DNQX
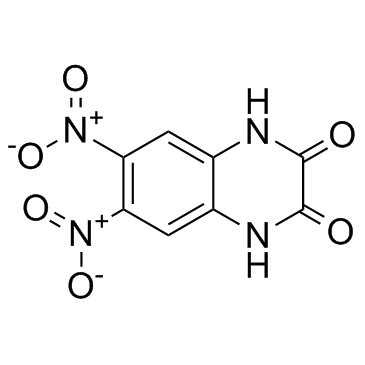
DNQX structure
|
Common Name | DNQX | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2379-57-9 | Molecular Weight | 252.141 | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 670.7ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H4N4O6 | Melting Point | >300°C | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 359.4ºC | |
Use of DNQXDNQX is a AMPA receptor antagonists.target: AMPA receptorIn vitro: DNQX, added 2 h after cell plating, induces a dose-dependent neurotoxicity. |
| Name | 6,7-Dinitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | DNQX is a AMPA receptor antagonists.target: AMPA receptorIn vitro: DNQX, added 2 h after cell plating, induces a dose-dependent neurotoxicity. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 670.7ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | >300°C |
| Molecular Formula | C8H4N4O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 252.141 |
| Flash Point | 359.4ºC |
| Exact Mass | 252.013077 |
| PSA | 157.36000 |
| LogP | 1.13 |
| Vapour Pressure | 1.33E-18mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.665 |
| Storage condition | Desiccate at RT |
| Stability | Store in freezer at -20°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|
~% 
DNQX CAS#:2379-57-9 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 35, # 18 p. 3319 - 3324 |
|
~% 
DNQX CAS#:2379-57-9 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 35, # 18 p. 3319 - 3324 |
|
~% 
DNQX CAS#:2379-57-9 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 35, # 18 p. 3319 - 3324 |
|
~% 
DNQX CAS#:2379-57-9 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 35, # 18 p. 3319 - 3324 |
|
~% 
DNQX CAS#:2379-57-9 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 35, # 18 p. 3319 - 3324 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Ammonium increases Ca(2+) signalling and upregulates expression of Cav1.2 gene in astrocytes in primary cultures and in the in vivo brain.
Acta Physiol. (Oxf.) 214 , 261-74, (2015) The primary aim of this study was to identify the effects of hyperammonaemia on functional expression of Cav1.2 L-type Ca(2+) channels in astroglia.Primary cultures of mouse astrocytes were used to st... |
|
|
Phasic, nonsynaptic GABA-A receptor-mediated inhibition entrains thalamocortical oscillations.
J. Neurosci. 34(21) , 7137-47, (2014) GABA-A receptors (GABA-ARs) are typically expressed at synaptic or nonsynaptic sites mediating phasic and tonic inhibition, respectively. These two forms of inhibition conjointly control various netwo... |
|
|
Abnormal excitability and episodic low-frequency oscillations in the cerebral cortex of the tottering mouse.
J. Neurosci. 35(14) , 5664-79, (2015) The Ca(2+) channelopathies caused by mutations of the CACNA1A gene that encodes the pore-forming subunit of the human Cav2.1 (P/Q-type) voltage-gated Ca(2+) channel include episodic ataxia type 2 (EA2... |
| 6,7-Dinitro-1,4-dihydro-2,3-quinoxalinedione |
| 6,7-dinitroquinoxaline-2,3-diol |
| 2,3-Quinoxalinedione, 1,4-dihydro-6,7-dinitro- |
| MFCD00069257 |
| 6,7-Dinitroquinoxaline-2,3(1H,4H)-dione |
| 6,7-Dinitro-1,4-dihydroquinoxaline-2,3-dione |
| DNQX |
![7-nitro-5H-tetrazolo[1,5-a]quinoxalin-4-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/293/143007-11-8.png)

![7-nitrotetrazolo[1,5-a]quinoxaline structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/017/143007-18-5.png)
 CAS#:2379-61-5
CAS#:2379-61-5
