CGP 55845 hydrochloride
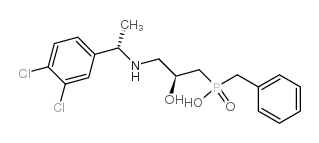
CGP 55845 hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | CGP 55845 hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 149184-22-5 | Molecular Weight | 402.25200 | |
| Density | 1.332g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 647.9ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H22Cl2NO3P | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 345.6ºC | |
Use of CGP 55845 hydrochlorideCGP55845 hydrochloride is a potent and selective GABAB receptor antagonist with an IC50 of 6 nM. CGP55845 hydrochloride can be used for neurological research[1][2]. |
| Name | CGP 55845 hydrochloride,(2S)-3-[[(1S)-1-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)ethyl]amino-2-hydroxypropyl](phenylmethyl)phosphinicacidhydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | CGP55845 hydrochloride is a potent and selective GABAB receptor antagonist with an IC50 of 6 nM. CGP55845 hydrochloride can be used for neurological research[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | In the mouse visual cortex, CGP 55845 hydrochloride (1 μM) increases the frequency of spontaneous Ca2+ transients and spontaneous and miniature IPSCs (mIPSCs) but does not affect mIPSC amplitudes or kinetics. CGP55845 hydrochloride significantly increases evoked IPSC (eIPSC) amplitudes and decreases the paired-pulse ratio (PPR)[3]. |
| In Vivo | CGP55845 hydrochloride (i.p.; once; 0.5 mg/kg) treatment increases the number of PSD95 positive puncta as well as density and maturation of dendritic spines in the perirhinal cortex (PRC), and restores novel object recognition (NOR) memory in Cdkl5 KO mice[1]. Animal Model: Cdkl5 +/Y and Cdkl5 -/Y male mice (2-month-old)[1] Dosage: 0.5 mg/kg Administration: i.p.; once Result: Altered NOR recognition memory in Cdkl5 -/Y mice |
| References |
| Density | 1.332g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 647.9ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C18H22Cl2NO3P |
| Molecular Weight | 402.25200 |
| Flash Point | 345.6ºC |
| Exact Mass | 401.07100 |
| PSA | 79.37000 |
| LogP | 4.86640 |
| Vapour Pressure | 1.14E-17mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.591 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|---|
| RTECS | SZ4680000 |
|
Persistent sodium current drives conditional pacemaking in CA1 pyramidal neurons under muscarinic stimulation.
J. Neurosci. 33(38) , 15011-21, (2013) Hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons are normally quiescent but can fire spontaneously when stimulated by muscarinic agonists. In brain slice recordings from mouse CA1 pyramidal neurons, we examined the ... |
|
|
Dopamine triggers heterosynaptic plasticity.
J. Neurosci. 33(16) , 6759-65, (2013) As a classic neuromodulator, dopamine has long been thought to modulate, rather than trigger, synaptic plasticity. In contrast, our present results demonstrate that within the parallel projections of ... |
|
|
Increased astrocytic ATP release results in enhanced excitability of the hippocampus.
Glia 61(2) , 210-24, (2013) Astrocytes, a major subtype of glia, interact with neurons as a supportive partner supplying energy sources and growth factors. Astrocytes regulate the activity of neighboring neurons by releasing che... |
| CGP 55845 hydrochloride |