Cholesterol Stearate

Cholesterol Stearate structure
|
Common Name | Cholesterol Stearate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 35602-69-8 | Molecular Weight | 653.115 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 671.7±34.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C45H80O2 | Melting Point | 79-83ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 360.6±13.2 °C | |
Use of Cholesterol StearateCholesteryl stearate is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research. |
| Name | cholesteryl stearate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Cholesteryl stearate is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 671.7±34.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 79-83ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C45H80O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 653.115 |
| Flash Point | 360.6±13.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 652.615845 |
| PSA | 26.30000 |
| LogP | 19.21 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.505 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
A rapid and precise method for quantification of fatty acids in human serum cholesteryl esters by liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 960 , 222-9, (2014) We described a rapid and precise method for simultaneous quantification of eleven fatty acids in human serum cholesteryl esters (CEFAs) by liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)... |
|
|
Accelerated separation of GC-amenable lipid classes in plant oils by countercurrent chromatography in the co-current mode.
Anal. Bioanal. Chem 407 , 9019-28, (2015) Triacylglycerols represent the major part (>90%) in most plant oils and have to be eliminated, when the minor compounds such as phytosterols or tocopherols should be analyzed. Here, we used an all liq... |
|
|
Modification of composition of a nanoemulsion with different cholesteryl ester molecular species: effects on stability, peroxidation, and cell uptake.
Int. J. Nanomedicine 5 , 679-86, (2010) Use of lipid nanoemulsions as carriers of drugs for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes has been increasingly studied. Here, it was tested whether modifications of core particle constitution could affe... |
| (3S,8S,9S,10R,13R,14S,17R)-10,13-Dimethyl-17-[(2R)-6-methyl-2-heptanyl]-2,3,4,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl stearate |
| Stéarate de (3S,8S,9S,10R,13R,14S,17R)-10,13-diméthyl-17-[(2R)-6-méthyl-2-heptanyl]-2,3,4,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tétradécahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phénanthrén-3-yle |
| Cholestryl stearate |
| (3β)-cholest-5-en-3-yl octadecanoate |
| Cholesterol, stearate (8CI) |
| (3β)-Cholest-5-en-3-yloctadecanoat |
| 5-Cholesten-3beta-yl octadecanoate |
| EINECS 252-637-0 |
| cholesterol n-octadecanoate |
| 18:0-cholesterol |
| (3β)-Cholest-5-en-3-yl stearate |
| 5-Cholesten-3β-ol stearate |
| cholesteryl stearate |
| 18:0 Cholesteryl ester |
| MFCD00003639 |
| Stearic Acid Cholesterol Ester |
| 5-Cholesten-3b-ol stearate |
| Cholesteryl octadecanoate |
| Cholesterol, stearate |
| Stéarate de (3β)-cholest-5-én-3-yle |
| CE(18:0) |
| (3b)-Cholest-5-en-3-yl stearate |
| (3S,8S,9S,10R,13R,14S,17R)-10,13-Dimethyl-17-[(2R)-6-methyl-2-heptanyl]-2,3,4,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yloctadecanoat |
| [(3S,8S,9S,10R,13R,14S,17R)-10,13-dimethyl-17-[(2R)-6-methylheptan-2-yl]-2,3,4,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl] octadecanoate |
| Cholesterol Stearate |
| Octadecanoic acid, (3β)-cholest-5-en-3-yl ester |
 CAS#:638-08-4
CAS#:638-08-4![3β-[(Tetrahydro-2H-pyran)-2-yloxy]cholest-5-ene Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/185/6252-45-5.png) CAS#:6252-45-5
CAS#:6252-45-5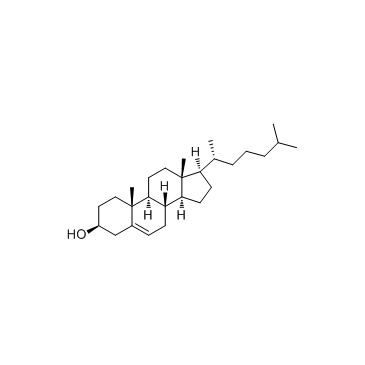 CAS#:57-88-5
CAS#:57-88-5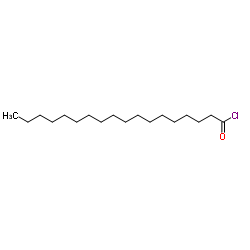 CAS#:112-76-5
CAS#:112-76-5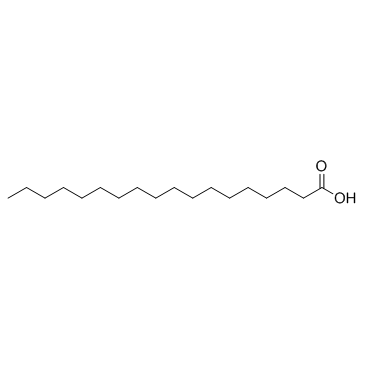 CAS#:57-11-4
CAS#:57-11-4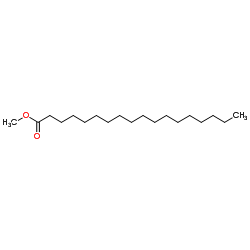 CAS#:112-61-8
CAS#:112-61-8 CAS#:555-43-1
CAS#:555-43-1 CAS#:303-43-5
CAS#:303-43-5 CAS#:112-80-1
CAS#:112-80-1 CAS#:119-64-2
CAS#:119-64-2
