Amprenavir
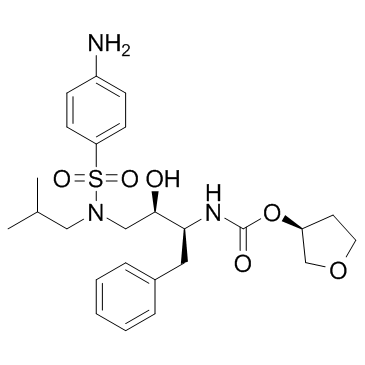
Amprenavir structure
|
Common Name | Amprenavir | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 161814-49-9 | Molecular Weight | 505.627 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 722.5±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C25H35N3O6S | Melting Point | 72-74ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 390.8±35.7 °C | |
Use of AmprenavirAmprenavir (Agenerase) is a HIV protease inhibitor(Ki=0.6 nM) used to treat HIV infection.IC50 Value: 0.6 nM (Ki); Against wild-type clinical HIV isolates:14.6 +/- 12.5 ng/mL (mean +/- SD) [1].Target: HIV proteasein vitro: Amprenavir has an enzyme inhibition constant (Ki = 0.6 nM) that falls within the Ki range of the other protease inhibitors. Amprenavir's in vitro 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) against wild-type clinical HIV isolates is 14.6 +/- 12.5 ng/mL (mean +/- SD) [1]. Amprenavir had direct inhibitory effects on invasion of Huh-7 hepatocarcinoma cell lines, inhibiting MMP proteolytic activation [2].in vivo: Amprenavir was able to promote regression of hepatocarcinoma growth in vivo by anti-angiogenetic and overall anti-tumor activities, independently by PI3K/AKT related pathways that at today is one of the more suggestive hypothesis to explain the anti-tumor effects of the different protease inhibitors [2]. Amprenavir efficiently activated PXR and induced PXR target gene expression in vitro and in vivo. Short-term exposure to amprenavirsignificantly increased plasma total cholesterol and atherogenic low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in wild-type mice, but not in PXR-deficient mice [3]. Amprenavir has been approved for adults and children; the recommended capsule doses are 1200 mg twice daily for adults and 20 mg/kg twice daily or 15 mg/kg 3 times daily for children < 13 years of age or adolescents < 50 kg [1].Clinical trial: A Study to Compare Three Doses of T-20 When Given in Combination With Abacavir, Amprenavir, Ritonavir, and Efavirenz to HIV-Infected Adults. Phase 2 |
| Name | amprenavir |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Amprenavir (Agenerase) is a HIV protease inhibitor(Ki=0.6 nM) used to treat HIV infection.IC50 Value: 0.6 nM (Ki); Against wild-type clinical HIV isolates:14.6 +/- 12.5 ng/mL (mean +/- SD) [1].Target: HIV proteasein vitro: Amprenavir has an enzyme inhibition constant (Ki = 0.6 nM) that falls within the Ki range of the other protease inhibitors. Amprenavir's in vitro 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) against wild-type clinical HIV isolates is 14.6 +/- 12.5 ng/mL (mean +/- SD) [1]. Amprenavir had direct inhibitory effects on invasion of Huh-7 hepatocarcinoma cell lines, inhibiting MMP proteolytic activation [2].in vivo: Amprenavir was able to promote regression of hepatocarcinoma growth in vivo by anti-angiogenetic and overall anti-tumor activities, independently by PI3K/AKT related pathways that at today is one of the more suggestive hypothesis to explain the anti-tumor effects of the different protease inhibitors [2]. Amprenavir efficiently activated PXR and induced PXR target gene expression in vitro and in vivo. Short-term exposure to amprenavirsignificantly increased plasma total cholesterol and atherogenic low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in wild-type mice, but not in PXR-deficient mice [3]. Amprenavir has been approved for adults and children; the recommended capsule doses are 1200 mg twice daily for adults and 20 mg/kg twice daily or 15 mg/kg 3 times daily for children < 13 years of age or adolescents < 50 kg [1].Clinical trial: A Study to Compare Three Doses of T-20 When Given in Combination With Abacavir, Amprenavir, Ritonavir, and Efavirenz to HIV-Infected Adults. Phase 2 |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 722.5±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 72-74ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C25H35N3O6S |
| Molecular Weight | 505.627 |
| Flash Point | 390.8±35.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 505.224670 |
| PSA | 139.57000 |
| LogP | 4.68 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.602 |
| Storage condition | -20°C Freezer |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: soluble20mg/mL, clear |
| RIDADR | 3077 |
|---|---|
| HS Code | 2935009090 |
| HS Code | 2935009090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2935009090 other sulphonamides VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:35.0% |
|
A comparison of in vitro ADME properties and pharmacokinetics of azithromycin and selected 15-membered ring macrolides in rodents.
Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 39(4) , 263-76, (2014) The purpose of this study was to evaluate the impact of structural modifications on the 15-membered macrolactone ring and/or substituents on the in vitro ADME properties and in vivo pharmacokinetic (P... |
|
|
Parallel ultra high pressure liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for the quantification of HIV protease inhibitors using dried spot sample collection format.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 965 , 244-53, (2014) An assay was developed and validated for the quantification of eight protease inhibitors (indinavir (IDV), ritonavir (RTV), lopinavir (LPV), saquinavir (SQV), amprenavir (APV), nelfinavir (NFV), ataza... |
|
|
HZ08 reverse P-glycoprotein mediated multidrug resistance in vitro and in vivo.
PLoS ONE 10(2) , e0116886, (2015) Multidrug efflux transporter P-glycoprotein (P-gp) is highly expressed on membrane of tumor cells and is implicated in resistance to tumor chemotherapy. HZ08 is synthesized and studied in order to fin... |
| Vertex |
| Benzenesulfonamide, 4-amino-N-[(2R,3S)-2-hydroxy-3-[[(1E)-hydroxy[[(3S)-tetrahydro-3-furanyl]oxy]methylene]amino]-4-phenylbutyl]-N-(2-methylpropyl)- |
| VX-478 |
| (3S)-tetrahydro-3-furyl N-[(1S,2R)-3-(4-amino-N-isobutylbenzenesulfonamido)-1-benzyl-2-hydroxypropyl]carbamate |
| (3S)-Tetrahydro-3-furanyl hydrogen [(2S,3R)-4-{[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](isobutyl)amino}-3-hydroxy-1-phenyl-2-butanyl]carbonimidate |
| (3S)-Tetrahydro-3-furanyl [(2S,3R)-4-{[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](isobutyl)amino}-3-hydroxy-1-phenyl-2-butanyl]carbamate |
| [(1S,2R)]-[3-[[(4-Aminophenyl)sulfonyl](2-methylpropyl)amino]-2-hydroxy-1-(phenylmethyl)propyl]carbamic Acid (3S)-tetrahydro-3-furanyl Ester |
| Amprenavir (agenerase) |
| (3S)-tetrahydrofuran-3-yl [(2S,3R)-4-{[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](2-methylpropyl)amino}-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]carbamate |
| Prozei |
| carbamic acid, [(1S,2R)-3-[[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](2-methylpropyl)amino]-2-hydroxy-1-(phenylmethyl)propyl]-, (3S)-tetrahydro-3-furanyl ester |
| [(3S)-oxolan-3-yl] N-[(2S,3R)-4-[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl-(2-methylpropyl)amino]-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]carbamate |
| 141W94 |
| (3S)-Tetrahydrofuran-3-yl [(2S,3R)-4-{[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](isobutyl)amino}-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]carbamate |
| 4-Amino-N-((2syn,3S)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl-3-((S)-tetrahydrofuran-3-yloxycarbonylamino)-butyl)-N-isobutylbenzene Sulfonamide |
| Vertex VX478 |
| Carbamic acid, N-[(1S,2R)-3-[[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](2-methylpropyl)amino]-2-hydroxy-1-(phenylmethyl)propyl]-, (3S)-tetrahydro-3-furanyl ester |
| Amprenavir |
| Agenerase |