MRTX849 acid
Modify Date: 2024-01-12 23:54:02
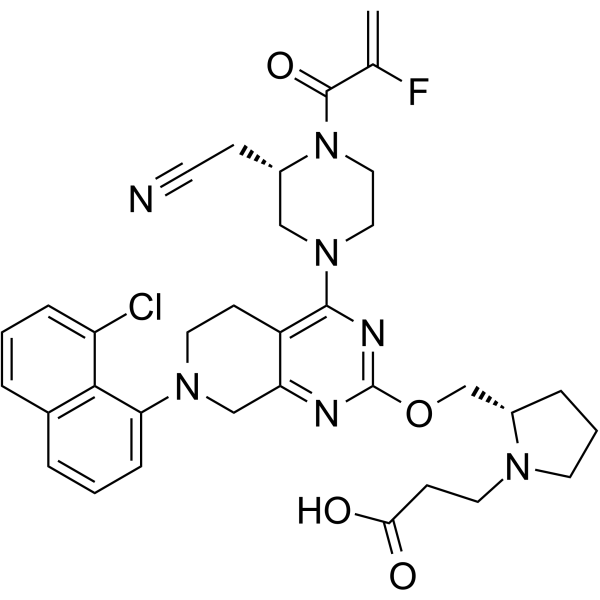
MRTX849 acid structure
|
Common Name | MRTX849 acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2561529-96-0 | Molecular Weight | 662.15 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C34H37ClFN7O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of MRTX849 acidMRTX849 acid, a derivative of MRTX849, can be used in the synthesis of PROTAC LC-2 (HY-137516). LC-2 is a potent and first-in-class PROTAC capable of degrading endogenous KRAS G12C (DC50s between 0.25 and 0.76 μM)[1][2]. |
| Name | MRTX849 acid |
|---|
| Description | MRTX849 acid, a derivative of MRTX849, can be used in the synthesis of PROTAC LC-2 (HY-137516). LC-2 is a potent and first-in-class PROTAC capable of degrading endogenous KRAS G12C (DC50s between 0.25 and 0.76 μM)[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
KRas G12C |
| In Vitro | LC-2 induces degradation of endogenous KRASG12C in multiple KRAS mutant cancer cell (NCI-H2030, MIA PaCa-2, SW1573, NCI-H23 and NCI-H358 cells) with DC50s between 0.25 and 0.76 μM. LC-2-induced KRASG12C degradation occurs via a bona fide PROTAC mechanism. MIA PaCa-2, NCI-H23, and SW1573 cells are treated with 2.5 μM of LC-2 for 6, 24, 48, and 72 h. In all three cell lines, maximal KRAS degradation occurred within 24 h and was sustained up to 72 h[1]. LC-2-induced (2.5 μM; 6-24 hours) KRAS G12C degradation modulates Erk signaling in homozygous and heterozygous KRAS mutant cell lines[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C34H37ClFN7O4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 662.15 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|