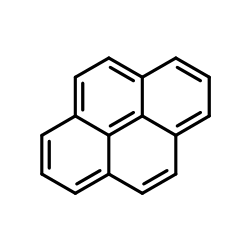
(2H10)Pyrene

(2H10)Pyrene structure
|
Common Name | (2H10)Pyrene | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1718-52-1 | Molecular Weight | 212.31200 | |
| Density | 1.31 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 404ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C16D10 | Melting Point | 145-148ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 168.8ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of (2H10)PyrenePyrene-d10 is the deuterium labeled Pyrene[1]. |
| Name | 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10-decadeuteriopyrene |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Pyrene-d10 is the deuterium labeled Pyrene[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.31 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 404ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 145-148ºC(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C16D10 |
| Molecular Weight | 212.31200 |
| Flash Point | 168.8ºC |
| Exact Mass | 212.14100 |
| LogP | 4.58400 |
| Vapour Pressure | 2.28E-06mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.851 |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R10;R22;R36;R37;R38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9 / PGIII |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 28459000 |
|
~95% 
(2H10)Pyrene CAS#:1718-52-1 |
| Literature: Duttwyler, Simon; Butterfield, Anna M.; Siegel, Jay S. Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2013 , vol. 78, # 5 p. 2134 - 2138 |
|
~% 
(2H10)Pyrene CAS#:1718-52-1 |
| Literature: Journal of the Chemical Society, , p. 429 Journal of the Chemical Society, , p. 851,853, 854 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
Distribution and Sources of Petroleum Hydrocarbons in Recent Sediments of the Imo River, SE Nigeria.
Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 70 , 372-82, (2016) The distribution of aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments of the lower course of the Imo River (Nigeria) was investigated to determine the sources and fate of these compounds. The a... |
|
|
Polycyclic Aromatic Acids Are Primary Metabolites of Alkyl-PAHs-A Case Study with Nereis diversicolor.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 49 , 5713-21, (2015) Although concentrations of alkylated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (alkyl-PAHs) in oil-contaminated sediments are higher than those of unsubstituted PAHs, only little attention has been given to me... |
|
|
The effects of flow rate and temperature on SPMD measurements of bioavailable PAHs in seawater.
Mar. Pollut. Bull. 97 , 217-23, (2015) This work investigates the dependence of the sampling rate (Rs) of semi-permeable membrane devices (SPMDs) on flow rate and temperature. The in situ Rs values were obtained using performance reference... |
| Pyrene-d |
| [10-2H]Pyrene |
| Decadeuterio-pyren |
| decadeuteriopyrene |
| (2H10)Pyrene |
| Pyrene-d10 |
| pyrene-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10-d10 |
| (H)Pyrene |
| L666 B6 2AB PJ &&d-10 |
| perdeiteriopyrene |
| [2H10]Pyrene |
| Perdeuteriopyrene |