DL-O-Tyrosine
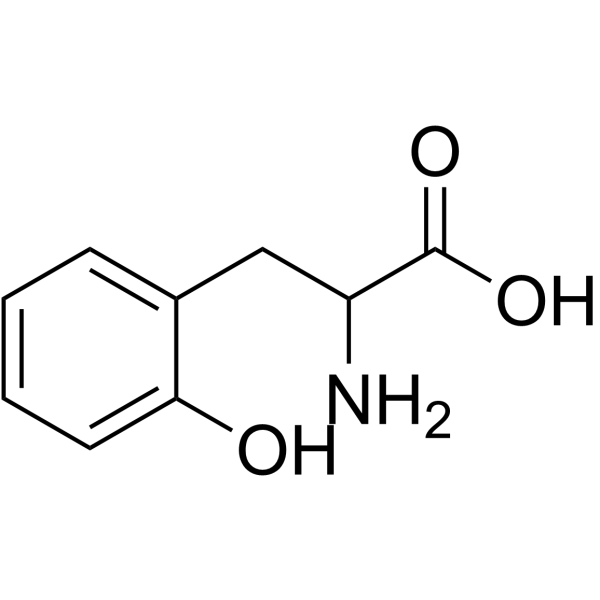
DL-O-Tyrosine structure
|
Common Name | DL-O-Tyrosine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2370-61-8 | Molecular Weight | 181.18900 | |
| Density | 1.333g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 369ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H11NO3 | Melting Point | 260ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 177ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of DL-O-TyrosineDL-O-Tyrosine is a tyrosine derivative[1]. |
| Name | dl-o-tyrosine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | DL-O-Tyrosine is a tyrosine derivative[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Amino acids and amino acid derivatives have been commercially used as ergogenic supplements. They influence the secretion of anabolic hormones, supply of fuel during exercise, mental performance during stress related tasks and prevent exercise induced muscle damage. They are recognized to be beneficial as ergogenic dietary substances[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.333g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 369ºC at 760mmHg |
| Melting Point | 260ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C9H11NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 181.18900 |
| Flash Point | 177ºC |
| Exact Mass | 181.07400 |
| PSA | 83.55000 |
| LogP | 1.04690 |
| Vapour Pressure | 5.14E-18mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | -20°C Freezer |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water, and DMSO (Heated). |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | YP2285000 |
| HS Code | 2922509090 |
| HS Code | 2922509090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2922509090. other amino-alcohol-phenols, amino-acid-phenols and other amino-compounds with oxygen function. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Ion-pairing reversed-phase liquid chromatography fractionation in combination with isotope labeling reversed-phase liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry for comprehensive metabolome profiling
J. Chromatogr. A. 1218(23) , 3689-94, (2011) We report a novel two-dimensional (2D) separation strategy aimed at improving the detectability of liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC–MS) for metabolome analysis. It is based on the use of io... |
|
|
Concomitant tumor resistance: the role of tyrosine isomers in the mechanisms of metastases control.
Cancer Res. 72(5) , 1043-50, (2012) Concomitant tumor resistance (CR) is a phenomenon in which a tumor-bearing host is resistant to the growth of secondary tumor implants and metastasis. Although previous studies indicated that T-cell-d... |
|
|
Mass spectrometric quantification of 3-nitrotyrosine, ortho-tyrosine, and o,o'-dityrosine in brain tissue of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3, 6-tetrahydropyridine-treated mice, a model of oxidative stress in Parkinson's disease.
J. Biol. Chem. 274(49) , 34621-8, (1999) Oxidative stress is implicated in the death of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson's disease and in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3, 6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) model of Parkinson's disease. Oxidative speci... |
| 2,5-Diaminopentanoic acid |
| EINECS 219-134-8 |
| 2-Amino-3-(2-hydroxyphenyl)propionic Acid |
| L-2,5-Diaminopentanoic acid |
| MFCD00021725 |
| D,L-o-tyrosine |
| DL-o-Tyrosine |

