Allopurinol
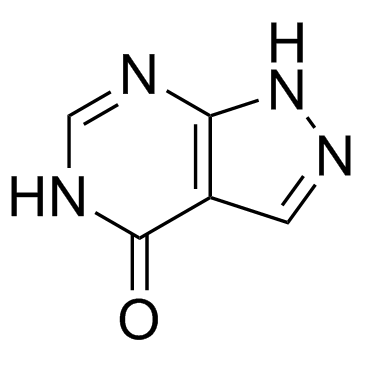
Allopurinol structure
|
Common Name | Allopurinol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 315-30-0 | Molecular Weight | 136.111 | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 290.8ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H4N4O | Melting Point | 350 ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 129.7ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of AllopurinolAllopurinol (Zyloprim) is a xanthine oxidase inhibitor with an IC50 of 7.82±0.12 μM.Target: XAOAllopurinol (Zyloprim, and generics) is a drug used primarily to treat hyperuricemia (excess uric acid in blood plasma) and its complications, including chronic gout. It is a xanthine oxidase inhibitor which is administered orally. A common misconception is that allopurinol is metabolized by its target, xanthine oxidase, but this action is principally carried out by Aldehyde oxidase. The active metabolite of allopurinol is oxypurinol, which is also an inhibitor of xanthine oxidase. Allopurinol is almost completely metabolized to oxypurinol within two hours of oral administration, whereas oxypurinol is slowly excreted by the kidneys over 18–30 hours. For this reason, oxypurinol is believed responsible for the majority of allopurinol's effect.Allopurinol is a purine analog; it is a structural isomer of hypoxanthine (a naturally occurring purine in the body) and is an inhibitor of the enzyme xanthine oxidase. In addition to blocking uric acid production, inhibition of xanthine oxidase causes an increase in hypoxanthine and xanthine. While xanthine cannot be converted to purine ribotides, hypoxanthine can be salvaged to the purine ribotides adenosine and guanosine monophosphates. Increased levels of these ribotides may cause feedback inhibition of amidophosphoribosyl transferase, the first and rate-limiting enzyme of purine biosynthesis. Allopurinol, therefore, decreases uric acid formation and may also inhibit purine synthesis. |
| Name | allopurinol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Allopurinol (Zyloprim) is a xanthine oxidase inhibitor with an IC50 of 7.82±0.12 μM.Target: XAOAllopurinol (Zyloprim, and generics) is a drug used primarily to treat hyperuricemia (excess uric acid in blood plasma) and its complications, including chronic gout. It is a xanthine oxidase inhibitor which is administered orally. A common misconception is that allopurinol is metabolized by its target, xanthine oxidase, but this action is principally carried out by Aldehyde oxidase. The active metabolite of allopurinol is oxypurinol, which is also an inhibitor of xanthine oxidase. Allopurinol is almost completely metabolized to oxypurinol within two hours of oral administration, whereas oxypurinol is slowly excreted by the kidneys over 18–30 hours. For this reason, oxypurinol is believed responsible for the majority of allopurinol's effect.Allopurinol is a purine analog; it is a structural isomer of hypoxanthine (a naturally occurring purine in the body) and is an inhibitor of the enzyme xanthine oxidase. In addition to blocking uric acid production, inhibition of xanthine oxidase causes an increase in hypoxanthine and xanthine. While xanthine cannot be converted to purine ribotides, hypoxanthine can be salvaged to the purine ribotides adenosine and guanosine monophosphates. Increased levels of these ribotides may cause feedback inhibition of amidophosphoribosyl transferase, the first and rate-limiting enzyme of purine biosynthesis. Allopurinol, therefore, decreases uric acid formation and may also inhibit purine synthesis. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 290.8ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 350 ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C5H4N4O |
| Molecular Weight | 136.111 |
| Flash Point | 129.7ºC |
| Exact Mass | 136.038513 |
| PSA | 74.43000 |
| LogP | -1.46 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.816 |
| Water Solubility | 0.35 g/L (25 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H317 |
| Precautionary Statements | Missing Phrase - N15.00950417-P280 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves;type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T:Toxic |
| Risk Phrases | R25;R36/37/38;R43 |
| Safety Phrases | S28-S36/37-S45-S36/37/39-S26-S24 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | UR0785000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|
~66% 
Allopurinol CAS#:315-30-0 |
| Literature: Tominaga; Honkawa; Hara; Hosomi Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry, 1990 , vol. 27, # 3 p. 775 - 783 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
The efficacy of short and repeated high-pressure processing treatments on the reduction of non-O157:H7 Shiga-toxin producing Escherichia coli in ground beef patties.
