Chaetocin

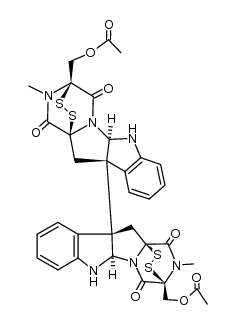
Chaetocin structure
|
Common Name | Chaetocin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 28097-03-2 | Molecular Weight | 696.840 | |
| Density | 1.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C30H28N6O6S4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of ChaetocinChaetocin is a specific inhibitor of the histone methyltransferase (HMT) SU(VAR)3-9 with an IC50 of 0.6 μM for SU(VAR)3-9. It also inhibits thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) with an IC50 of 4 μM. |
| Name | Chaetocin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Chaetocin is a specific inhibitor of the histone methyltransferase (HMT) SU(VAR)3-9 with an IC50 of 0.6 μM for SU(VAR)3-9. It also inhibits thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) with an IC50 of 4 μM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 0.6 μM (HMT)[1], 4 μM (TrxR)[2] |
| In Vitro | Chaetocin is initially isolated from the fermentation broth of chaetomium minutum and belongs to the class of 3-6 epidithio-diketopiperazines (ETPs). The IC50 for SU(VAR)3-9 is 0.6 μM and acts as a competitive inhibitor for S-adenosylmethionine. Chaetocin inhibits the human ortholog of dSU(VAR)3-9 with a similar IC50 value of 0.8 μM. It inhibits other known Lys9-specific HMTs such as mouse G9a and Neurospora crassa DIM5 with a higher IC50 values of 2.5 and 3 mM, respectively[1]. Chaetocin inhibits TrxR1-initiated turnover of the synthetic substrate DTNB in a cell-free assay in a dose-responsive manner with an IC50 of about 4 μM[2]. |
| In Vivo | SL-2 Drosophila tissue cells are cultured in the presence or absence of the inhibitor. Chaetocin has a toxic effect on cells grown in culture. Toxicity is highly dependent on the initial cell density when chaetocin is added to the culture. The number of H3 molecules dimethylated at Lys9 (H3K9me2) is markedly reduced when cells are grown in medium containing 0.5 μM chaetocin after 5 d. Histones isolated from cells treated with 0.1 μM and for a shorter time also shows a drop in Lys9 methylation, but not as strongly as with the higher concentration[1]. |
| Cell Assay | HeLa cells are transfected with 1 μg pcDNA or pcDNA-Trx. Twenty four h after transfection the cells are treated with either DMSO, 100 nM chaetocin or 100 nM doxorubicin for 24 h. The cells are then trypsinized and manually counted in trypan blue to exclude dead cells. For immunoblotting (24 h after transfections), cells are trypsinized, ished in cold PBS, and lysed in CelLytic lysis buffer containing protease inhibitors. Protein is analyzed by BCA assay and lysates are electrophoresed on 15% SDS-PAGE gels and transferred to nitrocellulose. Immunoblotting for thioredoxin and actin is then performed[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C30H28N6O6S4 |
| Molecular Weight | 696.840 |
| Exact Mass | 696.095337 |
| PSA | 246.96000 |
| LogP | 3.10 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.930 |
| Storage condition | 2~8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 + H312 + H332 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | 20/21/22 |
| RIDADR | UN 1544 |
| RTECS | FM3032000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
|
~89% 
Chaetocin CAS#:28097-03-2 |
| Literature: Kim, Justin; Movassaghi, Mohammad Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010 , vol. 132, # 41 p. 14376 - 14378 |
|
~43% 
Chaetocin CAS#:28097-03-2 |
| Literature: Iwasa, Eriko; Hamashima, Yoshitaka; Fujishiro, Shinya; Eisuke, Higuchi; Ito, Akihiro; Yoshida, Minoru; Sodeoka, Mikiko Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010 , vol. 132, # 12 p. 4078 - 4079 |
|
~6% 
Chaetocin CAS#:28097-03-2 |
| Literature: Iwasa, Eriko; Hamashima, Yoshitaka; Fujishiro, Shinya; Eisuke, Higuchi; Ito, Akihiro; Yoshida, Minoru; Sodeoka, Mikiko Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010 , vol. 132, # 12 p. 4078 - 4079 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
Inhibition of histone H3K9 methyltransferases by gliotoxin and related epipolythiodioxopiperazines.
J. Antibiot. 65(5) , 263-5, (2012)
|
|
|
Individual epigenetic status of the pathogenic D4Z4 macrosatellite correlates with disease in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy.
Clin. Epigenetics. 7(1) , 37, (2015) Both forms of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) are associated with aberrant epigenetic regulation of the chromosome 4q35 D4Z4 macrosatellite. Chromatin changes due to large deletions of h... |
|
|
Epidithiodiketopiperazine as a pharmacophore for protein lysine methyltransferase G9a inhibitors: reducing cytotoxicity by structural simplification.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 23(3) , 733-6, (2013) Chaetocin (1), a structurally complex epidithiodiketopiperazine (ETP) alkaloid produced by Chaetomium minutum, is a potent inhibitor of protein lysine methyltransferase G9a, which plays important role... |
| (3S,3'S)-3,3'-bis-hydroxymethyl-2,2'-dimethyl-(5at,10bt,5'at',10'bt')-2,3,5a,6,2',3',5'a,6'-octahydro-[10b,10'b]bi[3r,11ac-epidisulfano-pyrazino[1',2':1,5]pyrrolo[2,3-b]indolyl]-1,4,1',4'-tetraone |
| (+)-chaetocin A |
| (1S,1'S,3R,3'R,11R,11'R,14S,14'S)-14,14'-Bis(hydroxymethyl)-18,18'-dimethyl-3,3'-bi(15,16-dithia-10,12,18-triazapentacyclo[12.2.2.0.0.0]octadecane)-4,4',6,6',8,8'-hexaene-13,13',17,17 ;'-tetrone |
| 'bR,11aS,11'aS) |
| Chetocin |