C2 Ceramide
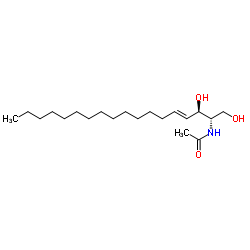
C2 Ceramide structure
|
Common Name | C2 Ceramide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 3102-57-6 | Molecular Weight | 341.529 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 532.4±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H39NO3 | Melting Point | 93-96ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 275.8±30.1 °C | |
Use of C2 CeramideC2 Ceramide (Ceramide 2) is the main lipid of the stratum corneum and a protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) activator. C2 Ceramide activates PP2A and ceramide-activated protein phosphatase (CAPP). C2 Ceramide induces cells differentiation and apoptosis, inhibits mitochondrial respiratory chain complex III. C2 Ceramide is also a skin conditioning agent that protects the epidermal barrier from water loss[1][2][3][4][5]. |
| Name | N-acetylsphingosine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | C2 Ceramide (Ceramide 2) is the main lipid of the stratum corneum and a protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) activator. C2 Ceramide activates PP2A and ceramide-activated protein phosphatase (CAPP). C2 Ceramide induces cells differentiation and apoptosis, inhibits mitochondrial respiratory chain complex III. C2 Ceramide is also a skin conditioning agent that protects the epidermal barrier from water loss[1][2][3][4][5]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Protein phosphatase 1[2] PP2A[4] Ceramide-activated protein phosphatase (CAPP)[4] Apoptosis[1] Mitochondrial respiratory chain complex III[1] |
| In Vitro | C2 Ceramide (5 nM-200 µM; 24 hours; primary mouse osteoblasts) treatment (≤500 nM) promots osteoblast viability, whilst concentrations ≥2 µM significantly reduces osteoblast viability in a dose- and time-dependent manner[1]. C2 Ceramide increases cytoplasmic histone-associated DNA fragments by 5.7- and 11.2-fold at 50 µM and 100 µM C2 Ceramide concentrations respectively in osteoblasts. At these higher concentrations, C2 Ceramide is a potent inducer of apoptosis in osteoblasts[1]. C2 Ceramide up-regulates mRNA expression of angiogenic genes in human dental pulp cells (HDPCs) and increases the migration and capillary tube formation of endothelial cells, whereas PP1 small interfering RNA shows opposite effects. Human dental pulp cells (HDPCs) increases levels of bone morphogenetic protein 2, phosphorylation of Smad 1/5/8, and mRNA expression of runt-related transcription factor 2 and osterix[2]. Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Line: Primary mouse osteoblasts Concentration: 5 nM-200 µM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Murine osteoblasts demonstrated a dose-dependent increase in their survival rate when exposed to low concentrations of 5-500 n M. Increasing concentrations of 20-200µM caused a dose-dependent decrease in mitochondrial succinate dehydrogenase activity and osteoblast survival. |
| In Vivo | The PP1 activator C2 Ceramide increases alkaline phosphatase activity, mineralizes nodule formation, and mRNA expression of dentin matrix protein 1 and dentin sialophosphoprotein. In contrast, knockdown by PP1 small interfering RNA inhibits odontoblastic differentiation[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 532.4±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 93-96ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C20H39NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 341.529 |
| Flash Point | 275.8±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 341.292999 |
| PSA | 69.56000 |
| LogP | 5.90 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.485 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924199090. other acyclic amides (including acyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Induction of apoptosis in prostate cancer cells by the novel ceramidase inhibitor ceranib-2.
In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 51 , 1056-63, (2015) Ceramidases are key enzymes that decrease ceramide levels in cells. A reduction in ceramide concentration impairs ceramide signalling, and results in apoptosis resistance in cancer cells. This study i... |
|
|
Sphingolipids are required for efficient triacylglycerol loss in conjugated linoleic Acid treated adipocytes.
PLoS ONE 10(4) , e0119005, (2015) Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) reduces adiposity in human and mouse adipocytes. This outcome is achieved through a variety of biological responses including increased energy expenditure and fatty acid... |
|
|
C-jun N-terminal kinase mediates tumor necrosis factor-alpha suppression of differentiation in myoblasts.
Endocrinology 147 , 4363-73, (2006) The stress kinase c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) was recently shown to be involved in the pathophysiology of major inflammatory conditions, including Alzheimer's disease, stroke, obesity, and type II d... |
| N-Ethanoyl-D-erythro-sphingosine |
| MFCD00153903 |
| N-ACETYL-D-SPHINGOSINE |
| D-erythro-N-acetyl-sphingosine |
| C14 SPHINGOID BASE |
| C2:0 CERAMIDE |
| CERAMIDE C2 |
| N-ACETYLSPHINGOSINE |
| Acetamide, N-[(1S,2R,3E)-2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)-3-heptadecen-1-yl]- |
| C2-D-ERYTHRO-CERAMIDE |
| ACETYL CERAMIDE |
| N-acetyl-sphing-4-enine |
| C2-ceramide |
| Ceramide,N-Acetylsphingosine |
| TOC Ceramide |
| N-acetyl-d-erythro-sphingosine |
| C2 CERAMIDE |
| N-[(2S,3R,4E)-1,3-Dihydroxy-4-octadecen-2-yl]acetamide |
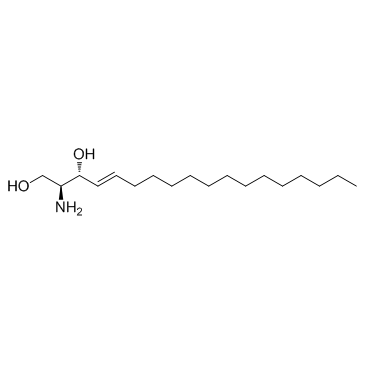 CAS#:123-78-4
CAS#:123-78-4 CAS#:75-36-5
CAS#:75-36-5 CAS#:108-24-7
CAS#:108-24-7 CAS#:78715-90-9
CAS#:78715-90-9 CAS#:765-13-9
CAS#:765-13-9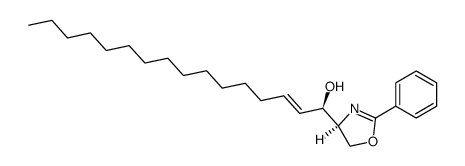 CAS#:78715-85-2
CAS#:78715-85-2 CAS#:78739-32-9
CAS#:78739-32-9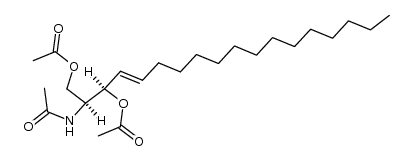 CAS#:2482-37-3
CAS#:2482-37-3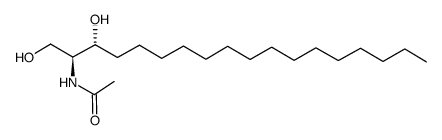 CAS#:13031-64-6
CAS#:13031-64-6