Etilevodopa hydrochloride
Modify Date: 2024-01-09 10:45:14
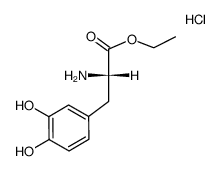
Etilevodopa hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Etilevodopa hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 39740-30-2 | Molecular Weight | 261.70200 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H16ClNO4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Etilevodopa hydrochlorideEtilevodopa (L-Dopa ethyl ester) hydrochloride, an ethyl-ester prodrug of Levodopa, is rapidly hydrolyzed to Levodopa and ethanol by nonspecific esterases in the gastrointestinal tract. Etilevodopa hydrochloride is used for the treatment of Parkinson disease (PD). Levodopa is the direct precursor of dopamine and is a suitable prodrug as it facilitates CNS penetration and delivers dopamine[1][2][3]. |
| Name | (S)-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine ethyl ester hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Etilevodopa (L-Dopa ethyl ester) hydrochloride, an ethyl-ester prodrug of Levodopa, is rapidly hydrolyzed to Levodopa and ethanol by nonspecific esterases in the gastrointestinal tract. Etilevodopa hydrochloride is used for the treatment of Parkinson disease (PD). Levodopa is the direct precursor of dopamine and is a suitable prodrug as it facilitates CNS penetration and delivers dopamine[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Etilevodopa (L-Dopa ethyl ester) hydrochloride passes unchanged through the stomach to the duodenum, where it is rapidly hydrolyzed by local esterases to Levodopa and ethanol, and is subsequently absorbed into the blood stream as Levodopa[1]. Compared with standard Levodopa, Etilevodopa hydrochloride has greater solubility in the stomach, faster passage to the small intestine, and a shortened time to maximum Levodopa concentration[2]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C11H16ClNO4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 261.70200 |
| Exact Mass | 261.07700 |
| PSA | 92.78000 |
| LogP | 2.03300 |
| L-DOPA Ethyl Ester Hydrochloride |