5-Indolol
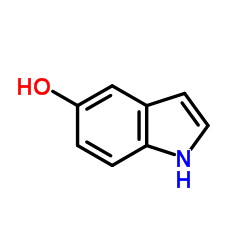
5-Indolol structure
|
Common Name | 5-Indolol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1953-54-4 | Molecular Weight | 133.147 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 343.2±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H7NO | Melting Point | 105-110ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 161.4±20.4 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 5-Indolol5-Hydroxyindole, a hydroxylated indole, can be found in a vast array of pharmacologically active agents and natural products. 5-Hydroxyindole slows desensitization of the 5-HT3 receptor-mediated ion current in N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells[1][2]. |
| Name | 1H-indol-5-ol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 5-Hydroxyindole, a hydroxylated indole, can be found in a vast array of pharmacologically active agents and natural products. 5-Hydroxyindole slows desensitization of the 5-HT3 receptor-mediated ion current in N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 343.2±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 105-110ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C8H7NO |
| Molecular Weight | 133.147 |
| Flash Point | 161.4±20.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 133.052765 |
| PSA | 36.02000 |
| LogP | 0.97 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.739 |
| Storage condition | 0-6°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | NM2430000 |
| HS Code | 29339990 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Validation and application of an UPLC-MS/MS method for the quantification of synthetic cannabinoids in urine samples and analysis of seized materials from the Portuguese market.
Forensic Sci. Int. 243 , 117-25, (2014) An UPLC-MS/MS method using ESI+ionization and MRM was developed and fully validated according to international guidelines for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of nine synthetic cannabinoids a... |
|
|
A separation of tyramine on a 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethylamine imprinted polymer: an answer from theoretical and experimental studies.
Talanta 129 , 155-64, (2014) A 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethylamine imprinted polymer (MIP) was successfully applied for the selective separation of tyramine. A computational analysis was used to predict the affinity of the polymer matr... |
|
|
Determination of selected synthetic cannabinoids and their metabolites by micellar electrokinetic chromatography--mass spectrometry employing perfluoroheptanoic acid-based micellar phase.
Talanta 150 , 568-76, (2016) Perfluoroheptanoic acid was employed as a volatile micellar phase in background electrolyte for micellar electrokinetic chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry separation and determination of 15 selec... |
| 5-hydroxyindol |
| 5-Hydroxyindole,5-Indolol |
| 5-hydroxy-1H-indol |
| EINECS 217-782-6 |
| 1H-Indol-5-ol |
| 5-Hydroxy-1H-indole |
| INDOL-5-OL |
| 1H-indole-5-ol |
| Hydroxy-5-indole |
| 5-Indolol |
| 5-hydroxylindole |
| 5-hydroxy-indole |
| 5-Hydroxyindole |
| MFCD00005677 |
| MFCD0005677 |
![1-[2-(5-Benzyloxy-2-nitrophenyl)vinyl]pyrrolidine Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/362/153805-85-7.png) CAS#:153805-85-7
CAS#:153805-85-7 CAS#:1215-59-4
CAS#:1215-59-4 CAS#:1006-94-6
CAS#:1006-94-6 CAS#:153969-91-6
CAS#:153969-91-6 CAS#:51145-58-5
CAS#:51145-58-5 CAS#:120-72-9
CAS#:120-72-9 CAS#:100-02-7
CAS#:100-02-7 CAS#:1145-76-2
CAS#:1145-76-2 CAS#:103404-89-3
CAS#:103404-89-3 CAS#:3414-19-5
CAS#:3414-19-5 CAS#:57477-39-1
CAS#:57477-39-1 CAS#:31271-90-6
CAS#:31271-90-6 CAS#:394-31-0
CAS#:394-31-0 CAS#:434958-85-7
CAS#:434958-85-7 CAS#:267875-62-7
CAS#:267875-62-7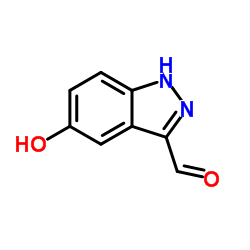 CAS#:882803-11-4
CAS#:882803-11-4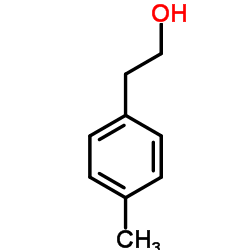 CAS#:699-02-5
CAS#:699-02-5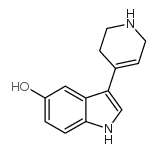 CAS#:127626-07-7
CAS#:127626-07-7
