L-Norleucine
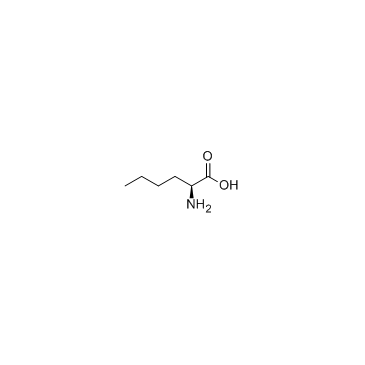
L-Norleucine structure
|
Common Name | L-Norleucine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 327-57-1 | Molecular Weight | 131.173 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 234.0±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H13NO2 | Melting Point | 300ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 95.3±22.6 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of L-NorleucineL-Norleucine is an isomer of leucine, specifically affects protein synthesis in skeletal muscle, and has antivirus activity. |
| Name | Hexanoic acid, 2-amino-, (S) |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | L-Norleucine is an isomer of leucine, specifically affects protein synthesis in skeletal muscle, and has antivirus activity. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | L-Norleucine is an isomer of leucine, specifically affecting protein synthesis in skeletal muscle[1]. L-Norleucine has antiviral activity. L-Norleucine interacts with hnRNPA2/B1 protein to suppresses the expressions of Twist1 and Snail, two inhibitors of E-cadherin, and promotes the expression of E-cadherin, resulting in the inhibition of tumor metastasis[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 234.0±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 300ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C6H13NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 131.173 |
| Flash Point | 95.3±22.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 131.094635 |
| PSA | 63.32000 |
| LogP | 0.92 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.465 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATAMUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H317 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R43 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | RC6308000 |
| HS Code | 29224995 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2922499990 other amino-acids, other than those containing more than one kind of oxygen function, and their esters; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
L-selenomethionine reduces platinum(IV) anticancer model compounds at strikingly faster rates than L-methionine.
Dalton Trans. 43(41) , 15328-36, (2014) L-Selenomethionine (SeMet), the predominant form of selenium acquired from the diet by humans, has been used as a supplement, and exhibit some important functions like cancer prevention and antioxidat... |
|
|
