Tyr-Phe
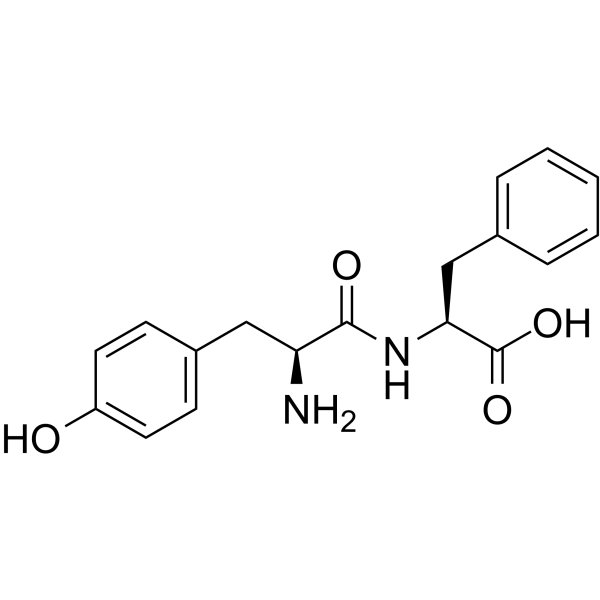
Tyr-Phe structure
|
Common Name | Tyr-Phe | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 17355-11-2 | Molecular Weight | 328.36200 | |
| Density | 1.3 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 642.2ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H20N2O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 342.2ºC | |
Use of Tyr-PheH-Tyr-Phe-OH (L-Tyrosyl-L-phenylalanine) is an orally active inhibitor of Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE), with an inhibiton rate of 48% at 50 μM. H-Tyr-Phe-OH can be used as an biomarker for differentiating benign thyroid nodules (BTN) from thyroid cancer (TC). H-Tyr-Phe-OH exhibits xanthine oxidase inhibition (uric acid lowering) activity and serves as regulator in IL-8 production in neutrophil-like cells[1][2][3][4]. |
| Name | 2-[[2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | H-Tyr-Phe-OH (L-Tyrosyl-L-phenylalanine) is an orally active inhibitor of Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE), with an inhibiton rate of 48% at 50 μM. H-Tyr-Phe-OH can be used as an biomarker for differentiating benign thyroid nodules (BTN) from thyroid cancer (TC). H-Tyr-Phe-OH exhibits xanthine oxidase inhibition (uric acid lowering) activity and serves as regulator in IL-8 production in neutrophil-like cells[1][2][3][4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Target: ACE (Angiotensin converting enzyme), xanthine oxidase[1] |
| References |
| Density | 1.3 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 642.2ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C18H20N2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 328.36200 |
| Flash Point | 342.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 328.14200 |
| PSA | 112.65000 |
| LogP | 2.16530 |
| Vapour Pressure | 2.27E-17mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.625 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| HS Code | 2924299090 |
| HS Code | 2924299090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924299090. other cyclic amides (including cyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
A new cytochrome C reducing dipeptide.
J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 82 , 113-116, (1990) Using absorption spectroscopy, it has been found that tyrosylphenylalanine specifically reduces cytochrome C. This effect is pH and concentration dependent with the EC +/- SE = 4.42 x 10(-3) M. At 10(... |
|
|
The effect of neighboring methionine residue on tyrosine nitration and oxidation in peptides treated with MPO, H2O2, and NO2(-) or peroxynitrite and bicarbonate: role of intramolecular electron transfer mechanism?
Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 484 , 134-145, (2009) Recent reports suggest that intramolecular electron transfer reactions can profoundly affect the site and specificity of tyrosyl nitration and oxidation in peptides and proteins. Here we investigated ... |
|
|
Interaction between cytochrome C and di- and tripeptides.
Life Sci. 48 , 523-530, (1991) By observing changes in the absorbance spectrum between 340 and 650 nm, we found that tyrosyltyrosylphenylalanine (TTP) interacts with cytochrome C (CC). TTP caused the characteristic changes of CC re... |
| H-Tyr-Phe-OH |
| Tyr-Phe |
| L-tyrosyl-L-phenylalanine |
| tyrosylphenylalanine |
| tyrosinylphenylalanine |
| L-Tyrosine-L-phenylalanine |