Ritonavir
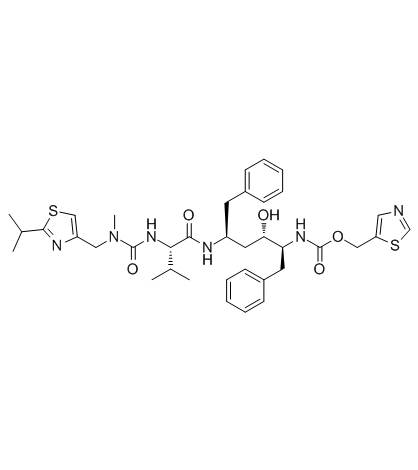
Ritonavir structure
|
Common Name | Ritonavir | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 155213-67-5 | Molecular Weight | 720.944 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 947.0±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C37H48N6O5S2 | Melting Point | 120-122°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 526.6±34.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of RitonavirRitonavir is an inhibitor of HIV protease used to treat HIV infection and AIDS. |
| Name | ritonavir |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ritonavir is an inhibitor of HIV protease used to treat HIV infection and AIDS. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Ritonavir is an inhibitor of CYP3A4 mediated testosterone 6β-hydroxylation with mean Ki of 19 nM and also inhibits tolbutamide hydroxylation with IC50 of 4.2 μM[1]. Ritonavir is found to be a potent inhibitor of CYP3A-mediated biotransformations (nifedipine oxidation with IC50 of 0.07 mM, 17alpha-ethynylestradiol 2-hydroxylation with IC50 of 2 mM; terfenadine hydroxylation with IC50 of 0.14 mM). Ritonavir is also an inhibitor of the reactions mediated by CYP2D6 (IC50=2.5 mM) and CYP2C9/10 (IC50=8.0 mM)[2]. Ritonavir results in an increase in cell viability in uninfected human PBMC cultures. Ritonavir markedly decreases the susceptibility of PBMCs to apoptosis correlated with lower levels of caspase-1 expression, decreases in annexin V staining, and reduces caspase-3 activity in uninfected human PBMC cultures. Ritonavir inhibits induction of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) production by PBMCs and monocytes in a time- and dose-dependent manner at nontoxic concentrations[3]. Ritonavir inhibits p-glycoprotein-mediated extrusion of saquinavir with an IC50 of 0.2 μM, indicating a high affinity of ritonavir for p-glycoprotein[4]. Ritonavir inhibits human liver microsomal metabolism of ABT-378 potently with Ki of 13 nM. Ritonavir combined with ABT-378 (at 3:1 and 29:1 ratios) inhibits CYP3A (IC50=1.1 and 4.6 μM), albeit less potently than Ritonavir (IC50=0.14 μM)[5]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 947.0±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 120-122°C |
| Molecular Formula | C37H48N6O5S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 720.944 |
| Flash Point | 526.6±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 720.312744 |
| PSA | 202.26000 |
| LogP | 5.28 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.600 |
| Storage condition | -20°C Freezer |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 + H312 + H332 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P301 + P312 + P330 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | R36/38:Irritating to eyes and skin . |
| Safety Phrases | 26-37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | XA5310000 |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
|
~% 
Ritonavir CAS#:155213-67-5 |
| Literature: WO2006/90264 A1, ; Page/Page column 23-24 ; |
|
~% 
Ritonavir CAS#:155213-67-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 41, # 4 p. 602 - 617 |
|
~% 
Ritonavir CAS#:155213-67-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 41, # 4 p. 602 - 617 |
|
~% 
Ritonavir CAS#:155213-67-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 41, # 4 p. 602 - 617 |
|
~% 
Ritonavir CAS#:155213-67-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 41, # 4 p. 602 - 617 |
|
~% 
Ritonavir CAS#:155213-67-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 41, # 4 p. 602 - 617 |
|
~% 
Ritonavir CAS#:155213-67-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 41, # 4 p. 602 - 617 |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
|---|
|
In vitro and in vivo release characteristics of Tacrolimus (FK506) from an episcleral drug-delivery implant.
J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 30(8) , 670-80, (2014) To investigate the in vitro and in vivo release characteristics of Tacrolimus (FK506) from an episcleral drug-delivery implant.For in vitro experiments, Tacrolimus-loaded implants (0.5 mL; at concentr... |
|
|
Cell-free microfluidic determination of P-glycoprotein interactions with substrates and inhibitors.
