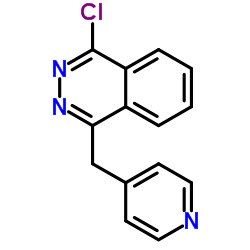
Vatalanib base

Vatalanib base structure
|
Common Name | Vatalanib base | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 212141-54-3 | Molecular Weight | 346.813 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 587.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H15ClN4 | Melting Point | 209-212ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 309.3±30.1 °C | |
Use of Vatalanib baseVatalanib (PTK787; ZK-222584; CGP-79787) is an inhibitor of VEGFR2/KDR with IC50 of 37 nM. |
| Name | N-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)phthalazin-1-amine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Vatalanib (PTK787; ZK-222584; CGP-79787) is an inhibitor of VEGFR2/KDR with IC50 of 37 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
VEGFR2:37 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Vatalanib also inhibits Flk, c-Kit and PDGFRβ with IC50 of 270 nM, 730 nM and 580 nM, respectively. Vatalanib shows the anti-proliferation effect by inhibiting thymidine incorporation induced by VEGF in HUVECs with and IC50 of 7.1 nM, and dose-dependently suppresses VEGF-induced survival and migration of endothelial cells in the same dose range without cytotoxic or antiproliferative effect on cells that do not express VEGF receptors[1]. A recent study shows that Vatalanib significantly inhibits the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and enhances the IFN/5-FU induced apoptosis by increasing proteins levels of Bax and reduced Bcl-xL and Bcl-2[2]. |
| In Vivo | Vatalanib induces dose-dependent inhibition of the angiogenic response to VEGF and PDGF in both a growth factor implant model and a tumor cell-driven angiogenesis model after once-daily oral dosing (25-100 mg/kg). In the same dose range, Vatalanib also inhibits the growth and metastasesof several human carcinomas in nude mice without significant effect on circulating blood cells or bone marrow leukocytes[1]. |
| Kinase Assay | Each GST-fused kinase is incubated under optimized buffer conditions. ATP in a total volume of 30 μL in the presence or absence of a test substance (Vatalanib) for 10 min at ambient temperature. The reaction is stopped by adding 10 μL of 250 mM EDTA[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Subconfluent HUVECs are seeded into 96-well plates coated with 1.5% gelatin. After 24 h, growth medium is replaced by basal medium containing 1.5% FCS and a constant concentration of VEGF (50 ng/mL), bFGF (0.5 ng/mL), or FCS (5%), in the presence or absence of Vatalanib. As a control, wells without growth factor are also included. After 24 h of incubation, BrdUrd labeling solution is added, and cells incubated an additional 24 h before fixation, blocking, and addition of peroxidase-labeled anti-BrdUrd antibody. Bound antibody is then detected using 3,3' 5,5'-tetramethylbenzidine substrate[1]. |
| Animal Admin | A porous Teflon chamber (volume, 0.5 mL) is filled with 0.8% w/v agar containing heparin (20 units/mL) with or without growth factor (3 μg/mL human VEGF, 2 μg/mL human PDGF) is implanted s.c. on the dorsal flank of C57/C6 mice. The mice are treated with Vatalanib (12.5, 25 or 50 mg/kg dihydrochloride p.o. once daily) or vehicle (water) starting 1 day before implantation of the chamber and continuing for 5 days after. At the end of treatment, the mice are killed, and the chambers are removed. The vascularized tissue growing around the chamber is carefully removed and weighed, and the blood content is assessed by measuring the hemoglobin content of the tissue[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 587.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 209-212ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C20H15ClN4 |
| Molecular Weight | 346.813 |
| Flash Point | 309.3±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 346.098511 |
| PSA | 50.70000 |
| LogP | 3.80 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.711 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
|
~80% 
Vatalanib base CAS#:212141-54-3 |
| Literature: Bold, Guido; Altmann, Karl-Heinz; Frei, Joerg; Lang, Marc; Manley, Paul W.; Traxler, Peter; Wietfeld, Bernhard; Brueggen, Josef; Buchdunger, Elisabeth; Cozens, Robert; Ferrari, Stefano; Furet, Pascal; Hofmann, Francesco; Martiny-Baron, Georg; Mestan, Juergen; Roesel, Johannes; Sills, Matthew; Stover, David; Acemoglu, Figan; Boss, Eugen; Emmenegger, Rene; Laesser, Laurent; Masso, Elvira; Roth, Rosemarie; Schlachter, Christian; Vetterli, Werner; Wyss, Dominique; Wood, Jeanette M. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2000 , vol. 43, # 12 p. 2310 - 2323 |
|
~% 
Vatalanib base CAS#:212141-54-3 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 43, # 12 p. 2310 - 2323 |
|
~% 
Vatalanib base CAS#:212141-54-3 |
| Literature: WO2006/2422 A2, ; Page/Page column 125-126 ; |
|
~% 
Vatalanib base CAS#:212141-54-3 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 43, # 12 p. 2310 - 2323 |
|
~% 
Vatalanib base CAS#:212141-54-3 |
| Literature: WO2006/2422 A2, ; Page/Page column 125 ; |
| Vatalanib base |
| N-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)phthalazin-1-amine |
| N-(4-Chlorophenyl)-4-(4-pyridinylmethyl)-1-phthalazinamine |
| Pynasunate |
| 1-phthalazinamine, N-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-(4-pyridinylmethyl)- |
| PTK/ZK |
| vatalanib |
| Vatalanib (free base) |
![4-[(Pyridin-4-yl)Methyl]-2H-phthalazin-1-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/197/107558-48-5.png)