Leucine and alpha-ketoisocaproic acid, but not norleucine, stimulate skeletal muscle protein synthesis in neonatal pigs.
J. Nutr. 140(8) , 1418-24, (2010) The branched-chain amino acid, leucine, acts as a nutrient signal to stimulate protein synthesis in skeletal muscle of young pigs. However, the chemical structure responsible for this effect has not b... |
|
|
Changes in Serum Amino Acids in Migraine Patients without and with Aura and their Possible Usefulness in the Study of Migraine Pathogenesis.
CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 14(3) , 345-9, (2015) Results of several studies suggest that serum amino acids monitoring in migraine might be useful as an objective measurement of the disease status.The aim of the present work was to analyze the profil... |
| L-2-Aminohexanoic acid |
| EINECS 206-321-4 |
| (S)-Norleucine |
| Norleucine |
| (S)-2-amino-Hexanoic acid |
| (S)-(+)-2-Aminohexanoic acid |
| H-L-NLE-OH |
| Glycoleucine |
| H-L-NORLEUCINE |
| L-Norleucine |
| (S)-(+)-2-Aminohexanoic acid (S)-2-Aminocaproic acid |
| (S)-Aminohexanoic acid |
| (S)-a-Aminocaproic acid |
| L-2-Amino-hexanoic acid |
| L-Aminohexanoic acid |
| Norleucine, L- |
| (S)-2-Aminohexanoic acid |
| caprine |
| H-NLE-OH |
| H-ACPO(2)-OH |
| L-2-aminohexanoate |
| H-AHX(2)-OH |
| D,L-Norleucine |
| MFCD00064423 |
| L(+)-Norleucine |
| (S)-2-aminocaproic acid |
| N-NORLEUCINE |
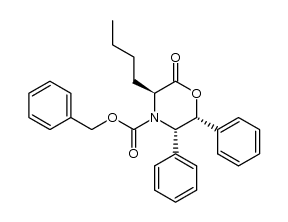 CAS#:100516-59-4
CAS#:100516-59-4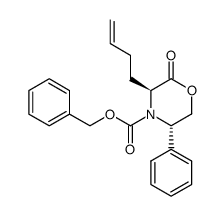 CAS#:625824-28-4
CAS#:625824-28-4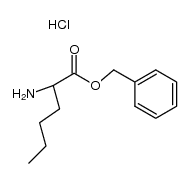 CAS#:108488-49-9
CAS#:108488-49-9 CAS#:7682-16-8
CAS#:7682-16-8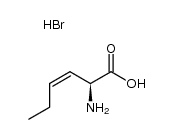 CAS#:127644-00-2
CAS#:127644-00-2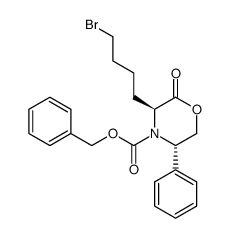 CAS#:625824-32-0
CAS#:625824-32-0 CAS#:616-06-8
CAS#:616-06-8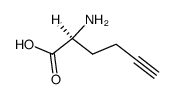 CAS#:98891-36-2
CAS#:98891-36-2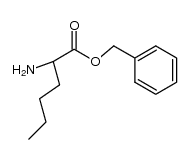 CAS#:108488-50-2
CAS#:108488-50-2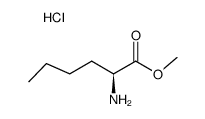 CAS#:3844-54-0
CAS#:3844-54-0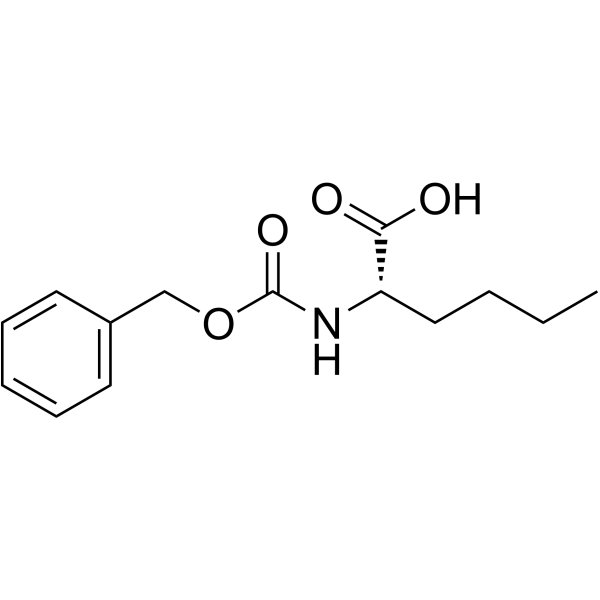 CAS#:39608-30-5
CAS#:39608-30-5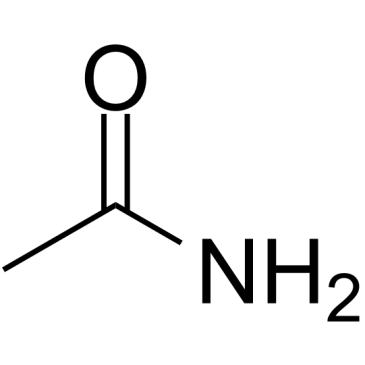 CAS#:60-35-5
CAS#:60-35-5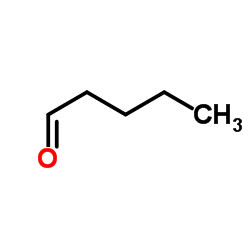 CAS#:110-62-3
CAS#:110-62-3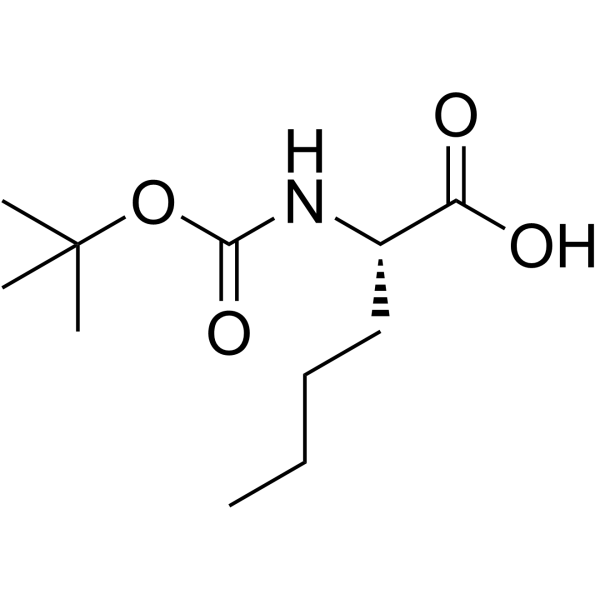 CAS#:6404-28-0
CAS#:6404-28-0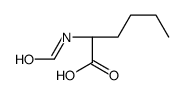 CAS#:133388-96-2
CAS#:133388-96-2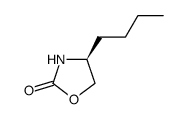 CAS#:158249-51-5
CAS#:158249-51-5 CAS#:117903-25-0
CAS#:117903-25-0 CAS#:1118-90-7
CAS#:1118-90-7
