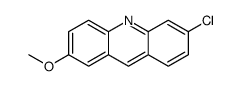
9-AMINO-6-CHLORO-2-METHOXYACRIDINE
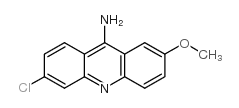
9-AMINO-6-CHLORO-2-METHOXYACRIDINE structure
|
Common Name | 9-AMINO-6-CHLORO-2-METHOXYACRIDINE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 3548-09-2 | Molecular Weight | 258.70300 | |
| Density | 1.367g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 475.1ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H11ClN2O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 241.2ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 9-AMINO-6-CHLORO-2-METHOXYACRIDINE9-Amino-6-chloro-2-methoxyacridine is a pH sensitive fluorescent probe. 9-Amino-6-chloro-2-methoxyacridine has been frequently used to measure changes in vacuolar pH when a specific substrate crosses the tonoplast through a putative H+/solute antiport system[1]. |
| Name | 9-Amino-6-chloro-2-methoxyacridine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 9-Amino-6-chloro-2-methoxyacridine is a pH sensitive fluorescent probe. 9-Amino-6-chloro-2-methoxyacridine has been frequently used to measure changes in vacuolar pH when a specific substrate crosses the tonoplast through a putative H+/solute antiport system[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.367g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 475.1ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C14H11ClN2O |
| Molecular Weight | 258.70300 |
| Flash Point | 241.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 258.05600 |
| PSA | 48.14000 |
| LogP | 4.21340 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.734 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335-H351 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P281-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 22-26-36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | AR7330000 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|
~68% 
9-AMINO-6-CHLOR... CAS#:3548-09-2 |
| Literature: Bonse, Susanne; Santelli-Rouvier, Christiane; Barbe, Jacques; Krauth-Siegel, R. Luise Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 1999 , vol. 42, # 26 p. 5448 - 5454 |
|
~84% 
9-AMINO-6-CHLOR... CAS#:3548-09-2 |
| Literature: Gemma, Sandra; Kukreja, Gagan; Tripaldi, Pierangela; Altarelli, Maria; Bernetti, Matteo; Franceschini, Silvia; Savini, Luisa; Campiani, Giuseppe; Fattorusso, Caterina; Butini, Stefania Tetrahedron Letters, 2008 , vol. 49, # 13 p. 2074 - 2077 |
|
~% 
9-AMINO-6-CHLOR... CAS#:3548-09-2 |
| Literature: , vol. 39, # 11 p. 1626 - 1628 |
|
~% 
9-AMINO-6-CHLOR... CAS#:3548-09-2 |
| Literature: Nippon Kagaku Zasshi, , vol. 75, p. 475,476 Chem.Abstr., , p. 10297 |
|
~% 
9-AMINO-6-CHLOR... CAS#:3548-09-2 |
| Literature: , vol. 39, # 11 p. 1626 - 1628 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Vma9p need not be associated with the yeast V-ATPase for fully-coupled proton pumping activity in vitro.
Biochemistry 54(3) , 853-8, (2015) Vacuolar-type ATPases (V-ATPases) acidify numerous intracellular compartments in all eukaryotic cells and are responsible for extracellular acidification in some specialized cells. V-ATPases are large... |
|
|
Adaptation by the collecting duct to an exogenous acid load is blunted by deletion of the proton-sensing receptor GPR4.
Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 309 , F120-36, (2015) We previously reported that the deletion of the pH sensor GPR4 causes a non-gap metabolic acidosis and defective net acid excretion (NAE) in the GPR4 knockout mouse (GPR4-/-) (Sun X, Yang LV, Tiegs BC... |
|
|
Copper transport and compartmentation in grape cells.
Plant Cell Physiol. 53(11) , 1866-80, (2012) Copper-based fungicides have been widely used against several grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) diseases since the late 1800s when the Bordeaux mixture was developed, but their intensive use has raised ph... |
| MFCD00083236 |
| 6-chloro-2-methoxyacridin-9-amine |

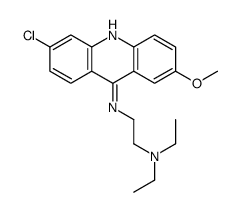 CAS#:67947-04-0
CAS#:67947-04-0