Methyl γ-linolenate
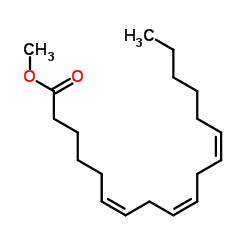
Methyl γ-linolenate structure
|
Common Name | Methyl γ-linolenate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 16326-32-2 | Molecular Weight | 292.456 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 385.4±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H32O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 101.5±23.2 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Methyl γ-linolenateγ-Linolenic Acid methyl ester (Methyl GLA) is an esterified version of γ-Linolenic Acid (GLA), which is an ω-6 fatty acid, serves as melanoma cell proliferation inhibitors. γ-Linolenic Acid methyl ester inhibits ADP-induced blood platelet aggregation and induces apoptosis[1][2][3][4][5]. |
| Name | Methyl γ-linolenate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | γ-Linolenic Acid methyl ester (Methyl GLA) is an esterified version of γ-Linolenic Acid (GLA), which is an ω-6 fatty acid, serves as melanoma cell proliferation inhibitors. γ-Linolenic Acid methyl ester inhibits ADP-induced blood platelet aggregation and induces apoptosis[1][2][3][4][5]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | γ-Linolenic Acid methyl ester (1-4 μg/mL; 72 h) induces apoptosis in vitro A-549 lung cancer cell lines using SRB assay. However GLA is due to its action at the gene/oncogene level and by altering BCl-2 expression[1]. Apoptosis Analysis[1] Cell Line: A-549 lung cancer cell line Concentration: 1, 2, 3, and 4 μg/mL Incubation Time: 72 hours; observed at 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h Result: Showed cytotoxicity potentially due to the induction of apoptosis of tumor cells by augmenting free radical generation only in the tumor cells but not normal cells. |
| In Vivo | γ-Linolenic Acid methyl ester decreases the hepatic triglycerides and histological evidence of fatty liver induced by EtOH[2]. γ-Linolenic Acid methyl ester could significantly decrease levels of plasma total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), MDA, atherosclerosis index (AI) and liver TC, MDA, and increase levels of high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) in both normal and hyperlipidemic rats[3]. Animal Model: Hepatic pathol rats model induced by EtOH (male Sprague-Dawley rats, 250-300 g)[2] Dosage: 90 mL, 50-60 mL Administration: Intraperitoneal injection; once daily; administrated 90 mL during day 1-5 and day 9, 50-60 mL during day 6-8 Result: Decreased the hepatic triglycerides of 25.6 mg/g compared with saline (40.2 mg/g) or olive oil (42.8 mg/g) treatment. Decreased liver index (the ratio of liver weight and body wight) in hyperlipidemic rats, but had no significant effect in normal rats. |
| References |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 385.4±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C19H32O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 292.456 |
| Flash Point | 101.5±23.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 292.240234 |
| PSA | 26.30000 |
| LogP | 7.03 |
| Appearance of Characters | Liquid |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.476 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H225-H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P337 + P313-P403 + P235 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | F |
| Risk Phrases | 11 |
| Safety Phrases | 16 |
| RIDADR | UN 1993 / PGIII |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2916190090 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
| HS Code | 2916190090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2916190090 unsaturated acyclic monocarboxylic acids, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives。supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward)。VAT:17.0%。tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。general tariff:30.0% |
|
Weight regain after Roux-en-Y: a significant 20% complication related to PYY.
Nutrition 24 , 832-842, (2008) Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) produces rapid and dramatic weight loss in very heavy obese patients. Up to 20% cannot sustain their weight loss beyond 2 to 3 y after surgery.To identify putative etio... |
|
|
Effect of long-term dietary supplementation of high-gamma-linolenic canola oil versus borage oil on growth, hematology, serum biochemistry, and N-6 fatty acid metabolism in rats.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 52 , 3960-3966, (2004) Dietary supplementation of a high-gamma-linolenic acid canola oil (HGCO) containing approximately 36% (w/w) of gamma-linolenic acid (GLA, 18:3n-6) from the seeds of a genetically transformed canola st... |
|
|
Gamma-linolenate reduces weight regain in formerly obese humans.
J. Nutr. 137 , 1430-1435, (2007) The purpose of this study was to determine whether gamma-linolenate (GLA) supplementation would suppress weight regain following major weight loss. Fifty formerly obese humans were randomized into a d... |
| 6,9,12-Octadecatrienoic acid, methyl ester, (6Z,9Z,12Z)- |
| 6,9,12-Octadecatrienoic acid, methyl ester, (Z,Z,Z)- |
| γ-LINOLENIC ACID METHYL ESTER |
| Methyl (6Z,9Z,12Z)-6,9,12-octadecatrienoate |
| Methyl (6Z,9Z,12Z)-octadeca-6,9,12-trienoate |
| MFCD00010455 |
| Methyl g-linolenate |
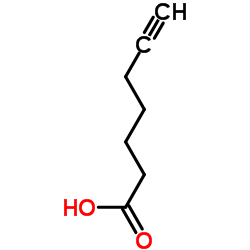 CAS#:30964-00-2
CAS#:30964-00-2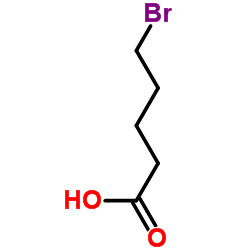 CAS#:2067-33-6
CAS#:2067-33-6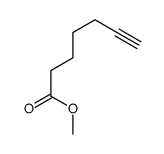 CAS#:56909-02-5
CAS#:56909-02-5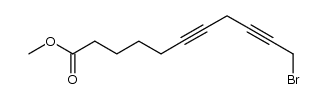 CAS#:209860-40-2
CAS#:209860-40-2 CAS#:67-56-1
CAS#:67-56-1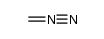 CAS#:186581-53-3
CAS#:186581-53-3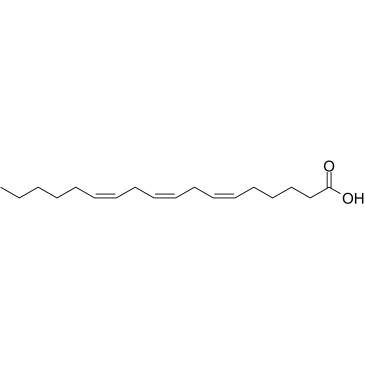 CAS#:506-26-3
CAS#:506-26-3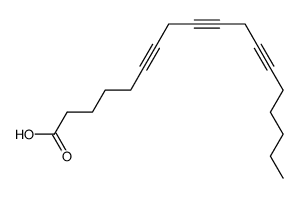 CAS#:4184-93-4
CAS#:4184-93-4
