H-Arg-OEt·2HCl
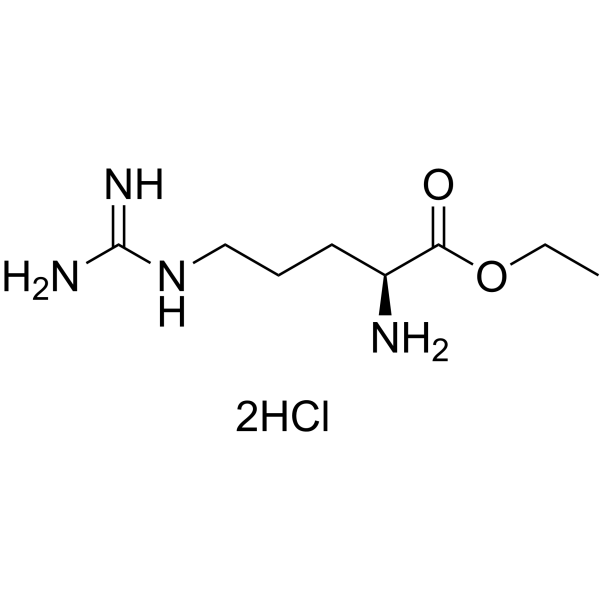
H-Arg-OEt·2HCl structure
|
Common Name | H-Arg-OEt·2HCl | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 36589-29-4 | Molecular Weight | 275.176 | |
| Density | 1.26g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 343.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H20Cl2N4O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 161.4ºC | |
Use of H-Arg-OEt·2HClL-Arginine ethyl ester dihydrochloride is an arginine derivative[1]. |
| Name | L-Arginine ethyl ester dihydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | L-Arginine ethyl ester dihydrochloride is an arginine derivative[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Amino acids and amino acid derivatives have been commercially used as ergogenic supplements. They influence the secretion of anabolic hormones, supply of fuel during exercise, mental performance during stress related tasks and prevent exercise induced muscle damage. They are recognized to be beneficial as ergogenic dietary substances[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.26g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 343.3ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C8H20Cl2N4O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 275.176 |
| Flash Point | 161.4ºC |
| Exact Mass | 274.096344 |
| PSA | 114.22000 |
| LogP | 2.63530 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.543 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2925290090 |
| HS Code | 2925290090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2925290090 other imines and their derivatives; salts thereof。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
Intracellular l-arginine concentration does not determine NO production in endothelial cells: Implications on the “l-arginine paradox”
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 414 , 660-663, (2011) Highlights ► Our findings provide a possible solution to the “l-arginine paradox”. ► Extracellular l-arginine concentration is the major determinant of NO production. ► Cellular l-arginine action is l... |
|
|
L-arginine and arginine ethyl ester enhance proliferation of endothelial cells and preadipocytes - how an arginine ethyl ester-releasing biomaterial could support endothelial cell growth in tissue engineering.
Biomed Mater Eng 25 , 289-97, (2015) Adipose tissue engineering is a promising solution for the reconstruction of soft tissue defects. An insufficient neovascularisation within the scaffolds that leads to necrosis and tissue loss is stil... |
| MFCD00038949 |
| L-Arginine, ethyl ester, hydrochloride (1:2) |
| H-Arg-OEt*2HCl |
| (S)-Ethyl 2-amino-5-guanidinopentanoate dihydrochloride |
| H-Arg-Oet·2Hcl |
| ethyl (2S)-2-amino-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)pentanoate,dihydrochloride |
| Arg-Oet 2HCl |
| Ethyl L-argininate dihydrochloride |
| L-Arginine Ethyl Ester Dihydrochloride |
| H-Arg-OEt.2HCl |

