Valpromide
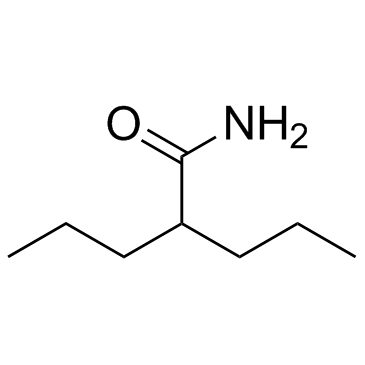
Valpromide structure
|
Common Name | Valpromide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2430-27-5 | Molecular Weight | 143.22700 | |
| Density | 0.885g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 274.6ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H17NO | Melting Point | 123-125°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 119.9ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of ValpromideValpromide is an amide derivative of valproic acid and inhibits human epoxide hydrolase. |
| Name | valpromide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Valpromide is an amide derivative of valproic acid and inhibits human epoxide hydrolase. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
epoxide hydrolase[1] |
| References |
| Density | 0.885g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 274.6ºC at 760mmHg |
| Melting Point | 123-125°C |
| Molecular Formula | C8H17NO |
| Molecular Weight | 143.22700 |
| Flash Point | 119.9ºC |
| Exact Mass | 143.13100 |
| PSA | 43.09000 |
| LogP | 2.38840 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.00535mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.44 |
| Storage condition | room temp |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S36/37 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | YV5965500 |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924199090. other acyclic amides (including acyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
The synergistic effects of DNA-damaging drugs cisplatin and etoposide with a histone deacetylase inhibitor valproate in high-risk neuroblastoma cells.
Int. J. Oncol. 47 , 343-52, (2015) High-risk neuroblastoma remains one of the most important therapeutic challenges for pediatric oncologists. New agents or regimens are urgently needed to improve the treatment outcome of this fatal tu... |
|
|
Amidic modification of valproic acid reduces skeletal teratogenicity in mice.
Birth Defects Res. B Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 71(1) , 47-53, (2004) The antiepileptic drug valproic acid (VPA) is well known to cause neural tube and skeletal defects in both humans and animals. The amidic VPA analogues valpromide (VPD) and valnoctamide (VCD) have muc... |
|
|
Polycomb homologs are involved in teratogenicity of valproic acid in mice.
Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 70(11) , 870-9, (2004) Valproic acid (VPA) is widely used to treat epilepsy and bipolar disorder and is also a potent teratogen, but its teratogenic mechanisms are unknown. We have attempted to describe a fundamental role o... |
| Depamide |
| 2-Propylvaleramide |
| Valpromide |
| 2,2-Di-n-propylacetamide |
| Pentanamide,2-propyl |
| EINECS 219-394-2 |
| MFCD00051534 |
| 2-Ethylvaleramide |
| 2-propylpentamide |
| 2,2-BIS(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)PROPANOL |
| 2-propylpentanamide |
| Dipropylacetamide |
| Valpramide |

