poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate)
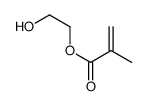
poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) structure
|
Common Name | poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 25249-16-5 | Molecular Weight | 130.14200 | |
| Density | 1.054g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 189ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H10O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 97.2ºC | |
Use of poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate)Poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (MW 1000000) is one of the most important hydrogels in the biomaterials world. Poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) is the basic component of contact lenses, and is also used in implantation of soft tissues, synthetic transplant for gristle and bone, regeneration of neurotic tissue, transmission of drug and etc[1]. |
| Name | poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) macromolecule |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (MW 1000000) is one of the most important hydrogels in the biomaterials world. Poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) is the basic component of contact lenses, and is also used in implantation of soft tissues, synthetic transplant for gristle and bone, regeneration of neurotic tissue, transmission of drug and etc[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (PolyHEMA) retains moisture content similar to the live tissue and is resistant to degradation and absorption by the host cells. It can be easily manufactured in a variety of shapes and can be readily sterilized[1]. Proliferation rate of the cells that had been cultured on Poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) is reduced; Poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) does not induce cell death in the hRPE cultures. Human retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells cultured on Poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) formed many giant spheroid colonies. The giant colonies are re-cultured and the presence of retinal progenitor markers and markers of hRPE cells are detected in cell cultures on Poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate)[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.054g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 189ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C6H10O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 130.14200 |
| Flash Point | 97.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 130.06300 |
| PSA | 46.53000 |
| LogP | 0.09800 |
| Appearance of Characters | powder |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.159mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.442 |
| Water Solubility | ethanol: 120 mg/mL |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | 24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
Increased protein sorption in poly(acrylic acid)-containing films through incorporation of comb-like polymers and film adsorption at low pH and high ionic strength.
Langmuir 29(9) , 2946-54, (2013) In principle, incorporation of comb-like block copolymers in multilayer polyelectrolyte films can both increase film thickness relative to coatings containing linear polymers and provide more swollen ... |
|
|
Hydrogels that mimic developmentally relevant matrix and N-cadherin interactions enhance MSC chondrogenesis.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110(25) , 10117-22, (2013) Methacrylated hyaluronic acid (HA) hydrogels provide a backbone polymer with which mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can interact through several cell surface receptors that are expressed by MSCs, includi... |
|
|
S100A7 acts as a dual regulator in promoting proliferation and suppressing squamous differentiation through GATA-3/caspase-14 pathway in A431 cells.
Exp. Dermatol. 24 , 342-8, (2015) S100A7 is expressed in many squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs), such as SCC of the skin, and well-differentiated SCC always displays stronger staining of this protein. A431 cells, an epidermal cancer cel... |
| 2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate |
| MFCD00084374 |