K-7174 (dihydrochloride)
Modify Date: 2024-01-09 13:05:17
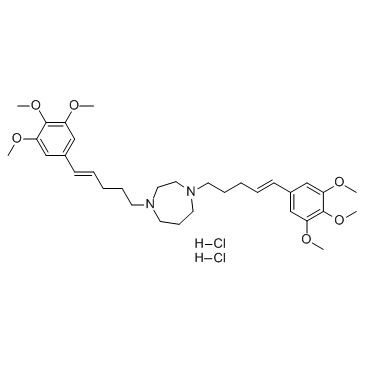
K-7174 (dihydrochloride) structure
|
Common Name | K-7174 (dihydrochloride) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 191089-60-8 | Molecular Weight | 641.67 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 689.9±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C33H50Cl2N2O6 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 171.2±28.7 °C | |
Use of K-7174 (dihydrochloride)K-7174 dihydrochloride is a novel cell adhesion inhibitor; inhibits the expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) induced by either IL-1β or TNF-α.IC50 value:Target: GATA-specific inhibitorin vitro: K-7174 inhibited the expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) induced by either tumor necrosis factor alpha or interleukin-1beta, without affecting the induction of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 or E-selectin. K-7174 had no effect on the stability of VCAM-1 mRNA.K-7174 did not influence the binding to any of the following binding motifs: octamer binding protein, AP-1, SP-1, ets, NFkappaB, or interferon regulatory factor [1]. Addition of 10 microM K-7174 rescued these inhibitions of Epo protein production and promoter activity induced by IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, or L-NMMA, respectively [2]. K-7174 had the potential to induce endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress evidenced by induction of GRP78 and CHOP.Other inducers of ER stress completely reproduced the effects of K-7174 including suppression of lipid accumulation, blockade of induction of adiponection and PPARgamma and maintenance of MCP-1 expression [3].in vivo: K-7174, one of proteasome inhibitory homopiperazine derivatives, exhibits a therapeutic effect, which is stronger when administered orally than intravenously, without obvious side effects in a murine myeloma model. Moreover, K-7174 kills bortezomib-resistant myeloma cells carrying a β5-subunit mutation in vivo and primary cells from a patient resistant to bortezomib [4]. |
| Name | 1,4-Bis[(4E)-5-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-4-penten-1-yl]-1,4-diazepane |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | K-7174 dihydrochloride is a novel cell adhesion inhibitor; inhibits the expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) induced by either IL-1β or TNF-α.IC50 value:Target: GATA-specific inhibitorin vitro: K-7174 inhibited the expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) induced by either tumor necrosis factor alpha or interleukin-1beta, without affecting the induction of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 or E-selectin. K-7174 had no effect on the stability of VCAM-1 mRNA.K-7174 did not influence the binding to any of the following binding motifs: octamer binding protein, AP-1, SP-1, ets, NFkappaB, or interferon regulatory factor [1]. Addition of 10 microM K-7174 rescued these inhibitions of Epo protein production and promoter activity induced by IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, or L-NMMA, respectively [2]. K-7174 had the potential to induce endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress evidenced by induction of GRP78 and CHOP.Other inducers of ER stress completely reproduced the effects of K-7174 including suppression of lipid accumulation, blockade of induction of adiponection and PPARgamma and maintenance of MCP-1 expression [3].in vivo: K-7174, one of proteasome inhibitory homopiperazine derivatives, exhibits a therapeutic effect, which is stronger when administered orally than intravenously, without obvious side effects in a murine myeloma model. Moreover, K-7174 kills bortezomib-resistant myeloma cells carrying a β5-subunit mutation in vivo and primary cells from a patient resistant to bortezomib [4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 689.9±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C33H50Cl2N2O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 641.67 |
| Flash Point | 171.2±28.7 °C |
| LogP | 5.61 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.552 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| 1,4-Bis[(4E)-5-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-4-penten-1-yl]-1,4-diazepane |
| 1H-1,4-Diazepine, hexahydro-1,4-bis[(4E)-5-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-4-penten-1-yl]- |
| K-7174 (dihydrochloride) |