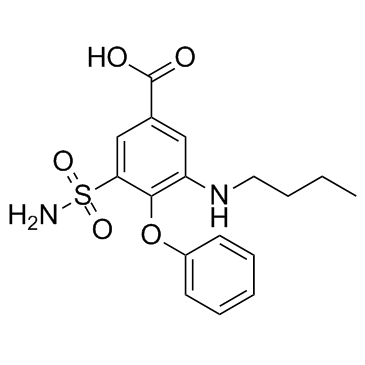
sodium 3-(aminosulphonyl)-5-(butylamino)-4-phenoxybenzoate
Modify Date: 2024-01-07 11:06:56
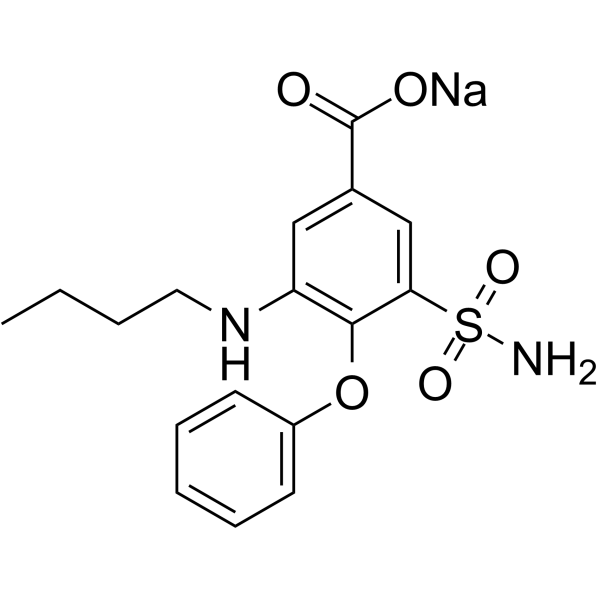
sodium 3-(aminosulphonyl)-5-(butylamino)-4-phenoxybenzoate structure
|
Common Name | sodium 3-(aminosulphonyl)-5-(butylamino)-4-phenoxybenzoate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 28434-74-4 | Molecular Weight | 386.39800 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 571.2ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H19N2NaO5S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 299.3ºC | |
Use of sodium 3-(aminosulphonyl)-5-(butylamino)-4-phenoxybenzoateBumetanide sodium, a highly potent loop diuretic, is a Na+-K+-Cl+ cotransporter (NKCC) blocker. Bumetanide sodium is a selective NKCC1 inhibitor, and also inhibits NKCC2, with IC50s of 0.68 and 4.0 μM for hNKCC1A and hNKCC2A, respectively[1][2]. |
| Name | sodium,3-(butylamino)-4-phenoxy-5-sulfamoylbenzoate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Bumetanide sodium, a highly potent loop diuretic, is a Na+-K+-Cl+ cotransporter (NKCC) blocker. Bumetanide sodium is a selective NKCC1 inhibitor, and also inhibits NKCC2, with IC50s of 0.68 and 4.0 μM for hNKCC1A and hNKCC2A, respectively[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Bumetanide sodium has inhibitory effects for the two major human splice variants of NKCCs, hNKCC1A and hNKCC2A [1]. Bumetanide sodium (0.03-100 μM; 5 minutes) inhibits the 86Rb+ uptake in NKCC1A-expressing oocytes in a dose-dependent manner[1]. Bumetanide sodium inhibits NKCC2 isoform B in HEK-293 cells with an IC50 value of 0.54 μM[2]. |
| In Vivo | Bumetanide sodium (7.6-30.4 mg/kg; i.v.) attenuates the decrease in apparent diffusion coefficients (ADC) ratios for both cortex and striatum (by 40-67%), indicating reduced edema formation[3]. Bumetanide sodium also reduces infarct size[3]. Bumetanide sodium shows different half-lives of 21.4 min, 53.8 min and 137 min following 2 mg/kg, 8 mg/kg and 20 mg/kg intravenous injection, respectively, in rats[4]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 571.2ºC at 760mmHg |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H19N2NaO5S |
| Molecular Weight | 386.39800 |
| Flash Point | 299.3ºC |
| Exact Mass | 386.09100 |
| PSA | 129.93000 |
| LogP | 3.55590 |
| Vapour Pressure | 6.89E-14mmHg at 25°C |
|
~97% 
sodium 3-(amino... CAS#:28434-74-4 |
| Literature: Ong, Winston; Cheung, Eugene Y.; Schultz, Karen A.; Smith, Cartney; Bourassa, James; Hickey, Magali B. CrystEngComm, 2012 , vol. 14, # 7 p. 2428 - 2434 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| Sodium 3-(aminosulphonyl)-5-(butylamino)-4-phenoxybenzoate |
| Sodium 3-(butylamino)-4-phenoxy-5-sulfamoylbenzoate |
| Benzoic acid,3-(aminosulfonyl)-5-(butylamino)-4-phenoxy-,sodium salt (1:1) |
| SODIUM 3-(AMINOSULFONYL)-5-(BUTYLAMINO)-4-PHENOXYBENZOATE |
| Benzoic acid,3-(butylamino)-4-phenoxy-5-sulfamoyl-,monosodium salt (8CI) |
| EINECS 249-015-6 |
| sodium bumetanide |
| Benzoicacid,3-(aminosulfonyl)-5-(butylamino)-4-phenoxy-,monosodium salt (9CI) |