescence can easily be detected and measured by a microplate fluorescence reader[2]. Calcein-AM is a highly lipophilic vital dye that rapidly enters viable cells, is converted by intracellular esterases to calcein that produces an intense green (530-nm) signal, and is retained by cells with intact plasma membrane. From dying or damaged cells with compromised membrane integrity or from cells expressing multidrug resistance protein (MRP), unhydrolyzed substrates and their fluorescent products are rapidly extruded from cells. The calcein-AM assay has been used to assess the cell viability, cytotoxicity and tp quantitate apoptosis[3]. |
| In Vivo | Calcein-AM is found to be suitable for in vivo studies, because it has no deleterious effects on cell function and is, indeed, a marker of cell viability[2]. |
| Cell Assay | K562, Daudi, and Chang liver cells are labeled with calcein-AM. Calcein-AM's excitation and emission wavelengths are 496 nm and 520 nm, respectively. The filter/mirror combination used to detect calcein-AM's green fluorescence includes the 490-nm excitation and 520-nm emission filters with a dichroic mirror. Differences in the automatic fluorescence readings between the test and control wells determine the results[1]. A simple and sensitive cell-cell adhesion microplate assay is established using the calcein-AM. The procedure involves three steps: the labeling of lymphocytes with an adequate concentration of calcein-AM (20 μM) during a short incubation period (30 min); the adhesion of 2×105 labeled lymphocytes per well to confluent keratinocyte or fibroblast monolayers grown in microtiter plates for 90 min; and, finally, measurement of the fluorescent signal utilizing a new system of cold-light microfluorimetry[2]. Cells are incubated for 15 min in 1 mL of a 1% saponin solution in PBS buffer, pH 7.4, containing 0.05% sodium azide. After saponin permeabilization, 4×105 RBCs in suspension in PBS buffer containing 0.1% saponin and 0.05% sodium azide are incubated (37°C in the dark for 45 min) with calcein-AM to a final concentration of 5 μM, ished three times with the same PBS buffer containing 0.1% saponin and 0.05% sodium azide, and the cell viability is analyzed by flow cytometry[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 982.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C46H46N2O23 |
| Molecular Weight | 994.86 |
| Flash Point | 548.1±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 994.249146 |
| LogP | 3.49 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.611 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
|
Sclerotium rolfsii lectin induces stronger inhibition of proliferation in human breast cancer cells than normal human mammary epithelial cells by induction of cell apoptosis.
PLoS ONE 9(11) , e110107, (2014) Sclerotium rolfsii lectin (SRL) isolated from the phytopathogenic fungus Sclerotium rolfsii has exquisite binding specificity towards O-linked, Thomsen-Freidenreich (Galβ1-3GalNAcα1-Ser/Thr, TF) assoc... |
|
|
Developmental tightening of cerebellar cortical synaptic influx-release coupling.
J. Neurosci. 35(5) , 1858-71, (2015) Tight coupling between Ca(2+) channels and the sensor for vesicular transmitter release at the presynaptic active zone (AZ) is crucial for high-fidelity synaptic transmission. It has been hypothesized... |
|
|
Establishment of lipofection for studying miRNA function in human adipocytes.
PLoS ONE 9(5) , e98023, (2014) miRNA dysregulation has recently been linked to human obesity and its related complications such as type 2 diabetes. In order to study miRNA function in human adipocytes, we aimed for the modulation o... |
| Calcein-AM |