H-Lys-OMe.2HCl
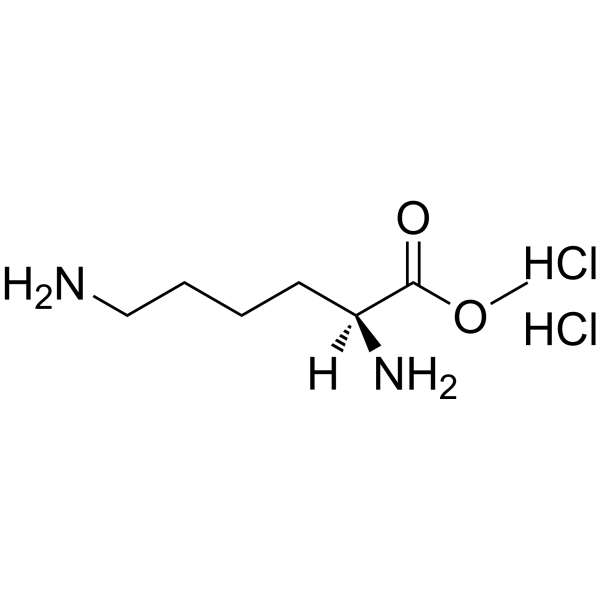
H-Lys-OMe.2HCl structure
|
Common Name | H-Lys-OMe.2HCl | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 26348-70-9 | Molecular Weight | 233.136 | |
| Density | 1.031g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 243.9ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H18Cl2N2O2 | Melting Point | 213-215°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 93.5ºC | |
Use of H-Lys-OMe.2HClH-Lys-OMe.2HCl is a lysine derivative[1]. |
| Name | methyl (2S)-2,6-diaminohexanoate,dihydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | H-Lys-OMe.2HCl is a lysine derivative[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Amino acids and amino acid derivatives have been commercially used as ergogenic supplements. They influence the secretion of anabolic hormones, supply of fuel during exercise, mental performance during stress related tasks and prevent exercise induced muscle damage. They are recognized to be beneficial as ergogenic dietary substances[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.031g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 243.9ºC at 760mmHg |
| Melting Point | 213-215°C |
| Molecular Formula | C7H18Cl2N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 233.136 |
| Flash Point | 93.5ºC |
| Exact Mass | 232.074539 |
| PSA | 78.34000 |
| LogP | 2.62030 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0313mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 17 ° (C=5, H2O) |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2922499990 other amino-acids, other than those containing more than one kind of oxygen function, and their esters; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
pH-responsive, lysine-based hydrogels for the oral delivery of a wide size range of molecules.
Int. J. Pharm. 478(2) , 496-503, (2015) Hydrogels synthesized from poly(l-lysine isophthalamide) (PLP) crosslinked with l-lysine methyl ester were investigated as drug delivery systems for a wide size range of molecules (0.3-2000kDa). PLP i... |
|
|
A neutral polydisulfide containing Gd(III) DOTA monoamide as a redox-sensitive biodegradable macromolecular MRI contrast agent.
Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 11 , 32-40, (2016) This work aims to develop safe and effective gadolinium (III)-based biodegradable macromolecular MRI contrast agents for blood pool and cancer imaging. A neutral polydisulfide containing macrocyclic G... |
|
|
Characterization of the chemical degradation of hyaluronic acid during chemical gelation in the presence of different cross-linker agents.
Carbohydr. Res. 342 , 2776-2792, (2007) Dynamic light scattering (DLS) and rheological experiments have been performed on semidilute aqueous hyaluronic acid (HA) solutions during the chemical cross-linking process with a water-soluble carbo... |
| DL-lysine methyl ester dihydrochloride |
| L-Lysine methyl ester 2HCl |
| MFCD00039067 |
| L-2,6-diaminohexanoic acid methyl ester dihydrochloride |
| L-Lysine Methyl Ester Dihydrochloride |
| (+)-(2S)-lysine methyl ester dihydrochloride |
| Lys-OMe*2HCl |
| EINECS 247-625-7 |
| H-Lys-Ome.2Hcl |
| H-Lys-OMe .2HCl |
| L-Lysine, methyl ester, hydrochloride (1:2) |
| methyl (2S)-2,6-diaminohexanoate dihydrochloride |
| (S)-Methyl 2,6-diaminohexanoate dihydrochloride |
| LysOMe dihydrochloride |
| Methyl L-lysinate dihydrochloride |
| L-Lysine, methyl ester, dihydrochloride |
| H-Lys-OMe·2HCl |

