Tempol
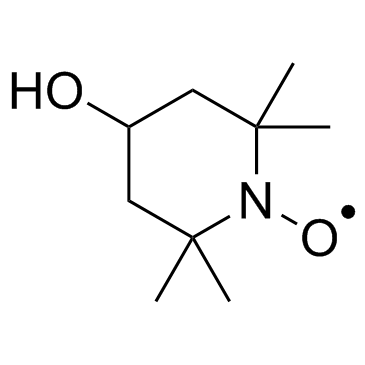
Tempol structure
|
Common Name | Tempol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2226-96-2 | Molecular Weight | 172.24 | |
| Density | 1.187 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 269ºC | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H18NO2* | Melting Point | 69-71 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of TempolTempol is a general superoxide dismutase (SOD)-mimetic drug that efficiently neutralizes reactive oxygen species (ROS). |
| Name | 4-Hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-piperidinooxy |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Tempol is a general superoxide dismutase (SOD)-mimetic drug that efficiently neutralizes reactive oxygen species (ROS). |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
ROS[1] |
| In Vitro | Tempol significantly attenuates H2O2-mediated decrease in mitochondrial respiration and increase in LDH release from rat PT cells, indicating a reduction in cell injury and death. The beneficial actions of Tempol are similar to those obtained using the Fe2+ chelator DEF. However, coadministration of DEF and Tempol does not produce any additional beneficial actions against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury or against oxidative stress-mediated PT cell injury/death[2]. |
| In Vivo | SOD-mimetic Tempol is able to mimic resveratrol’s effects on heart function. Tempol is administered daily by gavage. Mice treated with Met or Tmp had decreased PR and QTc intervals and increased heart rates compared to peroral vehicle (VEH). These results are similar to that obtained by treatment with RSV. Pre- and post-treatment profiles of individual mice are illustrated[1]. Tempol, a membrane-permeable radical scavenger, reduces oxidant stress-mediated renal dysfunction and injury in the rat. Tempol significantly reduces the increase in urea, creatinine, γGT, AST, NAG, and FENa produced by renal ischemia/reperfusion, suggesting an improvement in both renal function and injury. Tempol also significantly reduces kidney MPO activity and MDA levels, indicating a reduction in PMN infiltration and lipid peroxidation, respectively. Tempol reduces the histologic evidence of renal damage associated with ischemia/reperfusion and caused a substantial reduction in the staining for nitrotyrosine and PARS, suggesting reduced nitrosative and oxidative stress[2]. |
| Cell Assay | To investigate the effect of Tempol, DEF, and DEF coadministered with Tempol on H2O2-mediated cell injury and death, confluent cultures of PT cells are preincubated (10 min at 37°C) with Tempol (0.03 to 10 mM), DEF (0.03 to 10 mM), or DEF (3 mM) in combination with Tempol (3 mM). The ranges of concentrations of Tempol and DEF are based on those previously shown in this laboratory to reduce on H2O2-mediated cell injury and death in (1) cultured rat cardiac myoblasts (Tempol) and (2) primary cultures of rat PT cells (DEF ). PT cell cultures are then incubated with H2O2 (1 mM) for four hours, after which cellular injury and death are assessed. Upon completion of incubations, cellular injury and death are assessed using the spectrophotometric assays described later in this article[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] Female or male BALB/c mice (5-7 weeks of age) are used. Mice are infected intraperitoneally (i.p.) with 102 blood trypomastigote forms of the type I Colombian strain of T. cruzi. Treatments are performed daily for 30 days from the establishment of CCC (60 dpi) by i.p. injection of 15 mg/kg trans-resveratrol (10% ethanol/PBS), vehicle (10% ethanol/PBS), 5 mg/Kg EX527 (0.1% DMSO), or peroral administration of 40 mg/Kg Resveratrol (10%ethanol-PBS), 500 mg/kg Metformin (dissolved in water), 100 mg/kg Tempol (dissolved in water), Benznidazole (25 mg/Kg, dissolved in water) and vehicle (water or 10%ethanol-PBS). Rats[2] 83 male Wistar rats weighing 230 to 320 g are used.Upon completion of surgical procedures, the animals are randomly allocated to the eight groups. At one minute before commencement of reperfusion, animals received a bolus injection of either vehicle (saline, 4 mL/kg, IV), Tempol (30 mg/kg in saline, IV), DEF (40 mg/kg in saline, IV), or DEF (40 mg/kg in saline, IV) in combination with Tempol (30 mg/kg in saline, IV). The corresponding groups then received a continuous infusion of one of the following throughout the reperfusion period: vehicle (saline, 4 mL/kg/h, IV), Tempol (30 mg/kg/h in saline, IV), DEF (40 mg/kg/h in saline, IV), or Tempol and DEF in combination (30 and 40 mg/kg/h, respectively, in saline, IV). To elucidate the effects of Tempol or DEF on cardiovascular hemodynamics and organ function in sham-operated rats, respective groups of animals received the treatments described previously in this article and as outlined. The concentration of Tempol administered in vivo is based on those previously demonstrated by us to provide significant protection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in an in vivo rat model. Similarly, the concentration of DEF used is identical to that which we have previously used to provide significant protection against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in in vivo rat and rabbit models. |
| References |
| Density | 1.187 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 269ºC |
| Melting Point | 69-71 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C9H18NO2* |
| Molecular Weight | 172.24 |
| PSA | 23.47000 |
| LogP | 1.28370 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R36/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36-S37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | TN8991000 |
| HS Code | 29333999 |
| HS Code | 29333999 |
|---|
|
NADPH oxidase 2-derived superoxide downregulates endothelial KCa3.1 in preeclampsia.