Pharm. Res. 31(12) , 3415-25, (2014) The membrane protein P-glycoprotein (P-gp) plays key roles in the oral bioavailability of drugs, their blood brain barrier passage as well as in multidrug resistance. For new drug candidates it is man... |
|
|
Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a rainbow trout liver Oatp.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 280(3) , 534-42, (2014) Cyanobacterial blooms have an impact on the aquatic ecosystem due to the production of toxins (e.g. microcystins, MCs), which constrain fish health or even cause fish death. However the toxicokinetics... |
| [5S-(5R*,8R*,10R*,11R*)]-10-Hydroxy-2-methyl-5-(1-methylethyl)-1-[2-(1-methylethyl)-4-thiazolyl]-3,6-dioxo-8,11-bis(phenylmethyl)-2,4,7,12-tetraazatridecan-13-oic acid 5-thiazolylmethyl ester |
| Norvir |
| Ritonavir |
| EINECS 208-127-9 |
| N-[(2S,4S,5S)-4-Hydroxy-1,6-diphenyl-5-{[(1,3-thiazol-5-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]amino}hexan-2-yl]-N-{[(2-isopropyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)methyl](methyl)carbamoyl}-L-valinamide |
| Ritonavi |
| Carbamic acid, N-[(1S,2S,4S)-2-hydroxy-4-[[(2S)-3-methyl-2-[[[methyl[[2-(1-methylethyl)-4-thiazolyl]methyl]amino]carbonyl]amino]-1-oxobutyl]amino]-5-phenyl-1-(phenylmethyl)pentyl]-, 5-thiazolylmethyl ester |
| ABT-538 |
| (1E,2S)-N-[(2S,4S,5S)-4-Hydroxy-5-{(E)-[hydroxy(1,3-thiazol-5-ylmethoxy)methylene]amino}-1,6-diphenyl-2-hexanyl]-2-[(E)-(hydroxy{[(2-isopropyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)methyl](methyl)amino}methylene)amino]-3-methylbutanimidic acid |
| 1,3-Thiazol-5-ylmethyl-[(1S,2S,4S)-1-benzyl-2-hydroxy-4-({(2S)-3-methyl-2-[(methyl{[2-(1-methylethyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]methyl}carbamoyl)amino]butanoyl}amino)-5-phenylpentyl]carbamat |
| N-[(1S,3S,4S)-1-benzyl-3-hydroxy-5-phenyl-4-{[(1,3-thiazol-5-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]amino}pentyl]-N-(methyl{[2-(1-methylethyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]methyl}carbamoyl)-L-valinamide |
| [(1S,2S,4S)-1-benzyl-2-hydroxy-4-({(2S)-3-méthyl-2-[(méthyl{[2-(1-méthyléthyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]méthyl}carbamoyl)amino]butanoyl}amino)-5-phénylpentyl]carbamate de 1,3-thiazol-5-ylméthyle |
| Butanimidic acid, N-[(1S,3S,4S)-3-hydroxy-4-[[(1E)-hydroxy(5-thiazolylmethoxy)methylene]amino]-5-phenyl-1-(phenylmethyl)pentyl]-2-[[(1E)-hydroxy[methyl[[2-(1-methylethyl)-4-thiazolyl]methyl]amino]methylene]amino]-3-methyl-, (1E,2S)- |
| N-[(2S,4S,5S)-4-Hydroxy-1,6-diphenyl-5-{[(1,3-thiazol-5-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]amino}-2-hexanyl]-N-{[(2-isopropyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)methyl](methyl)carbamoyl}-L-valinamide |
| carbamic acid, [(1S,2S,4S)-2-hydroxy-4-[[(2S)-3-methyl-2-[[[methyl[[2-(1-methylethyl)-4-thiazolyl]methyl]amino]carbonyl]amino]-1-oxobutyl]amino]-5-phenyl-1-(phenylmethyl)pentyl]-, 5-thiazolylmethyl es |
| N-[(2S,4S,5S)-4-hydroxy-1,6-diphenyl-5-{[(1,3-thiazol-5-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]amino}hexan-2-yl]-N2-(methyl{[2-(propan-2-yl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]methyl}carbamoyl)-L-valinamide |
| Liponavir Core |
| 1,3-thiazol-5-ylmethyl [(1S,2S,4S)-1-benzyl-2-hydroxy-4-({(2S)-3-methyl-2-[(methyl{[2-(1-methylethyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]methyl}carbamoyl)amino]butanoyl}amino)-5-phenylpentyl]carbamate |
| A-84538 ABT-538 Abbott 84538 |
| Norvi |
| (2S,3S,5S)-5-[N-[N-[[N-methyl-N-[(2-isopropyl-4-thiazolyl)methyl]amino]carbonyl]valinyl]amino]-2-[N-[(5-thiazolyl)methoxycarbonyl]amino]-1,6-diphenyl-3-hydroxyhexane |
| RITONA |
| MFCD04115732 |
| carbamic acid, [(1S,2S,4S)-2-hydroxy-4-[[(2S)-3-methyl-2-[[[methyl[[2-(1-methylethyl)-4-thiazolyl]methyl]amino]carbonyl]amino]-1-oxobutyl]amino]-5-phenyl-1-(phenylmethyl)pentyl]-, 5-thiazolylmethyl ester |
![2,5-DIOXOPYRROLIDIN-1-YL N-{N-[(2-ISOPROPYL-1,3-THIAZOL-4-YL)METHYL]-N-METHYLCARBAMOYL}-L-VALINATE structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/082/224631-15-6.png)



![N-[2-Isopropylthiazol-4-ylmethyl(methyl)carbamoyl]-L-valine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/072/154212-61-0.png)

