Antibacterial agent 123
Modify Date: 2024-01-12 15:30:30
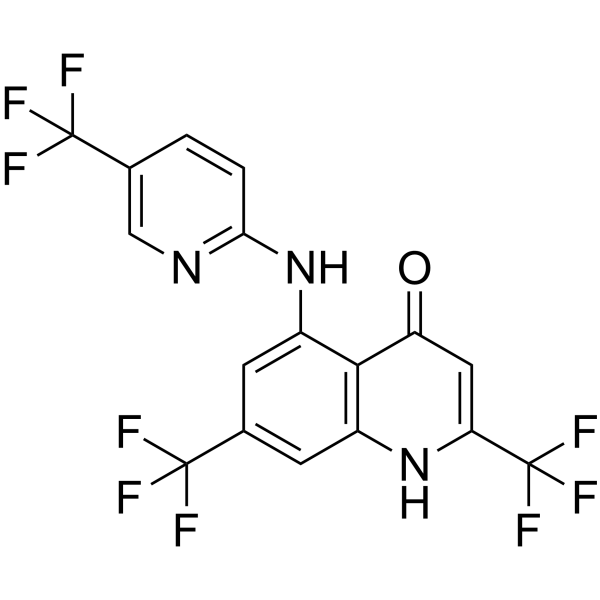
Antibacterial agent 123 structure
|
Common Name | Antibacterial agent 123 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2615254-55-0 | Molecular Weight | 441.25 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H8F9N3O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Antibacterial agent 123Antibacterial agent 123 (compound 111) is a potent membrane-disrupting agent to combat antibiotic-resistant Gram-positive bacteria[1]. |
| Name | Antibacterial agent 123 |
|---|
| Description | Antibacterial agent 123 (compound 111) is a potent membrane-disrupting agent to combat antibiotic-resistant Gram-positive bacteria[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Antibacterial agent 123 (compound 111) shows excellent activity (MIC<0.0625 μg/mL) toward S. aureus strains[1]. |
| In Vivo | Antibacterial agent 123 (compound 111) (p.o. (10 mg/kg) and i.v. (0.5 mg/kg); once) exhibits favorable pharmacokinetics profiles[1]. Animal Model: Female CD-1 mice[1] Dosage: 0.5 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg Administration: p.o. (10 mg/kg) and i.v. (0.5 mg/kg); once (Pharmacokinetic Analysis) Result: Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Antibacterial agent 123 in Female CD-1 Mice[1]. pharmacokinetic indices dose i.v., p.o. (mg/kg) AUC0-24 (i.v., h·ng/mL) Vd (i.v., mL/kg) CL (i.v., mL/(kg·h)) t1/2 (i.v., h) AUC0-24 (p.o., h·ng/mL) Cmax (p.o., ng/mL) F (%) compound 111 0.5, 10 (4.20 × 103) ± 308 322 ± 24 119 ± 9.2 1.88 ± 0.08 (4.33 × 104) ± 543 (3.10 × 103) ± 780 51.6 ± 5.2 |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C17H8F9N3O |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 441.25 |