DIPPA hydrochloride
Modify Date: 2024-01-09 07:48:11
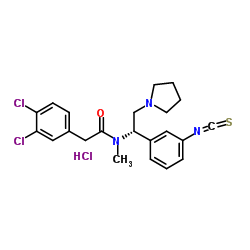
DIPPA hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | DIPPA hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 155512-52-0 | Molecular Weight | 484.870 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H24Cl3N3OS | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of DIPPA hydrochlorideDIPPA (hydrochloride) is an irreversible, long-lasting, selective and high affinity κ-opioid receptor antagonist. DIPPA (hydrochloride) can be used for the research of anxiety and antidepressant[1][2][3][4]. |
| Name | 2-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-N-[(1S)-1-(3-isothiocyanatophenyl)-2-(1-pyrrolidinyl)ethyl]-N-methylacetamide hydrochloride (1:1) |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | DIPPA (hydrochloride) is an irreversible, long-lasting, selective and high affinity κ-opioid receptor antagonist. DIPPA (hydrochloride) can be used for the research of anxiety and antidepressant[1][2][3][4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
κ-opioid receptor[1] |
| In Vivo | DIPPA (2.5 and 5 mg/kg; s.c.) hydrochloride decreases the latency to feed in Wistar Kyoto rats, but treatment did not alter approach latencies in SD rats[2]. DIPPA (1 and 5 mg/kg; s.c.) hydrochloride high dose increases immobility in SD rats compared to the saline-treated strain control group[2]. DIPPA (5 mg/kg) hydrochloride decreases consumption in SD rats compared to the 5 mg/kg group of Wistar Kyoto rats. DIPPA hydrochloride significantly decreases burying time in both strains. DIPPA (5 mg/kg) hydrochloride decreases burying in both strains compared to the within strain control groups. DIPPA hydrochloride tends to decrease consumption in SD rats in the home cage but significantly increases feeding in the novel cage where potential anxiolytic-like effects of DIPPA hydrochloride may oppose the hypophagic effects of the compound[2]. Animal Model: Wistar Kyoto rats and SD rats (250–300 g)[2] Dosage: 2.5 and 5 mg/kg Administration: S.c. Result: Decreased the latency to feed in Wistar Kyoto rats, but treatment did not alter approach latencies in SD rats. Animal Model: Wistar Kyoto rats and SD rats (250–300 g)[2] Dosage: 1 and 5 mg/kg Administration: S.c. Result: High dose increased immobility in SD rats compared to the saline-treated strain control group. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C22H24Cl3N3OS |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 484.870 |
| Exact Mass | 483.070557 |
| Benzeneacetamide, 3,4-dichloro-N-[(1S)-1-(3-isothiocyanatophenyl)-2-(1-pyrrolidinyl)ethyl]-N-methyl-, hydrochloride (1:1) |
| 2-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-N-[(1S)-1-(3-isothiocyanatophenyl)-2-(1-pyrrolidinyl)ethyl]-N-methylacetamide hydrochloride (1:1) |
| 2-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-N-[(1S)-1-(3-isothiocyanatophenyl)-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethyl]-N-methylacetamide hydrochloride (1:1) |