Free Radic. Biol. Med. 57 , 10-21, (2013) Endothelial dysfunction is associated with KCa3.1 dysfunction and contributes to the development of hypertension in preeclampsia. However, evidence of endothelial KCa3.1 dysfunction in the vascular sy... |
|
|
Gastrokine 1 inhibits the carcinogenic potentials of Helicobacter pylori CagA.
Carcinogenesis 35(11) , 2619-29, (2014) Helicobacter pylori CagA directly injected by the bacterium into epithelial cells via a type IV secretion system, leads to cellular changes such as morphology, apoptosis, proliferation and cell motili... |
|
|
Organic Radical Contrast Agents Based on Polyacetylenes Containing 2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidine 1-Oxyl (TEMPO): Targeted Magnetic Resonance (MR)/Optical Bimodal Imaging of Folate Receptor Expressing HeLa Tumors in Vitro and in Vivo(a).
Macromol. Biosci. 15 , 788-98, (2015) Nitroxides have great potential as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents for tumor detection. Polyacetylenes(PAs) containing 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-piperidine oxyl (TEMPO) and poly(ethylene gl... |
| 4-Hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine 1-oxyl,TEMPOL |
| HYDROXY-TEMPO |
| (4-Hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-1-piperidinyl)oxidanyl |
| 4-Hydroxy-TEMPO Free Radical |
| EINECS 218-761-4 |
| Tempol |
| (4-Hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-1-yl)oxidanyl |
| 4-Oxypiperidol |
| Tetramethylpiperidino-N-oxyl |
| TMPN |
| 4-Hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine N-oxide |
| 4-Hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-1-piperidin-1-yloxy, free radical |
| Tanol |
| 4-Hydroxy-TEMPO |
| 4-Hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinoxyl |
| 4-Hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine 1-oxyl free radical |
| 4-Hydroxy-2,2,6,6-te |
| NR-I |
| 4-hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethyl piperidinyloxy,free radical |
| 4-hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinoxy radical |
| nr1 |
| 2,2,6,6-Tetramethyl-4-piperidinol 1-oxyl |
| 2,2,6,6-Tetramethyl-4-hydroxypiperidinooxy |
| 4-Hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinooxyl |
| nitroxyl2 |
| OH-Tempo, 4-Hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine 1-Oxyl Free Radical |
| 2,2,6,6-Tetramethyl-4-hydroxy-1-piperidinyloxy radical |
| 4-Hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-1-piperidin-1-yloxy,free radical |
| 4-Hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl |
| Tetramethylpiperidinol N-oxyl |
| 2,2,6,6-Tetramethyl-4-hydroxypiperidinooxy radical |
| 4-OH-TEMPO |
| 4-hydroxy-1-oxyl-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine |
| 4-hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-piperidinyloxy |
| 1-Piperidinyloxy, 4-hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethyl- |
| 4-Hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinooxy radical |
| 4-hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxy |
| MFCD00006478 |
 CAS#:78119-82-1
CAS#:78119-82-1 CAS#:760-93-0
CAS#:760-93-0 CAS#:3637-10-3
CAS#:3637-10-3 CAS#:132416-36-5
CAS#:132416-36-5 CAS#:122586-72-5
CAS#:122586-72-5 CAS#:87018-00-6
CAS#:87018-00-6 CAS#:290821-83-9
CAS#:290821-83-9
