Kos2602
Modify Date: 2024-01-02 23:43:43
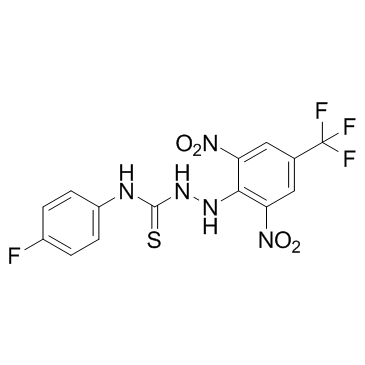
Kos2602 structure
|
Common Name | Kos2602 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 454453-49-7 | Molecular Weight | 419.311 | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 450.8±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H9F4N5O4S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 226.5±31.5 °C | |
Use of Kos2602kobe2602 is a novel and effective small-molecule compound inhibiting Ras–Raf interaction by SBDD; exhibits potent activity to competitively inhibit the binding of H-Ras·GTP to c-Raf-1 RBD with a Ki value of 149 ± 55 μM.IC50 value: 149 ± 55 uM (Ki) [1]Target: Ras-Raf These two compounds(Kobe0065 and Kobe2602), added to the culture medium at 2 and 20 μM, effectively reduced the amount of c-Raf-1 associated with H-Ras G12V in NIH 3T3 cells in a dose-dependent manner, indicating the inhibition of the cellular activity of Ras. A rough estimate of the IC50 value for the cellular Ras–Raf-binding inhibition was around 10 μM (Fig. 1B), which was not much different from the Ki values for the in vitro Ras–Raf-binding inhibition considering thequite low cellular concentration of Raf. A similar inhibitory effect was also observed with NIH 3T3 cells overexpressing K-Ras G12V. Both Kobe0065 and Kobe2602 at 20 μM efficiently inhibited the phosphorylation of MEK and ERK, downstream kinases of Raf in NIH 3T3 cells transiently expressingH-Ras G12V, although the effect was slightly weaker than that of2 μM sorafenib. |
| Name | 2-[2,6-Dinitro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-N-(4-fluorophenyl)hydrazinecarbothioamide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | kobe2602 is a novel and effective small-molecule compound inhibiting Ras–Raf interaction by SBDD; exhibits potent activity to competitively inhibit the binding of H-Ras·GTP to c-Raf-1 RBD with a Ki value of 149 ± 55 μM.IC50 value: 149 ± 55 uM (Ki) [1]Target: Ras-Raf These two compounds(Kobe0065 and Kobe2602), added to the culture medium at 2 and 20 μM, effectively reduced the amount of c-Raf-1 associated with H-Ras G12V in NIH 3T3 cells in a dose-dependent manner, indicating the inhibition of the cellular activity of Ras. A rough estimate of the IC50 value for the cellular Ras–Raf-binding inhibition was around 10 μM (Fig. 1B), which was not much different from the Ki values for the in vitro Ras–Raf-binding inhibition considering thequite low cellular concentration of Raf. A similar inhibitory effect was also observed with NIH 3T3 cells overexpressing K-Ras G12V. Both Kobe0065 and Kobe2602 at 20 μM efficiently inhibited the phosphorylation of MEK and ERK, downstream kinases of Raf in NIH 3T3 cells transiently expressingH-Ras G12V, although the effect was slightly weaker than that of2 μM sorafenib. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 450.8±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C14H9F4N5O4S |
| Molecular Weight | 419.311 |
| Flash Point | 226.5±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 419.031128 |
| LogP | 5.12 |
| Appearance of Characters | light yellow solid |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.683 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
| 2-[2,6-Dinitro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-N-(4-fluorophenyl)hydrazinecarbothioamide |
| Hydrazinecarbothioamide, 2-[2,6-dinitro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-N-(4-fluorophenyl)- |
| kobe 2602 |
| kobe2602 |