Meat Science 102 , 22-6, (2015) High pressure processing (HPP) has previously been shown to be effective at reducing Escherichia coli O157:H7 in meat products. However, few studies have determined whether HPP may be effective at red... |
|
|
In vitro Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Studies of Lippia nodiflora and Isolated Flavonoids and Phenylethanoid Glycosides as Potential Uric Acid-lowering Agents.
Nat. Prod. Commun. 10 , 945-8, (2015) Lippia nodiflora has been traditionally used for treatment of knee joint pain. Hitherto, no studies have been reported on the effective use of L. nodiflora against hyperuricemia, gout or other metabol... |
|
|
Pterostilbene and allopurinol reduce fructose-induced podocyte oxidative stress and inflammation via microRNA-377.
Free Radic. Biol. Med. 83 , 214-26, (2015) High dietary fructose is an important causative factor in the development of metabolic syndrome-associated glomerular podocyte oxidative stress and injury. Here, we identified microRNA-377 (miR-377) a... |
| Urosin |
| Urbol |
| 7H-Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-ol |
| Apurol |
| Pural |
| 1,5-Dihydro-4H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one |
| Anoprolin |
| HPP |
| Sigapurol |
| allopurinal |
| aloral |
| T56 BMN GN INJ FQ |
| Epidropal |
| Apurin |
| 4-HPP |
| 4-Hydroxypyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine |
| Zyloprim |
| Isopurinol |
| AL-100 |
| Takanarumin |
| 1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-ol |
| 4H-Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one, 1,7-dihydro- |
| Caplenal |
| Allopurinol |
| Remid |
| MFCD00599413 |
| Bleminol |
| EINECS 206-250-9 |
| Allopurin |
| Foligan |
| Anzief |
| 1H-Pyrazolo(3,4-d)pyrimidin-4-ol (4-Hydroxypyrazolo(3,4-d)pyrimidine |
| Hexanurat |
| Adenock |
| Cellidrin |
| Hexanuret |
| Zyloric (Trade name) |
| Zyloric |
| 1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4(5H)-one |
![3-methylsulfanyl-1,2-dihydropyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/180/90914-36-6.png)
![3-Bromo-1,5-dihydro-4H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/018/54738-73-7.png) CAS#:54738-73-7
CAS#:54738-73-7![3-IODO-1,5-DIHYDRO-4H-PYRAZOLO[3,4-D]PYRIMIDIN-4-ONE structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/294/144750-83-4.png) CAS#:144750-83-4
CAS#:144750-83-4 CAS#:5399-92-8
CAS#:5399-92-8![4H-Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine-4-thione,1,5-dihydro- structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/420/5334-23-6.png) CAS#:5334-23-6
CAS#:5334-23-6![1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine, 4-ethoxy- structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/242/32353-19-8.png) CAS#:32353-19-8
CAS#:32353-19-8![4-methylsulfanyl-1-prop-2-ynylpyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/091/328390-10-9.png) CAS#:328390-10-9
CAS#:328390-10-9![9-(hydroxymethyl)-2,4,8,9-tetrazabicyclo[4.3.0]nona-1,3,6-trien-5-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/389/79570-57-3.png) CAS#:79570-57-3
CAS#:79570-57-3![1,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/351/79570-58-4.png) CAS#:79570-58-4
CAS#:79570-58-4![2,5-dimethylpyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/096/57121-50-3.png) CAS#:57121-50-3
CAS#:57121-50-3![4H-Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one,1,5-dihydro-1,5-dimethyl- structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/251/5334-54-3.png) CAS#:5334-54-3
CAS#:5334-54-3
