3-Phenylbutyric acid
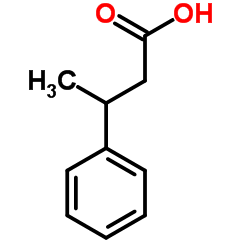
3-Phenylbutyric acid structure
|
Common Name | 3-Phenylbutyric acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4593-90-2 | Molecular Weight | 164.201 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 288.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H12O2 | Melting Point | 35-38 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 170.2±13.9 °C | |
Use of 3-Phenylbutyric acid3-Phenylbutyric acid is metabolized by initial oxidation of the benzene ring and by initial oxidation of the side chain. 3-Phenylbutyric acid can be used to isolate Rhodococcus rhodochrous PB1 from compost soil[1][2]. |
| Name | 3-phenylbutyric acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 3-Phenylbutyric acid is metabolized by initial oxidation of the benzene ring and by initial oxidation of the side chain. 3-Phenylbutyric acid can be used to isolate Rhodococcus rhodochrous PB1 from compost soil[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 288.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 35-38 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C10H12O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 164.201 |
| Flash Point | 170.2±13.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 164.083725 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 2.19 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.531 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | 1325 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 4.1 |
| HS Code | 2916399090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2916399090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2916399090 other aromatic monocarboxylic acids, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Adsorption of small hydroxy acids on glass: a pitfall in quantitative urinary organic acid analysis by GC-MS.
J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 22(3) , 293-6, (1999)
|
|
|
Induction of histone acetylation and growth regulation in eryrthroleukemia cells by 4-phenylbutyrate and structural analogs.
Anticancer Res. 19(3A) , 1971-6, (1999) The objective of this investigation was to study the relationship between histone acetylation and growth inhibition by 4-phenylbutyrate and structural analogs. Inhibition of growth of DS19 mouse eryth... |
|
|
Enantioselective Metabolism of Chiral 3-Phenylbutyric Acid, an Intermediate of Linear Alkylbenzene Degradation, by Rhodococcus rhodochrous PB1.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62(3) , 749-55, (1996) Rhodococcus rhodochrous PB1 was isolated from compost soil by selective culture with racemic 3-phenylbutyric acid as the sole carbon and energy source. Growth experiments with the single pure enantiom... |
| b-Phenylbutyric acid |
| 3-Phenylbutyric acid |
| MFCD00002725 |
| (RS)-3-Phenylbutanoic acid |
| (/-)-3-phenylbutyric acid |
| Benzenepropanoic acid, β-methyl- |
| EINECS 224-987-4 |
| RARECHEM AL BE 0683 |
| b-Phenyl-n-butyric acid |
| β-Phenyl-n-butyric acid |
| β-Methylbenzenepropanoic acid |
| 3-phenylbutyrate |
| 3-Phenylbutanoic acid |
| b-methyl benzenepropanoic acid |
| b-Methylbenzenepropanoic acid |
| 3-S-phenyl-1-butanoic acid |
 CAS#:201230-82-2
CAS#:201230-82-2 CAS#:98-83-9
CAS#:98-83-9 CAS#:108-86-1
CAS#:108-86-1 CAS#:107-93-7
CAS#:107-93-7 CAS#:16251-77-7
CAS#:16251-77-7 CAS#:104602-93-9
CAS#:104602-93-9 CAS#:704-79-0
CAS#:704-79-0 CAS#:591-51-5
CAS#:591-51-5 CAS#:1134-71-0
CAS#:1134-71-0 CAS#:6072-57-7
CAS#:6072-57-7 CAS#:1004-63-3
CAS#:1004-63-3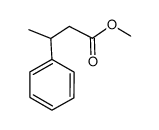 CAS#:3461-39-0
CAS#:3461-39-0![[1-(dichloromethyl)-1-methylpropyl]benzene structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/126/36318-77-1.png) CAS#:36318-77-1
CAS#:36318-77-1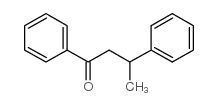 CAS#:1533-20-6
CAS#:1533-20-6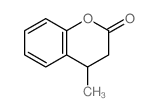 CAS#:18435-75-1
CAS#:18435-75-1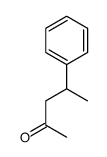 CAS#:17913-10-9
CAS#:17913-10-9 CAS#:767-59-9
CAS#:767-59-9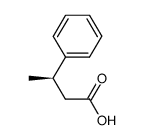 CAS#:772-14-5
CAS#:772-14-5